ESOP savings build long-term wealth by granting employees ownership stakes, aligning interests with company growth and fostering a sense of loyalty. ESPP savings offer employees the chance to purchase stock at a discounted price, providing immediate benefits and potential for short-term gains. Combining both plans can optimize financial growth by balancing ownership accumulation with accessible investment opportunities.
Table of Comparison
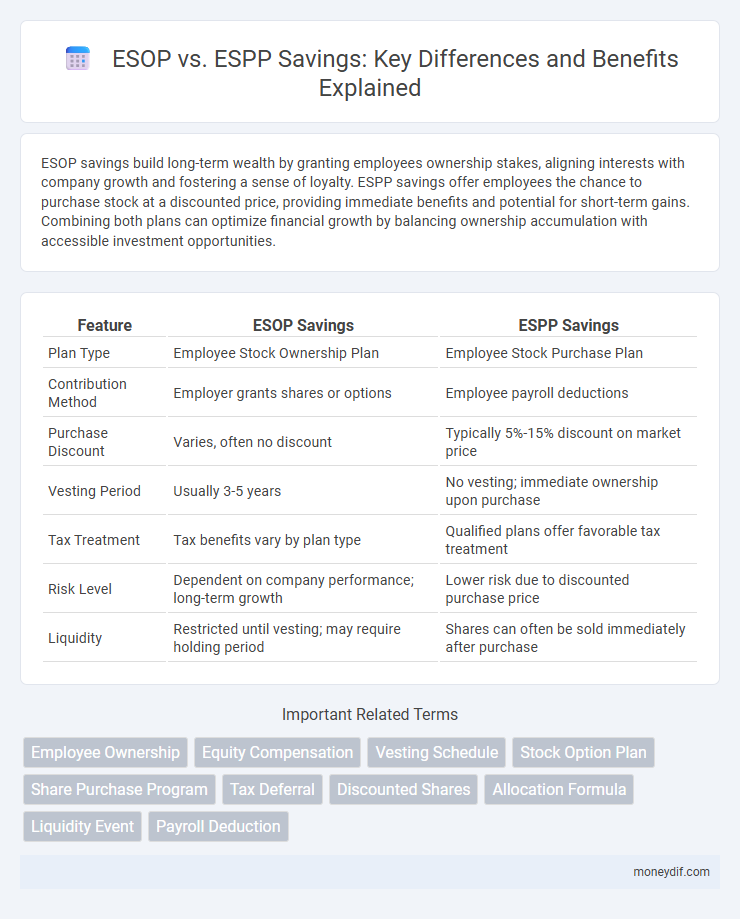
| Feature | ESOP Savings | ESPP Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Plan Type | Employee Stock Ownership Plan | Employee Stock Purchase Plan |
| Contribution Method | Employer grants shares or options | Employee payroll deductions |
| Purchase Discount | Varies, often no discount | Typically 5%-15% discount on market price |
| Vesting Period | Usually 3-5 years | No vesting; immediate ownership upon purchase |
| Tax Treatment | Tax benefits vary by plan type | Qualified plans offer favorable tax treatment |
| Risk Level | Dependent on company performance; long-term growth | Lower risk due to discounted purchase price |
| Liquidity | Restricted until vesting; may require holding period | Shares can often be sold immediately after purchase |
Understanding ESOP Savings: Definition and Basics
ESOP savings involve employees acquiring ownership stakes through employer-sponsored stock purchase plans, offering long-term retirement benefits by aligning employee interests with company growth. These plans typically provide shares at a discounted rate or as part of compensation, fostering workforce retention and motivation. Understanding the tax advantages and vesting schedules associated with ESOPs is essential for maximizing savings potential.
What is ESPP Savings? Key Features Explained
ESPP savings refer to Employee Stock Purchase Plan programs that allow employees to buy company stock at a discounted price, often through payroll deductions over a specific offering period. Key features include the purchase discount, which typically ranges from 5% to 15%, a defined offering period, and potential tax advantages depending on the holding period and plan specifics. ESPP savings provide employees with an opportunity to build equity ownership in their company while benefiting from stock price appreciation and discount incentives.
