Liquid savings provide immediate access to funds, offering flexibility for unexpected expenses or short-term goals, while fixed savings involve locking money for a predetermined period to earn higher interest rates. Choosing between liquid and fixed savings depends on individual financial priorities, balancing the need for accessibility against the desire for better returns. Understanding these differences helps optimize savings strategies for both security and growth.
Table of Comparison
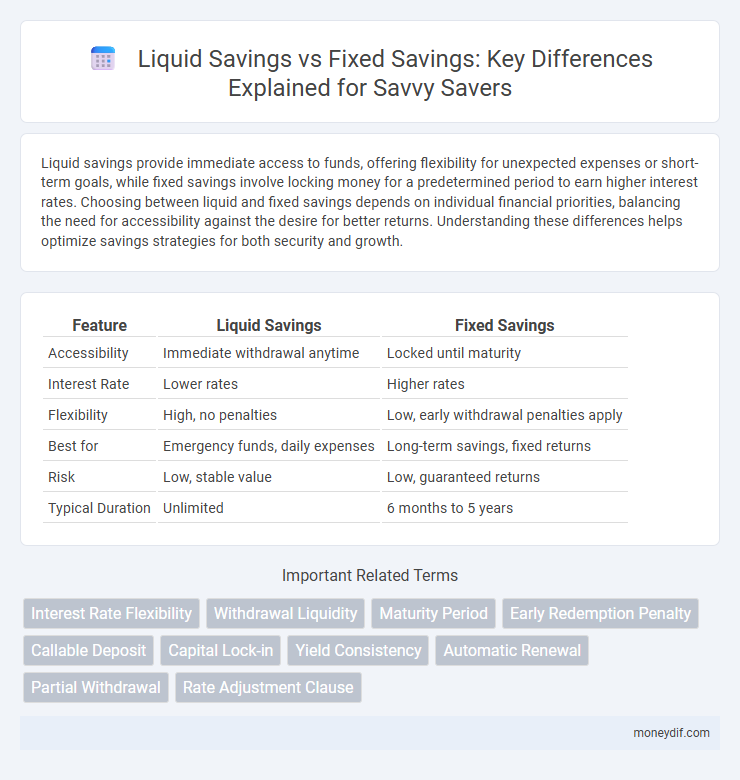
| Feature | Liquid Savings | Fixed Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Immediate withdrawal anytime | Locked until maturity |
| Interest Rate | Lower rates | Higher rates |
| Flexibility | High, no penalties | Low, early withdrawal penalties apply |
| Best for | Emergency funds, daily expenses | Long-term savings, fixed returns |
| Risk | Low, stable value | Low, guaranteed returns |
| Typical Duration | Unlimited | 6 months to 5 years |
Understanding Liquid Savings: Flexibility and Accessibility
Liquid savings offer unparalleled flexibility and immediate accessibility, allowing account holders to withdraw or transfer funds without penalties or delays. Unlike fixed savings, which lock funds for a predetermined term to earn higher interest rates, liquid savings prioritize ease of access for emergency expenses or short-term financial goals. This liquidity feature makes them ideal for users seeking convenience and financial agility in managing their day-to-day money needs.
What Are Fixed Savings? Stability and Higher Returns
Fixed savings refer to deposits held for a predetermined period, offering stability and potentially higher returns compared to liquid savings accounts. These accounts lock funds for terms ranging from a few months to several years, minimizing withdrawal flexibility but usually providing better interest rates. Fixed savings are ideal for individuals seeking consistent growth and protection from market volatility while earning guaranteed interest.
Key Differences Between Liquid and Fixed Savings
Liquid savings offer immediate access to funds without penalties, ideal for emergencies and short-term goals, while fixed savings require locking in money for a predetermined tenure, typically yielding higher interest rates. Liquid savings accounts often provide lower returns but greater flexibility, whereas fixed savings invest in instruments like fixed deposits or bonds that restrict withdrawals before maturity. The choice depends on prioritizing either accessibility with minimal risk or maximizing earnings through committed funds over time.
Pros and Cons of Liquid Savings Accounts
Liquid savings accounts offer easy access to funds, making them ideal for emergency savings and daily expenses. They typically provide lower interest rates compared to fixed savings accounts, which limits growth potential. However, the flexibility and immediate liquidity they provide outweigh the modest returns for those valuing accessibility over high yields.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Savings
Fixed savings offer higher interest rates compared to liquid savings, resulting in greater returns over a specified tenure, typically ranging from six months to five years. The primary disadvantage is limited liquidity, as premature withdrawal often incurs penalties or forfeiture of interest, restricting access to funds during emergencies. Fixed savings provide financial discipline and predictable growth but lack the flexibility found in liquid savings accounts.
Interest Rates: Liquid vs Fixed Savings Comparison
Liquid savings accounts offer lower interest rates compared to fixed savings accounts, reflecting their higher accessibility and flexibility. Fixed savings accounts typically lock funds for a predetermined term, providing higher interest rates as a reward for reduced liquidity. This interest rate differential incentivizes savers to choose fixed deposits for better returns, while liquid savings are preferred for emergency funds despite lower earnings.
