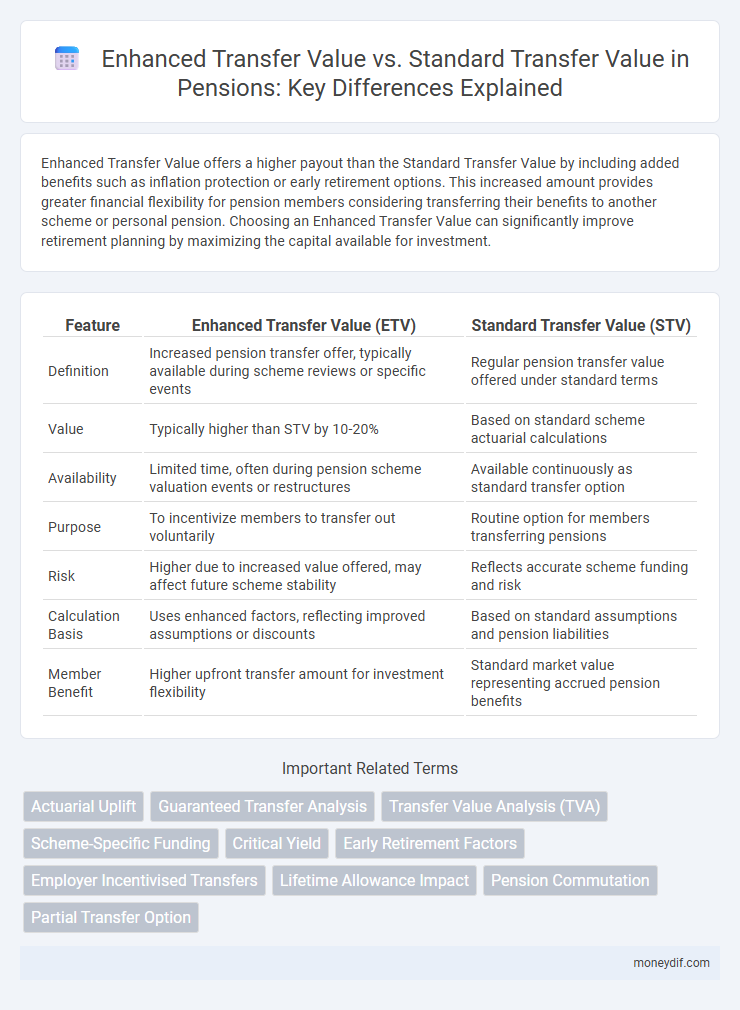
Enhanced Transfer Value offers a higher payout than the Standard Transfer Value by including added benefits such as inflation protection or early retirement options. This increased amount provides greater financial flexibility for pension members considering transferring their benefits to another scheme or personal pension. Choosing an Enhanced Transfer Value can significantly improve retirement planning by maximizing the capital available for investment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Enhanced Transfer Value (ETV) | Standard Transfer Value (STV) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increased pension transfer offer, typically available during scheme reviews or specific events | Regular pension transfer value offered under standard terms |
| Value | Typically higher than STV by 10-20% | Based on standard scheme actuarial calculations |
| Availability | Limited time, often during pension scheme valuation events or restructures | Available continuously as standard transfer option |
| Purpose | To incentivize members to transfer out voluntarily | Routine option for members transferring pensions |
| Risk | Higher due to increased value offered, may affect future scheme stability | Reflects accurate scheme funding and risk |
| Calculation Basis | Uses enhanced factors, reflecting improved assumptions or discounts | Based on standard assumptions and pension liabilities |
| Member Benefit | Higher upfront transfer amount for investment flexibility | Standard market value representing accrued pension benefits |
Understanding Pension Transfer Values
Enhanced Transfer Value (ETV) offers a higher payout compared to the Standard Transfer Value (STV), reflecting additional benefits such as early retirement options or inflation protection. Understanding pension transfer values involves evaluating the financial impact of transferring your pension pot, where ETVs compensate for future value enhancements within defined benefit schemes. Assessing these values helps in making informed decisions about whether to retain a pension or transfer it to a different provider for potential growth opportunities.
What Is a Standard Transfer Value?
A Standard Transfer Value (STV) represents the calculated cash amount a pension scheme offers to transfer a member's accrued benefits to another pension provider. It is based on actuarial assumptions reflecting current market conditions, mortality rates, and pension scheme rules to ensure fairness and consistency. Unlike Enhanced Transfer Values, which may provide higher sums due to specific circumstances like early retirement or ill health, STVs serve as the baseline transfer calculation for most pension members.
What Does Enhanced Transfer Value Mean?
Enhanced Transfer Value (ETV) represents a higher amount offered by pension schemes when transferring a pension pot to another provider, exceeding the Standard Transfer Value (STV). This uplift typically occurs if the member has specific benefits such as guaranteed pension increases or early retirement options that the scheme values more highly. ETVs provide greater flexibility and financial advantage for members considering pension consolidation or alternative retirement planning strategies.
Why Do Providers Offer Enhanced Transfer Values?
Providers offer Enhanced Transfer Values (ETVs) to encourage members to transfer their pension benefits out of defined benefit schemes, helping to reduce long-term liabilities and associated funding risks. ETVs typically provide a higher lump sum compared to Standard Transfer Values (STVs), making pension transfers more attractive for members evaluating alternative retirement options. This strategy supports scheme sustainability by managing payout obligations while offering flexibility to members seeking potentially higher investment returns or consolidated pension accounts.
