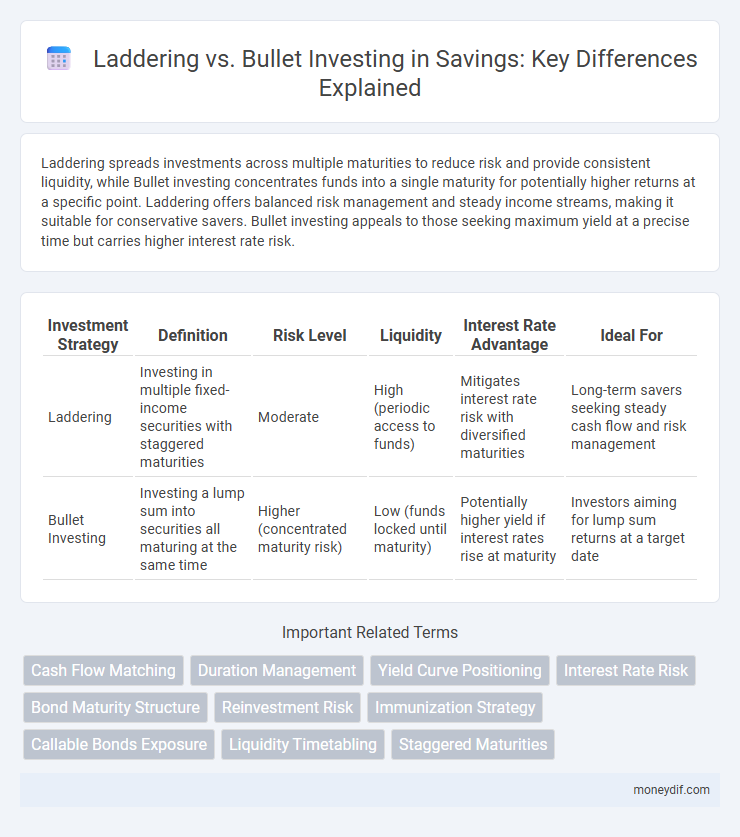
Laddering spreads investments across multiple maturities to reduce risk and provide consistent liquidity, while Bullet investing concentrates funds into a single maturity for potentially higher returns at a specific point. Laddering offers balanced risk management and steady income streams, making it suitable for conservative savers. Bullet investing appeals to those seeking maximum yield at a precise time but carries higher interest rate risk.
Table of Comparison
| Investment Strategy | Definition | Risk Level | Liquidity | Interest Rate Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laddering | Investing in multiple fixed-income securities with staggered maturities | Moderate | High (periodic access to funds) | Mitigates interest rate risk with diversified maturities | Long-term savers seeking steady cash flow and risk management |
| Bullet Investing | Investing a lump sum into securities all maturing at the same time | Higher (concentrated maturity risk) | Low (funds locked until maturity) | Potentially higher yield if interest rates rise at maturity | Investors aiming for lump sum returns at a target date |
Introduction to Laddering and Bullet Investing
Laddering involves spreading bond investments across multiple maturities to manage interest rate risk and provide regular income streams. Bullet investing focuses on purchasing bonds that mature around the same time, aiming for a lump sum payout to meet specific future expenses. Both strategies balance risk and liquidity but differ in timing and cash flow management.
Key Differences Between Laddering and Bullet Strategies
Laddering involves spreading investments across multiple maturities to reduce interest rate risk and enhance liquidity, while Bullet investing concentrates all funds into a single maturity date for potentially higher returns. Laddering allows for staggered reinvestment opportunities, balancing risk and flexibility, whereas Bullet investing emphasizes maximizing yield at one point in time but with less liquidity. The key difference lies in how these strategies manage timing, risk exposure, and income distribution across the investment horizon.
How Laddering Works in Savings
Laddering in savings involves dividing investments into multiple fixed-term deposits or bonds with staggered maturity dates, allowing regular access to funds while capturing higher interest rates from longer terms. This strategy reduces interest rate risk by spreading investments across different periods, ensuring liquidity and steady returns. By renewing matured deposits at current rates, laddering helps maximize earnings and maintain flexibility in fluctuating markets.
Understanding the Bullet Investment Approach
The Bullet investment approach involves purchasing bonds or fixed-income securities that all mature at the same time, providing a lump sum payout aligned with a specific financial goal. This strategy minimizes reinvestment risk by focusing on a single maturity date, making it ideal for targeting expenses like tuition payments or large purchases. Investors prioritize timing and interest rate predictions to maximize returns and ensure funds are available precisely when needed.
Benefits of Laddering for Savers
Laddering in savings allows investors to spread risk by staggering maturity dates across multiple fixed-income investments, providing regular access to funds and increasing liquidity. This strategy helps savers take advantage of fluctuating interest rates over time, potentially enhancing overall returns compared to bullet investing, where a lump sum matures at once. Diversification through laddering minimizes reinvestment risk and balances income streams, offering greater financial flexibility and stability for long-term planning.
Pros and Cons of Bullet Investing
Bullet investing offers a focused maturity date, which simplifies planning for future financial needs and can reduce reinvestment risk by timing all investments to mature together. However, this strategy concentrates risk, as a single economic downturn at maturity could impact the entire portfolio's value. Bullet investing may limit liquidity and flexibility compared to laddering, making it less adaptable to changing market conditions or personal circumstances.
