Career average pension schemes calculate retirement benefits based on the average earnings throughout an employee's entire working life, providing a steady and balanced approach to pension accrual. Final salary schemes base pension benefits on the employee's salary at or near retirement, often resulting in higher payouts for those with significant salary increases late in their careers. Understanding the difference between these two methods is crucial for effective retirement planning and ensuring financial security in later life.
Table of Comparison
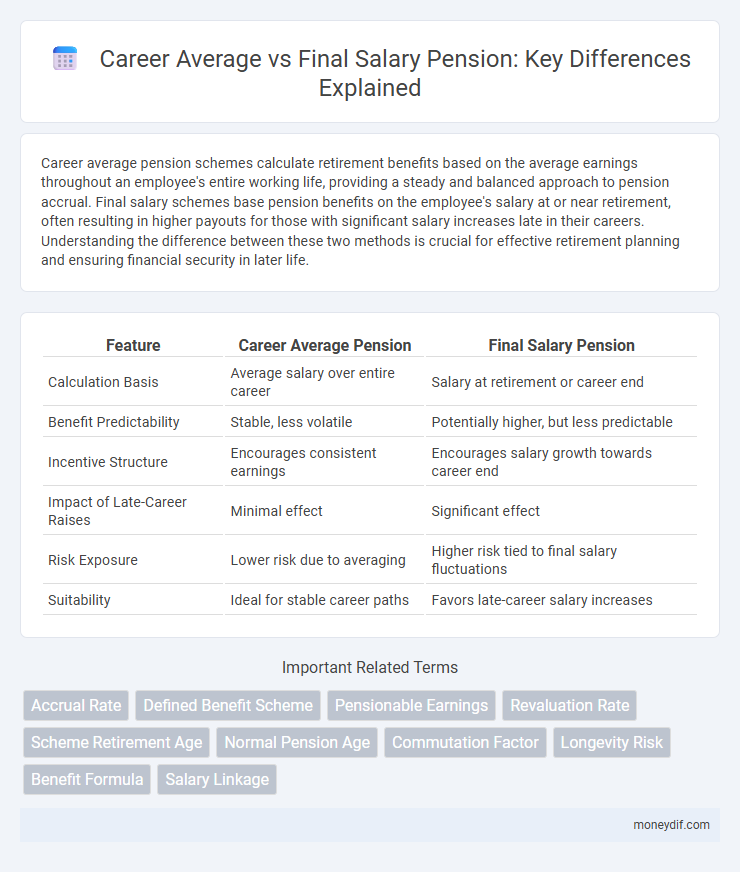
| Feature | Career Average Pension | Final Salary Pension |
|---|---|---|
| Calculation Basis | Average salary over entire career | Salary at retirement or career end |
| Benefit Predictability | Stable, less volatile | Potentially higher, but less predictable |
| Incentive Structure | Encourages consistent earnings | Encourages salary growth towards career end |
| Impact of Late-Career Raises | Minimal effect | Significant effect |
| Risk Exposure | Lower risk due to averaging | Higher risk tied to final salary fluctuations |
| Suitability | Ideal for stable career paths | Favors late-career salary increases |
Introduction to Career Average and Final Salary Pensions
Career Average pensions calculate retirement benefits based on the average earnings throughout an employee's entire career, adjusting annually for inflation to reflect current cost of living. Final Salary pensions determine benefits using the salary earned during the last few years of employment, typically the highest earning period, resulting in potentially higher payouts. Understanding the distinctions between these two pension schemes is essential for accurate retirement planning and financial security.
How Career Average Pension Schemes Work
Career Average Pension Schemes calculate retirement benefits based on an employee's average earnings throughout their career, rather than the salary at retirement. Contributions are made annually, and each year's pensionable earnings are indexed to inflation, ensuring that the accrued benefits maintain their value over time. This method provides a more equitable pension amount reflecting the overall career progression instead of just the peak earning years.
Understanding Final Salary Pension Schemes
Final salary pension schemes calculate retirement benefits based on the employee's salary at the end of their career or over the last few years, providing higher benefits for those with increasing earnings. Understanding these schemes requires recognizing that payouts are typically more predictable and often more generous than career average schemes, which base pensions on average earnings throughout the entire career. The value of final salary pensions is closely linked to consistent salary growth and length of service, making them highly valuable in long-term retirement planning.
Key Differences Between Career Average and Final Salary
Career average pensions calculate benefits based on the average earnings throughout an employee's entire career, providing a steady, proportional income replacement. Final salary pensions determine benefits using the salary at retirement or near retirement, potentially offering higher payouts if earnings increase significantly over time. This fundamental difference impacts pension value, with career average plans typically offering more predictable growth and final salary plans often benefiting long-term salary progression.
