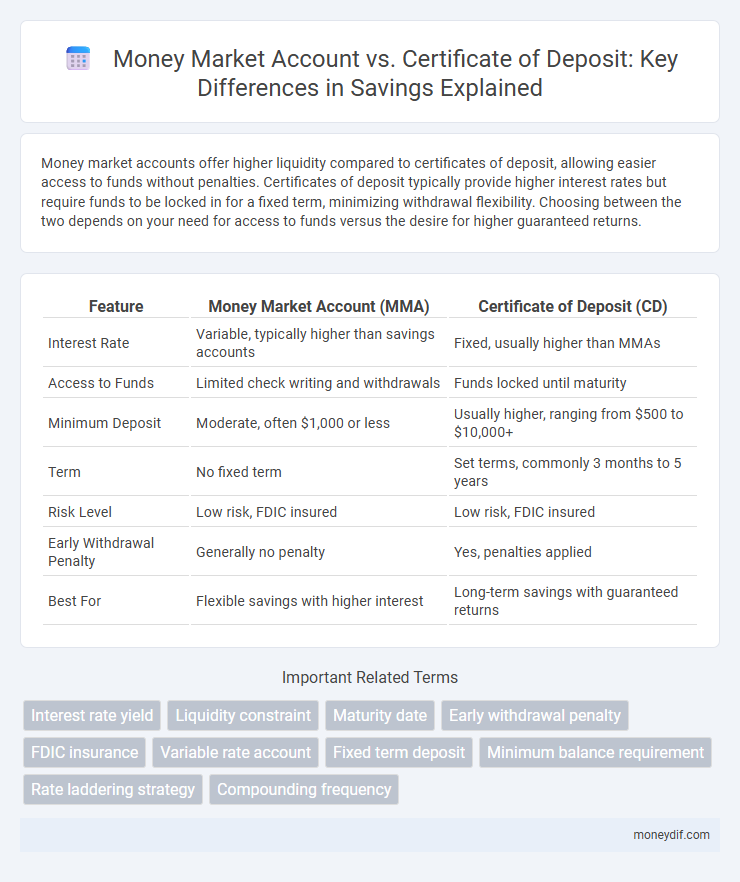
Money market accounts offer higher liquidity compared to certificates of deposit, allowing easier access to funds without penalties. Certificates of deposit typically provide higher interest rates but require funds to be locked in for a fixed term, minimizing withdrawal flexibility. Choosing between the two depends on your need for access to funds versus the desire for higher guaranteed returns.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Money Market Account (MMA) | Certificate of Deposit (CD) |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Variable, typically higher than savings accounts | Fixed, usually higher than MMAs |
| Access to Funds | Limited check writing and withdrawals | Funds locked until maturity |
| Minimum Deposit | Moderate, often $1,000 or less | Usually higher, ranging from $500 to $10,000+ |
| Term | No fixed term | Set terms, commonly 3 months to 5 years |
| Risk Level | Low risk, FDIC insured | Low risk, FDIC insured |
| Early Withdrawal Penalty | Generally no penalty | Yes, penalties applied |
| Best For | Flexible savings with higher interest | Long-term savings with guaranteed returns |
Understanding Money Market Accounts
Money market accounts offer higher interest rates than regular savings accounts while providing liquidity through check-writing and debit card access, making them ideal for short-term savings with moderate risk tolerance. Unlike certificates of deposit (CDs), which lock funds for a fixed term with penalties for early withdrawal, money market accounts allow more flexible access to funds without sacrificing competitive returns. Understanding these features helps savers choose the best option based on their need for accessibility versus guaranteed fixed returns.
What Is a Certificate of Deposit?
A Certificate of Deposit (CD) is a time-bound savings instrument offered by banks with a fixed interest rate and maturity date, providing higher returns than regular savings accounts. Unlike money market accounts, CDs require funds to be locked in for a specified period, often ranging from a few months to several years, with penalties for early withdrawal. CDs are ideal for risk-averse savers seeking guaranteed interest income without market fluctuations.
Interest Rate Comparison: MMA vs CD
Money market accounts (MMAs) typically offer variable interest rates that fluctuate with market conditions, often providing higher yields than regular savings accounts but generally lower than certificates of deposit (CDs). Certificates of deposit lock in a fixed interest rate for a specified term, usually resulting in higher guaranteed returns compared to MMAs, especially for long-term CDs. Investors seeking stable, predictable interest earnings often favor CDs, while those valuing liquidity and rate flexibility may prefer MMAs despite potentially lower rates.
Liquidity and Withdrawal Rules
Money market accounts offer higher liquidity with the ability to make up to six withdrawals or transfers per month without penalties, providing easy access to funds. Certificates of deposit (CDs) enforce fixed terms that restrict early withdrawals, typically incurring penalties and forfeiture of interest for accessing funds before maturity. Investors prioritizing flexibility should consider money market accounts, while those seeking higher interest rates and willing to lock in funds may prefer CDs.