ESOP vs ESPP: Core Differences in Savings Potential
Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs) offer tax-deferred growth and employer contributions, making them a powerful tool for long-term wealth accumulation compared to Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs), which provide employees with a discounted purchase price on company shares. ESOPs typically involve employer-funded stock allocations, increasing savings without immediate cash outflow, whereas ESPPs rely on employee payroll deductions to buy shares at a discount, offering shorter-term liquidity benefits. The core difference in savings potential lies in ESOPs fostering substantial retirement wealth through employer contributions and tax advantages, while ESPPs enable employees to grow savings via discounted stock purchases with less employer funding.
Tax Benefits: ESOP Savings Compared to ESPP Savings
ESOP savings offer significant tax advantages as contributions and earnings grow tax-deferred until distribution, often qualifying for favorable long-term capital gains treatment. ESPP savings provide tax benefits through the ability to purchase stock at a discount, with tax consequences varying based on holding periods and disposition types. ESOPs generally offer greater tax deferral and potentially lower tax rates compared to the immediate or ordinary income taxation that can apply to ESPP discounts upon stock sale.
Contribution Limits: ESOP and ESPP Savings Prospects
Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOP) typically have higher contribution limits compared to Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPP), allowing participants to accumulate more significant company stock savings over time. ESPPs usually cap contributions at a percentage of an employee's salary, often around 10-15%, while ESOP contributions can be made by the employer without such strict salary-based limits. The higher contribution capacity of ESOPs offers greater potential for long-term wealth accumulation through company stock ownership.
Risk Factors: ESOP Savings vs ESPP Savings
ESOP savings carry higher risk due to concentrated company stock exposure, which can lead to significant losses if the company underperforms or faces bankruptcy. ESPP savings diversify risk by allowing employees to purchase shares at a discount but typically limit the amount invested, reducing exposure to company-specific downturns. Both plans depend on market volatility, but ESOPs lack the built-in discount advantage and usually have less liquidity compared to ESPPs.
Liquidity and Access: ESOP vs ESPP Savings Options
ESOP savings typically have limited liquidity as shares vest over time and may require a qualifying event such as retirement or company sale for access, while ESPP savings offer more frequent access through regular purchase windows and the ability to sell shares shortly after purchase. ESPP plans often provide employees with quicker liquidity options due to shorter holding periods and market-based selling opportunities. ESOPs emphasize long-term wealth accumulation with restricted access, whereas ESPPs balance savings growth with greater flexibility and immediate access to funds.
Long-term Growth: Which Savings Plan Delivers More?
ESOP savings typically deliver higher long-term growth due to concentrated ownership in the company, aligning employee and shareholder interests with potential for substantial equity appreciation over time. ESPP savings offer consistent growth by enabling employees to purchase stock at a discount, providing built-in gains and reduced upfront risk, supporting steady wealth accumulation. Evaluating historical data, ESOPs often yield greater returns when the company performs well, while ESPPs balance growth with diversified purchase strategies, appealing to risk-averse investors.
Employee Eligibility: Who Can Save with ESOP or ESPP?
Employee eligibility for ESOPs typically includes full-time employees who meet specific tenure requirements, often favoring long-term service to encourage retention. ESPPs generally allow broader participation, including part-time and newly hired employees, enabling a wider workforce to benefit from company stock discounts. Understanding these eligibility criteria helps employees optimize their savings strategies by selecting the plan that aligns with their employment status and financial goals.
Making the Choice: ESOP Savings or ESPP Savings?
Choosing between ESOP savings and ESPP savings depends on the goals of equity accumulation and tax benefits. ESOPs offer long-term retirement savings through company stock ownership with potential for significant tax advantages and vested ownership. ESPPs provide employees the opportunity to purchase shares at a discount, creating immediate value and liquidity, but typically with shorter-term investment horizons and different tax implications.