Risk Management: Laddering vs Bullet Investing
Laddering mitigates interest rate risk by staggering bond maturities, ensuring liquidity and steady income over time, which diversifies reinvestment opportunities. Bullet investing concentrates maturities at a single point, exposing the portfolio to potential market timing risks and interest rate fluctuations at that maturity. Efficient risk management favors laddering for its ability to balance reinvestment risk and maintain portfolio stability.
Liquidity and Flexibility: A Comparative Analysis
Laddering investment strategies provide enhanced liquidity by staggering bond maturities, enabling investors to access funds periodically without sacrificing returns, whereas bullet investing concentrates maturities at a single point, limiting liquidity but potentially maximizing yield at that time. Laddered portfolios allow for greater flexibility in reinvestment decisions as market conditions change, while bullet strategies require commitment to a fixed timeline, reducing adaptability. Investors valuing steady cash flow and risk management typically prefer laddering, whereas those targeting specific future financial goals may choose bullet investing despite its liquidity constraints.
Which Strategy Suits Your Savings Goals?
Laddering involves spreading investments across multiple maturities to enhance liquidity and reduce interest rate risk, ideal for savers seeking steady income and flexibility. Bullet investing concentrates funds into a single maturity date, maximizing returns but requiring precise timing, suited for those with a specific future cash need. Choosing between laddering and bullet investing depends on your savings horizon, risk tolerance, and income requirements.
Choosing the Right Approach: Laddering or Bullet Investing
Choosing between laddering and bullet investing depends on your cash flow needs and interest rate outlook. Laddering spreads maturity dates evenly, reducing interest rate risk and providing steady income, while bullet investing concentrates investments to mature at a single point, maximizing returns if timed correctly. Evaluating market conditions and liquidity requirements will help determine the optimal strategy for building a savings portfolio.
Important Terms
Cash Flow Matching
Cash Flow Matching involves aligning asset cash inflows with liability cash outflows to ensure all obligations are met without selling assets prematurely, contrasting with Laddering which staggers maturities to manage reinvestment risk, and Bullet Investing which concentrates maturities at a single point for targeted funding needs. Cash Flow Matching offers precise funding certainty, while Laddering provides liquidity and risk diversification, and Bullet Investing maximizes yield but increases refinancing risk.
Duration Management
Duration management involves adjusting the sensitivity of a bond portfolio to interest rate changes by strategically selecting maturities, where laddering distributes investments across staggered bonds to mitigate reinvestment risk and maintain liquidity. Bullet investing concentrates bond maturities around a single target date, optimizing cash flow for specific future liabilities but increasing exposure to interest rate fluctuations at that horizon.
Yield Curve Positioning
Yield curve positioning involves strategically allocating bond maturities along the curve to optimize returns and manage interest rate risk, with laddering spreading investments evenly across various maturities to reduce reinvestment risk and enhance liquidity. Bullet investing concentrates maturities around a single point on the yield curve to capitalize on specific interest rate views, potentially increasing yield but also exposing the portfolio to greater duration risk compared to laddering.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk impacts laddering and bullet investing strategies differently, as laddering spreads bond maturities to reduce exposure to interest rate fluctuations, while bullet investing concentrates maturities at one point, increasing sensitivity to rate changes. Bond ladder portfolios typically offer more stable cash flow and lower price volatility compared to bullet strategies, which can suffer significant losses if rates rise sharply before maturity.
Bond Maturity Structure
Bond maturity structure influences risk and liquidity management, where laddering involves purchasing bonds with staggered maturities to reduce interest rate risk and provide steady cash flow, while bullet investing concentrates bond maturities around a single date to maximize potential returns at a specific time horizon. Laddering enhances portfolio diversification and reinvestment flexibility, whereas bullet strategies may benefit investors targeting a precise future liability or financial goal.
Reinvestment Risk
Reinvestment risk in laddering investing is minimized by staggering bond maturities, allowing investors to reinvest principal at varying interest rates over time, while bullet investing concentrates maturities, exposing investors to significant reinvestment risk when bonds mature simultaneously. Managing reinvestment risk effectively requires understanding the timing and interest rate environment associated with each strategy.
Immunization Strategy
Immunization strategy in fixed income portfolio management mitigates interest rate risk by matching asset duration to liability duration, ensuring consistent returns despite rate fluctuations. Laddering invests in bonds with staggered maturities to maintain liquidity and reduce reinvestment risk, while bullet investing concentrates maturities around a single target date, optimizing for specific future liabilities.
Callable Bonds Exposure
Callable bonds expose investors to reinvestment risk as issuers may redeem bonds before maturity, disrupting expected cash flows. Laddering bond investments mitigates this risk by staggering maturity dates, whereas bullet investing concentrates exposure at a single maturity, increasing vulnerability to call events.
Liquidity Timetabling
Liquidity timetabling involves strategically scheduling asset maturities to ensure cash availability, optimizing risk management by aligning inflows with liabilities. Laddering spreads investments across multiple maturities to maintain consistent liquidity and reduce reinvestment risk, whereas bullet investing concentrates maturities at a single point, maximizing yield but increasing cash flow timing risk.
Staggered Maturities
Staggered maturities in laddering involve spreading bond investments across multiple maturity dates to manage interest rate risk and maintain liquidity, while bullet investing concentrates bonds around a single maturity date for targeted cash flow needs. Laddering enhances portfolio diversification and reduces reinvestment risk compared to the lump-sum nature of bullet strategies.
Laddering vs Bullet investing Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com