Minimum Balance Requirements
Money market accounts typically require a higher minimum balance, often ranging from $1,000 to $2,500, to avoid fees and earn competitive interest rates. Certificates of deposit (CDs) usually have lower minimum deposit requirements, sometimes as low as $500, making them more accessible for fixed-term savings. Evaluating these minimum balance thresholds helps savers choose the best option based on liquidity needs and initial savings capacity.
Safety and FDIC Insurance
Money market accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs) both offer high safety due to FDIC insurance coverage up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank. Money market accounts provide liquidity with easy access to funds, while CDs tie up deposits for a fixed term but generally offer higher interest rates. Choosing between them depends on the balance between immediate access and maximizing FDIC-protected returns.
Fees and Penalties Explained
Money market accounts typically have lower fees and more flexible withdrawal options compared to certificates of deposit, which often impose early withdrawal penalties that can reduce earnings. Certificates of deposit may charge a fixed penalty equal to several months' interest, discouraging early access to funds and ensuring higher returns for those who maintain the investment until maturity. Understanding these fee structures helps investors choose the optimal savings vehicle based on liquidity needs and fee tolerance.
Who Should Choose a Money Market Account?
Individuals seeking easy access to their funds and higher interest rates than regular savings accounts should consider a money market account, ideal for emergency savings or short-term goals. Money market accounts typically offer check-writing privileges and debit card access, providing more liquidity compared to certificates of deposit (CDs), which require locking funds for a fixed term. Conservative savers who want flexibility without sacrificing decent returns benefit most from money market accounts.
Who Benefits Most from a CD?
Individuals seeking higher, fixed interest rates and willing to lock funds for a predetermined term benefit most from a Certificate of Deposit (CD). CDs offer predictable returns and are ideal for conservative savers prioritizing capital preservation over liquidity. Those with emergency savings in readily accessible accounts are well-positioned to allocate extra funds into CDs to maximize growth without risking principal.
Choosing the Best Savings Option for Your Needs
Money market accounts offer higher liquidity and typically variable interest rates, making them ideal for short-term savings and emergency funds. Certificates of deposit provide fixed interest rates with higher returns for a predetermined term, benefiting savers who do not need immediate access to their funds. Evaluating factors like access to funds, interest rate stability, and saving goals helps determine the best option between money market accounts and certificates of deposit.
Important Terms
Interest rate yield
Money market accounts typically offer variable interest rate yields with higher liquidity compared to certificates of deposit, which provide fixed yields locked for a specified term.
Liquidity constraint
Liquidity constraints significantly affect investment choices between a money market account and a certificate of deposit, as money market accounts offer higher liquidity with easy access to funds, whereas certificates of deposit typically impose penalties for early withdrawal, limiting immediate access to capital. Investors facing liquidity needs prefer money market accounts to maintain flexible cash flow, while those prioritizing higher interest rates and willing to lock funds choose certificates of deposit.
Maturity date
The maturity date for a Money Market Account (MMA) is typically flexible or may not have a fixed maturity, allowing easier access to funds without penalties. In contrast, a Certificate of Deposit (CD) has a fixed maturity date, ranging from a few months to several years, and withdrawing funds before this date often incurs early withdrawal penalties.
Early withdrawal penalty
Early withdrawal from a certificate of deposit (CD) typically incurs a penalty equivalent to several months of interest, reducing overall returns, while money market accounts generally offer greater liquidity with little to no early withdrawal penalties. Investors seeking short-term access to funds often prefer money market accounts due to minimal restrictions, whereas CDs are designed for fixed-term investments with higher yields but limited flexibility.
FDIC insurance
FDIC insurance covers up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank, for both money market accounts and certificates of deposit, ensuring equal protection for funds held in each type of account.
Variable rate account
Variable rate accounts offer interest rates that fluctuate with market conditions, providing more flexibility compared to the typically fixed rates of certificates of deposit, while often delivering higher returns than money market accounts with stable rates.
Fixed term deposit
Fixed term deposits offer higher interest rates than money market accounts but less liquidity than certificates of deposit, making them ideal for investors seeking predictable returns with moderate access to funds.
Minimum balance requirement
Money market accounts typically have lower minimum balance requirements than certificates of deposit, making them more accessible for investors seeking liquidity with moderate returns.
Rate laddering strategy
Rate laddering strategy optimizes returns by staggering investments across Money Market Accounts and Certificates of Deposit with varying maturities and interest rates to balance liquidity and yield.
Compounding frequency
Higher compounding frequency in money market accounts typically results in more frequent interest accrual compared to certificates of deposit, potentially increasing overall returns.
Money market account vs Certificate of deposit Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com