Important Terms
Employee Ownership
Employee ownership through ESOPs (Employee Stock Ownership Plans) often results in substantial retirement savings by allocating company stock directly to employees, creating long-term wealth accumulation. In contrast, ESPP (Employee Stock Purchase Plans) enable employees to buy company shares at a discount, offering more immediate investment benefits but typically with less impact on retirement savings compared to ESOPs.
Equity Compensation
Equity compensation through ESOPs (Employee Stock Ownership Plans) typically offers employees ownership stakes tied to company performance, enabling long-term wealth accumulation via stock appreciation and potential dividends. ESPPs (Employee Stock Purchase Plans) allow employees to purchase company shares at a discounted price, providing immediate savings benefits and potential gains from stock price growth, with more flexible liquidity compared to ESOPs.
Vesting Schedule
Vesting schedules determine the timeline over which employees earn ownership of ESOP shares, typically requiring several years before full rights are granted, while ESPP savings are immediately owned as employees purchase shares through payroll deductions without vesting restrictions. Understanding the differences in liquidity and ownership timing between ESOP and ESPP savings helps employees optimize their equity compensation strategy for long-term financial growth.
Stock Option Plan
Stock Option Plans grant employees the right to purchase company shares at a predetermined price, fostering long-term wealth accumulation, while ESOP savings involve ownership through a trust distributing shares as retirement benefits, enhancing employee retention. ESPP savings enable employees to buy stock at a discount through payroll deductions, providing immediate investment opportunities and liquidity compared to ESOP's deferred benefits.
Share Purchase Program
Share Purchase Programs (SPPs) allow employees to use ESOP savings or ESPP contributions to acquire company shares, often at a discounted price, enhancing ownership and long-term wealth accumulation. ESOP savings typically represent retirement benefits tied to employee stock ownership, while ESPP savings involve payroll deductions specifically allocated for purchasing shares within defined offering periods.
Tax Deferral
Tax deferral in Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs) allows employees to postpone taxes on contributions and earnings until distribution, potentially resulting in significant tax savings compared to Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs), where taxes are typically due upon purchase or sale of stock. ESOPs enable accumulation of tax-deferred retirement savings with preferential tax treatment on dividends and distributions, whereas ESPPs offer immediate tax benefits primarily through purchase discounts but require prompt tax reporting.
Discounted Shares
Discounted shares in Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOP) typically offer employees the right to purchase company stock at a predetermined price, often below market value, allowing for potential capital gains upon exercise, whereas Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPP) enable employees to buy shares at a discount, usually up to 15%, through payroll deductions over a specific offering period, promoting consistent savings and equity accumulation. ESOP savings focus on long-term wealth through stock options subject to vesting periods, while ESPP savings emphasize regular investment in discounted shares with immediate purchase, benefiting employees through systematic stock acquisition.
Allocation Formula
The allocation formula for ESOP savings versus ESPP savings typically depends on predefined company policies that balance employee ownership rates and participation incentives, optimizing long-term equity distribution and tax efficiency. ESOPs focus on retirement benefits through company stock allocation based on compensation, while ESPPs offer discounted stock purchase options, influencing savings growth through market performance and contribution limits.
Liquidity Event
Liquidity events, such as acquisitions or IPOs, unlock the value of ESOP savings by allowing employees to convert stock options into cash or shares, often benefiting from favorable tax treatment. In contrast, ESPP savings represent direct purchase discounts on company stock, providing liquidity primarily through stock sales post-vesting, typically with fewer tax advantages than ESOPs.
Payroll Deduction
Payroll deduction for ESOP savings enables employees to directly invest in company stock through stock ownership plans, promoting long-term wealth accumulation and employee retention. ESPP savings, facilitated via payroll deductions, allow employees to purchase company shares at a discounted price, offering a flexible and tax-advantaged method to enhance savings and participate in company growth.
ESOP savings vs ESPP savings Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com