Liquid savings offer immediate access to funds, ideal for emergencies or short-term needs, while fixed deposits lock money for a set period, providing higher interest rates and better returns. Choosing between liquid savings and fixed deposits depends on your financial goals and liquidity requirements. Balancing both options ensures flexibility and growth in your savings portfolio.
Table of Comparison
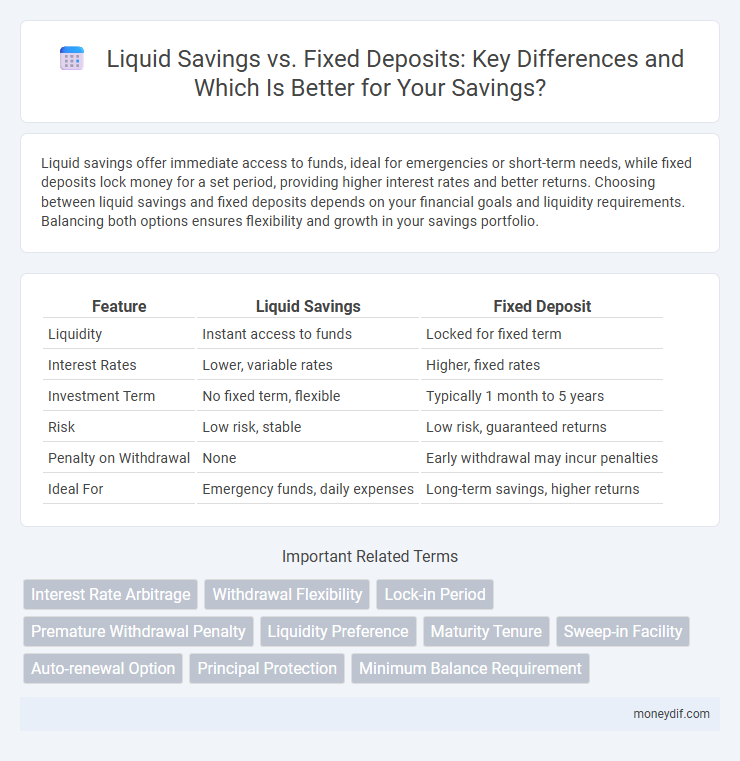
| Feature | Liquid Savings | Fixed Deposit |
|---|---|---|
| Liquidity | Instant access to funds | Locked for fixed term |
| Interest Rates | Lower, variable rates | Higher, fixed rates |
| Investment Term | No fixed term, flexible | Typically 1 month to 5 years |
| Risk | Low risk, stable | Low risk, guaranteed returns |
| Penalty on Withdrawal | None | Early withdrawal may incur penalties |
| Ideal For | Emergency funds, daily expenses | Long-term savings, higher returns |
Understanding Liquid Savings and Fixed Deposits
Liquid savings accounts offer immediate access to funds, providing flexibility for daily expenses and emergencies with minimal restrictions and no penalties on withdrawals. Fixed deposits lock in money for a predetermined term, ensuring higher interest rates and capital security, but restrict withdrawals until maturity to avoid penalties. Understanding the trade-off between liquidity and return is crucial for optimizing savings strategy according to cash flow needs and financial goals.
Key Differences Between Liquid Savings and Fixed Deposit Accounts
Liquid savings accounts offer immediate access to funds without penalties, making them ideal for emergency expenses and short-term savings, while fixed deposit accounts lock in money for a specified term, providing higher interest rates but limiting liquidity. Interest earned on liquid savings is generally lower compared to fixed deposits, which benefit from fixed rates over longer durations, enhancing overall returns. Fixed deposits impose withdrawal penalties or forfeiture of interest if funds are accessed before maturity, whereas liquid savings accounts allow unlimited deposits and withdrawals without restrictions.
Interest Rates: Liquid Savings vs Fixed Deposits
Interest rates for liquid savings accounts typically range from 0.1% to 1%, offering easy access to funds but lower returns. Fixed deposits provide higher interest rates, often between 4% and 7%, rewarding longer commitment with guaranteed returns. Choosing between the two depends on balancing liquidity needs against the desire for increased interest earnings.
Liquidity and Accessibility: What You Need to Know
Liquid savings accounts provide immediate access to funds without penalties, offering maximum liquidity ideal for emergencies. Fixed deposits lock money for a predetermined period, yielding higher interest but restricting withdrawals until maturity. Choosing between the two depends on your need for quick access versus earning potential.
Risk Factors in Liquid Savings and Fixed Deposits
Liquid savings accounts offer high liquidity but carry minimal risk due to insurance protection and stable interest rates, making them ideal for emergency funds. Fixed deposits present lower liquidity with funds locked for fixed terms, yet they offer higher interest rates and are shielded from market volatility, reducing credit risk. Both options are considered low-risk, but fixed deposits may face penalties for early withdrawal, impacting overall returns.
Returns and Growth Potential: A Comparative Analysis
Liquid savings accounts offer easy access to funds with lower interest rates, typically ranging from 0.5% to 1.5% annually, limiting their growth potential. Fixed deposits provide higher returns, often between 4% and 7% per annum, with guaranteed interest over a fixed tenure, enhancing capital growth for long-term savings objectives. The choice depends on prioritizing liquidity or maximizing interest income through time-bound investments.