Withdrawal Rules: Accessibility in Liquid vs Fixed Accounts
Liquid savings accounts offer immediate access to funds without penalties, providing high flexibility for withdrawal anytime. Fixed savings accounts restrict withdrawal until the maturity date, often imposing penalties or forfeiting interest for early withdrawals. This clear difference in accessibility makes liquid accounts ideal for emergency funds, while fixed accounts suit long-term saving goals with higher interest rates.
Ideal Scenarios for Using Liquid Savings
Liquid savings are ideal for emergency funds and short-term financial needs, offering quick access without penalties or delays. This type of savings suits unforeseen expenses, such as medical emergencies, car repairs, or urgent home maintenance. Using liquid savings ensures financial flexibility while maintaining immediate availability of funds.
When to Choose Fixed Savings Over Liquid Options
Fixed savings accounts are ideal when you seek higher interest rates and can commit funds for a set term without needing immediate access. Opt for fixed savings when planning for long-term financial goals, such as buying a home or funding education, where maximum growth outweighs liquidity. This choice minimizes the temptation of premature withdrawals that can affect returns, unlike liquid savings accounts designed for easy access and emergencies.
Strategic Savings: Balancing Liquid and Fixed Accounts
Strategic savings requires balancing liquid savings, which offer easy access and emergency fund flexibility, with fixed savings that provide higher interest rates through time-bound deposits. Prioritizing an optimal mix maximizes liquidity without sacrificing growth potential, ensuring both immediate fund availability and long-term financial gains. Effective allocation between liquid and fixed savings accounts enhances overall financial resilience and strategic wealth accumulation.
Important Terms
Interest Rate Flexibility
Interest rate flexibility in liquid savings accounts allows account holders to benefit from fluctuating market rates, enhancing potential returns compared to fixed savings that lock in a predetermined interest rate for a set period, offering stability but limited growth opportunity. This dynamic adjustment in liquid savings supports better liquidity management, whereas fixed savings prioritize certainty and protection against rate volatility.
Withdrawal Liquidity
Withdrawal liquidity in liquid savings accounts offers immediate access to funds without penalties, contrasting fixed savings where funds are locked for a predetermined term to earn higher interest rates. The trade-off between withdrawal liquidity and interest returns is a crucial consideration for optimizing savings strategies based on personal financial goals and cash flow needs.
Maturity Period
Maturity period significantly influences the liquidity of savings, with liquid savings typically allowing access to funds at any time without penalties, whereas fixed savings require a predetermined maturity period before withdrawal to earn interest. Understanding the maturity period helps optimize financial planning by balancing immediate access needs against higher returns offered by fixed savings with longer lock-in durations.
Early Redemption Penalty
Early redemption penalty is a fee charged when withdrawing funds from fixed savings before maturity, affecting overall returns by reducing the earned interest. Liquid savings accounts allow penalty-free withdrawals, offering greater flexibility but typically lower interest rates compared to fixed savings.
Callable Deposit
Callable deposits offer higher interest rates compared to regular liquid savings accounts, combining flexibility with better returns by allowing the bank to 'call' or withdraw the deposit with prior notice. Unlike fixed savings, callable deposits balance liquidity and yield, as they provide higher interest than liquid savings but with less commitment than fixed deposits, making them suitable for investors seeking moderate flexibility and enhanced earnings.
Capital Lock-in
Capital lock-in occurs when funds are tied in fixed savings accounts, restricting liquidity and access to cash compared to liquid savings that allow immediate withdrawals. Fixed savings typically offer higher interest rates as compensation for reduced flexibility, influencing investors' decisions based on their short-term cash needs versus long-term growth goals.
Yield Consistency
Yield consistency in liquid savings offers flexible access with variable interest rates, typically lower but more stable compared to fixed savings. Fixed savings provide higher, locked-in returns over a set term, ensuring predictable yield consistency but with limited liquidity.
Automatic Renewal
Automatic renewal in liquid savings allows seamless reinvestment of funds with immediate liquidity and daily interest accrual, whereas fixed savings automatic renewal locks the principal for a predetermined term with typically higher interest rates but limited access until maturity. Choosing between these depends on whether the priority is flexible access and lower risk or higher returns with fixed tenure.
Partial Withdrawal
Partial withdrawal from liquid savings allows immediate access to funds without penalties, whereas fixed savings accounts often impose restrictions and penalties for early withdrawals, making liquid savings more flexible for emergency use. Choosing between partial withdrawal options depends on the need for liquidity versus higher interest rates typically offered by fixed savings.
Rate Adjustment Clause
Rate Adjustment Clause in savings accounts defines the terms under which interest rates can change, significantly impacting the return on Liquid Savings compared to Fixed Savings. While Liquid Savings accounts typically offer variable interest rates subject to frequent adjustments, Fixed Savings accounts lock in a rate for the term duration, providing predictable earnings despite market fluctuations.
Liquid Savings vs Fixed Savings Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com