Key Differences Between Enhanced and Standard Transfer Values
Enhanced Transfer Values (ETVs) offer pension scheme members a higher cash equivalent than Standard Transfer Values (STVs), reflecting additional factors such as ill-health or specific career length criteria. ETVs are typically available to members meeting certain conditions, resulting in a more favorable calculation based on future pension benefits and inflation assumptions. Standard Transfer Values represent the basic valuation of accrued pension benefits without these enhancements, often leading to a lower transfer amount.
Factors Influencing Enhanced Transfer Offers
Factors influencing Enhanced Transfer Value (ETV) offers include the member's age, service length, and existing pension benefits, which are assessed to provide a tailored valuation often exceeding the Standard Transfer Value (STV). Scheme funding levels and actuarial assumptions around future investment returns and longevity also play critical roles in determining the magnitude of ETVs compared to STVs. Regulatory frameworks and scheme-specific rules further impact the eligibility and calculation methodology for Enhanced Transfer Offers.
Pros and Cons of Accepting an Enhanced Transfer Value
Accepting an Enhanced Transfer Value (ETV) offers the advantage of a higher lump sum compared to a Standard Transfer Value (STV), potentially increasing retirement flexibility and investment opportunities. However, ETVs often come with stricter eligibility criteria and may result in losing valuable pension guarantees, such as inflation protection or spouse benefits. The decision to accept an ETV requires careful evaluation of long-term financial security against the immediate benefit of a larger transfer amount.
Tax Implications of Pension Transfers
Enhanced Transfer Values (ETVs) often offer a larger lump sum compared to Standard Transfer Values (STVs), but selecting an ETV can trigger significant tax liabilities if the transfer exceeds the Lifetime Allowance (LTA). Transfers surpassing the LTA incur a tax charge of 25% if taken as income or 55% if taken as a lump sum, emphasizing the importance of careful tax planning. Understanding these potential tax implications is crucial when deciding between ETVs and STVs to optimize pension benefits and minimize unexpected tax burdens.
Evaluating If an Enhanced Transfer Value Is Right for You
Evaluating if an Enhanced Transfer Value (ETV) is right for your pension involves comparing it with the Standard Transfer Value (STV) by analyzing the potential financial benefits and risks. An ETV often offers a higher lump sum than the STV, reflecting factors like age, health, or leaving employment early, but it requires careful assessment of future pension income and investment risks. Consulting a pension advisor can help determine whether the increased transfer value outweighs the potential loss of guaranteed benefits under the existing pension scheme.
Seeking Professional Advice on Pension Transfer Decisions
Consulting a regulated financial advisor is crucial when considering Enhanced Transfer Value (ETV) versus Standard Transfer Value (STV) options in pension transfers, as ETVs offer higher lump sums but carry increased risk and complexity. Professional advice ensures a thorough assessment of individual circumstances, including tax implications, investment opportunities, and long-term retirement goals. Accurate valuation and tailored guidance help avoid costly mistakes and optimize the financial outcome of pension transfer decisions.
Important Terms
Actuarial Uplift
Actuarial Uplift quantifies the additional financial benefit in an Enhanced Transfer Value compared to a Standard Transfer Value by reflecting adjustments for factors like health, life expectancy, and pension scheme improvements.
Guaranteed Transfer Analysis
Guaranteed Transfer Analysis evaluates the financial impact by comparing Enhanced Transfer Value, which includes added benefits or higher payouts, against the baseline Standard Transfer Value for optimized decision-making.
Transfer Value Analysis (TVA)
Transfer Value Analysis (TVA) compares Enhanced Transfer Value, which includes bonuses and adjustments, to Standard Transfer Value, reflecting the basic pension fund transfer amount without additional enhancements.
Scheme-Specific Funding
Scheme-Specific Funding often influences the Enhanced Transfer Value, making it more advantageous compared to the Standard Transfer Value due to tailored actuarial assumptions and funding levels.
Critical Yield
Critical Yield determines the threshold at which Enhanced Transfer Value surpasses Standard Transfer Value in profitability and effectiveness.
Early Retirement Factors
Enhanced Transfer Value offers a higher payout than Standard Transfer Value, significantly impacting early retirement decisions by increasing available funds and influencing pension transfer attractiveness.
Employer Incentivised Transfers
Employer incentivised transfers often offer an Enhanced Transfer Value that exceeds the Standard Transfer Value to encourage employees to transfer their pension benefits within a specified timeframe.
Lifetime Allowance Impact
Enhanced Transfer Value often exceeds the Standard Transfer Value, significantly impacting Lifetime Allowance and potentially triggering higher tax charges.
Pension Commutation
Pension commutation allows pension holders to exchange a portion of their future pension income for a lump sum payment, with Enhanced Transfer Value (ETV) typically providing a higher lump sum than the Standard Transfer Value (STV) due to favorable scheme conditions or membership factors like ill health or early retirement. Enhanced Transfer Values offer greater financial flexibility by capitalizing on scheme-specific enhancements, whereas Standard Transfer Values reflect the regular calculated value without additional benefits.
Partial Transfer Option
Partial Transfer Option allows policyholders to move a portion of their policy's value, offering Enhanced Transfer Value rates that typically exceed Standard Transfer Value amounts by 20-30%, maximizing cash benefits during policy conversion.
Enhanced Transfer Value vs Standard Transfer Value Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com