Pros and Cons of Career Average Pensions
Career average pensions calculate benefits based on earnings throughout an entire career, offering a fair reflection of long-term contributions and reducing the risk for employees who have fluctuating incomes or change jobs frequently. They provide predictable and stable retirement income but may result in lower payouts compared to final salary schemes for individuals with significant salary increases late in their careers. Administrative complexity and the need for accurate record-keeping of annual earnings present challenges, while the scheme promotes equity among diverse employee groups.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Final Salary Pensions
Final salary pensions offer the advantage of predictable, inflation-linked retirement income based on the employee's highest or final salary, providing financial security and simplifying retirement planning. However, they can be costly for employers due to the need to guarantee defined benefits, and less flexible for employees who change jobs frequently or experience salary fluctuations. The reliance on final salary can also disadvantage those with shorter tenures or non-linear career progressions, limiting the pension's inclusivity and adaptability.
Impact of Career Progression on Pension Type
Career average pension schemes calculate benefits based on the average earnings throughout an employee's working life, resulting in pension amounts that reflect gradual salary growth and consistent contributions. Final salary pension schemes base benefits on the salary at retirement or near retirement, which can disproportionately reward those with significant salary increases later in their careers. Rapid career progression typically benefits final salary schemes more, while steady, moderate growth favors career average schemes in terms of pension outcomes.
Which Pension Scheme Is More Sustainable?
Career Average pension schemes accrue benefits based on an employee's earnings throughout their working life, offering a more predictable and controlled pension liability for employers compared to Final Salary schemes, where pensions are calculated based on the employee's highest or final salary. Final Salary schemes tend to be more costly and less sustainable due to their vulnerability to salary inflation and increasing life expectancy, which leads to higher pension payments over time. Career Average schemes provide greater financial sustainability by aligning pension growth with consistent economic factors and reducing long-term funding risks for both employers and pension funds.
Choosing the Best Pension Option for Your Future
Choosing between career average and final salary pension schemes impacts your retirement income stability and growth. Career average pensions calculate benefits based on earnings throughout your working life, offering steady accrual that reflects salary changes, while final salary schemes base benefits on your highest or final salary, potentially yielding larger payouts if your pay increases significantly near retirement. Assess your income trajectory, job stability, and pension scheme rules to determine which option aligns best with your long-term financial goals and retirement security.
Frequently Asked Questions: Career Average vs Final Salary
Career Average pension schemes calculate retirement benefits based on the average earnings over an employee's entire career, providing a balanced and predictable pension outcome. Final Salary schemes, also known as Defined Benefit plans, base pension benefits on the salary at or near retirement, often leading to higher payouts for those with substantial late-career pay increases. Frequently asked questions highlight differences in risk distribution, contribution levels, and benefit calculations between Career Average and Final Salary pension schemes.
Important Terms
Accrual Rate
The Accrual Rate determines how pension benefits accumulate annually, with Career Average schemes calculating based on earnings throughout employment while Final Salary schemes base benefits on the salary at retirement.
Defined Benefit Scheme
Career Average Defined Benefit Schemes calculate pensions based on an average of earnings throughout a member's career, while Final Salary Defined Benefit Schemes base pensions on the salary earned at the end of a member's career, typically resulting in different retirement income outcomes.
Pensionable Earnings
Career average pensionable earnings calculate retirement benefits based on the average salary over an entire career, whereas final salary schemes base pension benefits on the highest or final salary earned before retirement.
Revaluation Rate
The revaluation rate adjusts career average pension benefits to inflation, ensuring fair comparison with final salary schemes for accurate retirement income growth.
Scheme Retirement Age
Scheme retirement age often varies depending on whether the pension is calculated on a career average or final salary basis, with career average schemes typically offering more flexibility in retirement timing. Final salary schemes usually link retirement age closely to the accrual of maximum benefits, commonly around ages 60 to 65, ensuring higher pension payouts based on the last drawn salary.
Normal Pension Age
Normal Pension Age varies by scheme but typically impacts the calculation method where Career Average schemes smooth earnings over time, contrasting with Final Salary schemes that base benefits on the highest or last salary before retirement.
Commutation Factor
The commutation factor quantifies the lump sum value of pension benefits by converting future Career Average or Final Salary pension entitlements into a present cash equivalent, reflecting differences in calculation methods and retirement benefit projections.
Longevity Risk
Longevity risk significantly impacts pension schemes, where career average schemes calculate benefits based on the average earnings throughout employment, potentially offering more predictable payouts compared to final salary schemes, which base pensions on the last or highest salary and may expose employers to greater financial strain as retirees live longer. Actuaries must carefully assess longevity assumptions in these pension models to ensure sustainable funding and avoid underestimating the cost of lifetime retirement benefits.
Benefit Formula
Benefit Formula compares Career Average and Final Salary methods to calculate pension benefits, where Career Average calculates based on average earnings over the career, offering steady accrual, while Final Salary bases benefits on the last or highest salary period, often leading to higher payouts for late-career earners. Career Average formulas provide more equitable benefits across varying income trajectories, whereas Final Salary schemes can disproportionately favor employees with significant late-career salary increases.
Salary Linkage
Salary linkage between Career Average and Final Salary schemes impacts pension outcomes by determining whether contributions are based on career-wide earnings or final salary levels, influencing retirement benefits' predictability and fairness.
Career Average vs Final Salary Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com