Tax Implications for Liquid Savings and Fixed Deposits
Liquid savings accounts typically offer more flexibility with withdrawals but are subject to income tax on the interest earned at the individual's applicable slab rate. Fixed deposits attract tax on the interest income, which is added to the investor's total income and taxed according to the income slab, with banks deducting Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) if interest exceeds specified limits. Understanding the tax implications, including applicable TDS rates and income tax slabs, helps optimize returns between liquid savings and fixed deposits.
Who Should Choose Liquid Savings Over Fixed Deposits?
Individuals prioritizing flexibility and immediate access to funds should choose liquid savings over fixed deposits, as these accounts offer high liquidity without withdrawal penalties. Savers with uncertain cash flow needs or emergency funds benefit from the ability to withdraw anytime, whereas fixed deposits lock funds for a predetermined period with potentially higher interest rates. Younger professionals, freelance workers, and those building an emergency reserve typically find liquid savings accounts better suited to their financial goals.
When Are Fixed Deposits a Better Option?
Fixed deposits offer higher interest rates compared to liquid savings accounts, making them a better option for individuals seeking guaranteed returns over a fixed tenure, typically ranging from 7 days to 10 years. They provide financial discipline and protection against market volatility, ideal for emergency funds or planned expenses like education and retirement. Lock-in periods and penalties for premature withdrawal make fixed deposits suitable for savers with a low liquidity requirement aiming for capital preservation.
Making the Right Choice: Liquid Savings vs Fixed Deposits
Choosing between liquid savings and fixed deposits depends on your financial goals and liquidity needs. Liquid savings offer easy access to funds with modest interest rates, ideal for emergencies and short-term expenses. Fixed deposits provide higher returns by locking funds for a specified term, making them suitable for long-term wealth growth but with limited withdrawal options.
Important Terms
Interest Rate Arbitrage
Interest rate arbitrage involves exploiting the difference between the higher interest rates offered by fixed deposits and the lower, more liquid rates provided by savings accounts to maximize returns. Investors leverage fixed deposits' fixed terms and superior yields while maintaining liquidity through liquid savings for immediate cash needs or reinvestment flexibility.
Withdrawal Flexibility
Withdrawal flexibility in liquid savings accounts allows instant access to funds without penalties, contrasting with fixed deposits where premature withdrawal often incurs charges and loss of interest. This distinction makes liquid savings ideal for emergency funds, while fixed deposits serve better for long-term, higher-yield investments.
Lock-in Period
The lock-in period in fixed deposits restricts withdrawal of funds before a specified duration, typically ranging from 7 days to 5 years, ensuring higher interest rates compared to liquid savings accounts, which offer immediate access but generally lower returns. Understanding the lock-in period helps investors balance liquidity needs with the potential for higher earnings from fixed deposits versus the flexibility of liquid savings.
Premature Withdrawal Penalty
Premature withdrawal penalty for fixed deposits typically involves forfeiting a portion of the earned interest, which is substantially higher than the minimal or no penalties associated with liquid savings accounts, where funds can be accessed without losing accrued interest. Fixed deposits offer higher interest rates but lower liquidity, while liquid savings accounts provide immediate access to funds with lower returns, making penalty considerations crucial during early withdrawal.
Liquidity Preference
Liquidity preference reflects the tendency of investors to hold liquid savings that can be quickly accessed, rather than committing funds to fixed deposits which offer higher returns but limit immediate access. This behavior balances the opportunity cost of foregone interest against the need for financial flexibility in uncertain economic conditions.
Maturity Tenure
Maturity tenure significantly influences the choice between liquid savings and fixed deposits, as fixed deposits lock funds for predetermined periods ranging from 7 days to 10 years, offering higher interest rates compared to liquid savings accounts that provide immediate withdrawal options but lower returns. Investors prioritizing accessibility often prefer liquid savings for short-term financial needs, while fixed deposits suit those seeking guaranteed returns over specific maturity tenures without liquidity demands.
Sweep-in Facility
A Sweep-in Facility automatically transfers surplus funds from a savings account to a fixed deposit, maximizing interest earnings by combining the liquidity of liquid savings with the higher returns of fixed deposits. This facility ensures seamless fund movement without manual intervention, optimizing returns while maintaining easy access to funds.
Auto-renewal Option
The Auto-renewal option for Liquid Savings accounts allows seamless continuation of balance growth with instant liquidity, contrasting with Fixed Deposits where auto-renewal locks funds for a fixed term, often yielding higher interest rates but reduced flexibility. Choosing between Liquid Savings and Fixed Deposit auto-renewal depends on the preference for accessibility versus maximizing interest earnings.
Principal Protection
Principal protection ensures the original investment amount remains intact, a key factor distinguishing liquid savings accounts and fixed deposits. Liquid savings offer quick access with lower interest but minimal risk to principal, while fixed deposits lock funds for higher returns with guaranteed principal preservation over a fixed term.
Minimum Balance Requirement
Minimum balance requirement for liquid savings accounts typically ranges from $500 to $1,000, ensuring account accessibility and avoiding fees, whereas fixed deposit accounts may have higher minimum deposit thresholds, often starting at $1,000 to $5,000, reflecting their role in long-term investment with limited liquidity. Liquid savings offer immediate withdrawal flexibility without penalties, contrasting with fixed deposits that impose premature withdrawal fees but generally provide higher interest rates for funds locked in over fixed terms.
Liquid Savings vs Fixed Deposit Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com