Demand deposits offer immediate access to funds without penalties, making them ideal for everyday transactions and liquidity needs. Time deposits lock funds for a fixed term, typically providing higher interest rates as compensation for reduced accessibility. Choosing between demand and time deposits depends on balancing the need for liquidity against the desire for better returns.
Table of Comparison
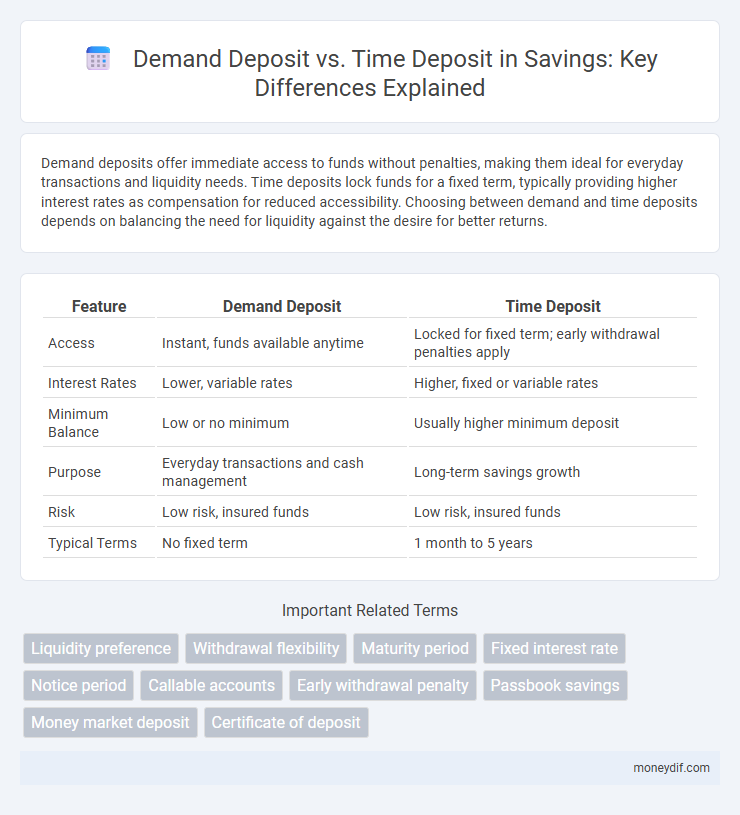
| Feature | Demand Deposit | Time Deposit |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Instant, funds available anytime | Locked for fixed term; early withdrawal penalties apply |
| Interest Rates | Lower, variable rates | Higher, fixed or variable rates |
| Minimum Balance | Low or no minimum | Usually higher minimum deposit |
| Purpose | Everyday transactions and cash management | Long-term savings growth |
| Risk | Low risk, insured funds | Low risk, insured funds |
| Typical Terms | No fixed term | 1 month to 5 years |
Understanding Demand Deposits: Key Features
Demand deposits offer immediate access to funds without withdrawal restrictions, making them ideal for daily transactions and liquidity management. These accounts typically do not earn significant interest compared to time deposits but provide high flexibility for account holders. Understanding the key features of demand deposits, such as unlimited withdrawals and no fixed maturity, is crucial for effective savings and cash flow planning.
What Are Time Deposits? Benefits and Drawbacks
Time deposits, also known as certificates of deposit (CDs), are fixed-term savings accounts that earn interest over a specified period, typically ranging from a few months to several years. They offer higher interest rates compared to demand deposits but impose penalties for early withdrawal, limiting liquidity. The benefits include predictable returns and low risk, while drawbacks involve reduced accessibility and potential inflation risk during the lock-in period.
Liquidity Comparison: Demand vs Time Deposits
Demand deposits offer high liquidity, allowing account holders to access funds instantly without penalties, making them ideal for daily transactions and emergencies. Time deposits, such as certificates of deposit (CDs), restrict withdrawals until a specified maturity date, resulting in lower liquidity but often higher interest rates. The trade-off between immediate accessibility and earning potential is a critical factor in choosing between demand and time deposits for savings management.
Interest Rates: Demand Deposit vs Time Deposit
Demand deposit accounts typically offer lower interest rates compared to time deposit accounts due to their high liquidity and easy access to funds. Time deposits, such as certificates of deposit (CDs), provide higher interest rates because the funds are locked in for a fixed term, reducing the bank's risk exposure. This interest rate differential reflects the trade-off between accessibility and earning potential in savings strategies.
Accessibility and Withdrawal Rules Explained
Demand deposits provide immediate access to funds with unlimited withdrawals and no penalties, making them ideal for daily expenses and emergencies. Time deposits require funds to be locked in for a predetermined period, offering higher interest rates but limited access until maturity, with penalties imposed on early withdrawals. Understanding withdrawal rules ensures optimal savings management based on liquidity needs and financial goals.
Safety and Risk Factors for Both Deposit Types
Demand deposits offer high liquidity with minimal risk, as funds are accessible anytime and typically insured up to $250,000 by the FDIC in the United States. Time deposits, such as certificates of deposit (CDs), provide greater interest rates but involve restricted access until maturity, posing a potential penalty risk for early withdrawal. Both deposit types carry low default risk due to federal insurance, but time deposits face market risk related to interest rate fluctuations if sold prior to maturity.
Which Deposit Suits Your Savings Goals?
Demand deposits offer flexibility with easy access to funds, ideal for emergency savings or frequent transactions, while time deposits provide higher interest rates suited for long-term savings goals. Choosing the right deposit depends on your liquidity needs and the desired growth of your savings. For short-term access, demand deposits are preferable, whereas time deposits maximize returns through fixed terms.
Fees and Charges: What to Expect
Demand deposits typically have lower fees and no penalties for withdrawals, providing flexibility without extra costs. Time deposits often involve fixed fees or minimum balance requirements and impose early withdrawal penalties that reduce overall returns. Understanding these fee structures helps savers choose the right account based on their liquidity needs and cost preferences.
Tax Implications of Demand and Time Deposits
Demand deposits typically offer greater liquidity but often generate interest income that is subject to regular income tax, impacting the net returns for account holders. Time deposits, while locking funds for a fixed term, may provide higher interest rates, and the earned interest is also taxable, sometimes at the same rate as demand deposit interest depending on jurisdiction. Understanding the specific tax regulations in your country is crucial, as some regions offer tax advantages or exemptions for certain time deposit products that can significantly affect overall savings growth.
Choosing Between Demand and Time Deposits: A Quick Guide
Demand deposits provide instant access to funds, ideal for everyday transactions and emergency needs, while time deposits offer higher interest rates in exchange for locking money for a fixed period, typically ranging from months to years. Selecting between demand and time deposits depends on your liquidity requirements and financial goals; opt for demand deposits if you need flexibility, and choose time deposits to maximize returns with limited withdrawals. Consider factors such as interest rates, maturity terms, and penalty charges for early withdrawals to make an informed decision aligned with your savings strategy.
Important Terms
Liquidity preference
Liquidity preference theory explains that investors prefer demand deposits for immediate access to funds while time deposits offer higher interest rates in exchange for reduced liquidity.
Withdrawal flexibility
Withdrawal flexibility is a key feature distinguishing demand deposits from time deposits, as demand deposits allow immediate access to funds without penalty, while time deposits typically impose restrictions and early withdrawal penalties to encourage savings over a fixed term. This difference impacts liquidity management and interest rates, with demand deposits offering lower interest due to higher accessibility, whereas time deposits provide higher returns in exchange for limited withdrawal flexibility.
Maturity period
Maturity period distinguishes demand deposits, which have no fixed term and allow immediate withdrawal, from time deposits that require funds to remain locked for a specified duration such as 6 months, 1 year, or longer to earn higher interest. Time deposits' fixed maturity periods incentivize longer-term savings, while demand deposits offer greater liquidity without penalty or time constraints.
Fixed interest rate
Fixed interest rates on time deposits typically offer higher returns than demand deposits, which usually have variable or lower interest rates due to their liquidity features.
Notice period
Notice periods for demand deposits are generally shorter or immediate, whereas time deposits require a fixed notice period before withdrawal to avoid penalties.
Callable accounts
Callable accounts allow banks to withdraw demand deposits on notice while time deposits remain fixed until maturity, balancing liquidity with interest benefits.
Early withdrawal penalty
Early withdrawal from a time deposit typically incurs a penalty that reduces earned interest, whereas demand deposits allow immediate access to funds without penalties.
Passbook savings
Passbook savings accounts combine the liquidity of demand deposits with the interest-earning advantages of time deposits, offering flexible access to funds while accruing higher interest than typical checking accounts.
Money market deposit
Money market deposits offer higher interest rates compared to demand deposits due to their limited liquidity and minimum balance requirements, making them more similar to time deposits in terms of earning potential. Unlike demand deposits, which allow unlimited withdrawals, money market deposits often have restrictions on the number of transactions, bridging the gap between the flexibility of checking accounts and the fixed terms of time deposits.
Certificate of deposit
A Certificate of Deposit (CD) is a time deposit offering higher interest rates than demand deposits by requiring funds to be locked for a fixed term.
Demand deposit vs Time deposit Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com