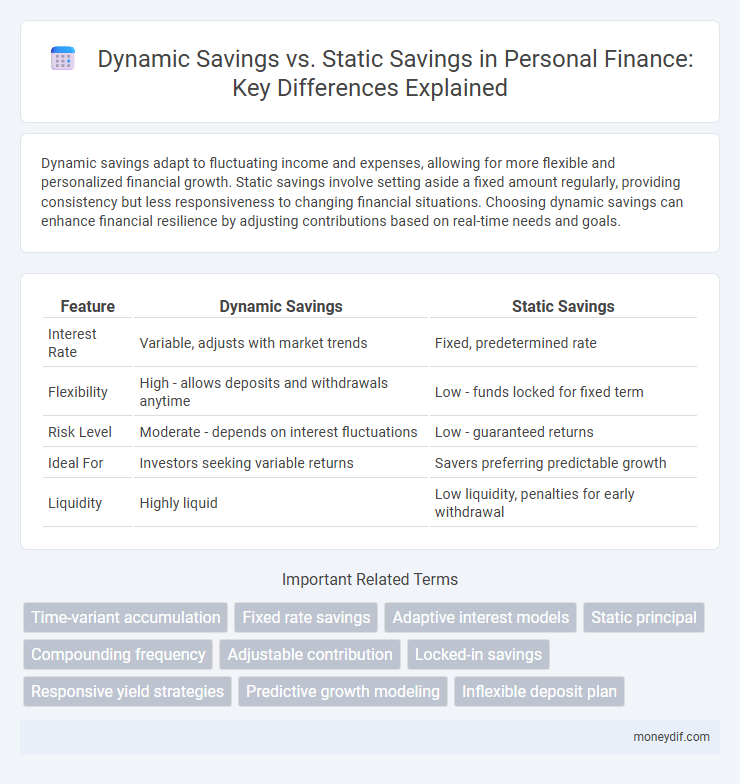
Dynamic savings adapt to fluctuating income and expenses, allowing for more flexible and personalized financial growth. Static savings involve setting aside a fixed amount regularly, providing consistency but less responsiveness to changing financial situations. Choosing dynamic savings can enhance financial resilience by adjusting contributions based on real-time needs and goals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dynamic Savings | Static Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Variable, adjusts with market trends | Fixed, predetermined rate |
| Flexibility | High - allows deposits and withdrawals anytime | Low - funds locked for fixed term |
| Risk Level | Moderate - depends on interest fluctuations | Low - guaranteed returns |
| Ideal For | Investors seeking variable returns | Savers preferring predictable growth |
| Liquidity | Highly liquid | Low liquidity, penalties for early withdrawal |
Understanding Dynamic Savings vs Static Savings
Dynamic savings adapt to changes in income and expenses, allowing for flexible contribution amounts that align with financial goals and market conditions. Static savings involve fixed, regular deposits that do not change over time, providing consistency but less responsiveness to fluctuating financial situations. Understanding the balance between dynamic and static savings strategies helps optimize financial planning by combining adaptability with discipline.
Key Features of Dynamic Savings Accounts
Dynamic savings accounts offer flexible interest rates that adjust based on market conditions, providing higher earning potential compared to static savings accounts with fixed rates. These accounts often include features such as automated deposits, real-time balance tracking, and tiered interest rates that reward higher balances. Enhanced liquidity options and personalized financial goals make dynamic savings accounts ideal for savers seeking adaptable and growth-oriented solutions.
Core Characteristics of Static Savings Methods
Static savings methods feature a fixed interest rate and predetermined maturity period, offering predictable returns and minimal risk. These methods prioritize capital preservation with limited flexibility for withdrawal or additional contributions during the term. Common examples include fixed deposits and traditional savings accounts, providing stability but less responsiveness to market fluctuations.
Interest Rates: Dynamic vs Static Savings
Dynamic savings accounts offer variable interest rates that adjust according to market conditions, often resulting in higher returns when rates increase. Static savings accounts provide fixed interest rates, delivering predictable but potentially lower earnings regardless of economic changes. Choosing between dynamic and static savings depends on your risk tolerance and desire for rate stability versus growth potential.
Flexibility and Accessibility Compared
Dynamic savings accounts offer greater flexibility by allowing variable deposit amounts and withdrawals without penalties, unlike static savings accounts that often require fixed contributions and limited access. Accessibility in dynamic savings is enhanced through digital platforms providing real-time account management, whereas static savings may involve more rigid banking procedures and longer processing times. Consumers seeking adaptable saving options benefit from dynamic accounts, which accommodate fluctuating financial situations and immediate fund availability.
Risk Factors in Dynamic and Static Savings
Dynamic savings involve regular adjustments to investment allocations based on market conditions, which introduces higher risk due to potential volatility and market timing errors. Static savings maintain a fixed allocation, offering lower risk but potentially less growth, as they do not adapt to changing market environments. Risk factors in dynamic savings include increased exposure to market fluctuations and decision-making errors, while static savings face risks of underperformance and inflation erosion.
Long-term Growth Prospects
Dynamic savings strategies adjust contributions and investment allocations based on market conditions and personal financial goals, enhancing long-term growth prospects through optimized compounding returns. Static savings maintain fixed contributions and allocations, potentially limiting growth potential by not capitalizing on fluctuating market opportunities or changing economic trends. Investors seeking maximum long-term wealth accumulation often benefit from dynamic approaches that respond to financial market dynamics and evolving risk tolerances.
Suitability for Different Financial Goals
Dynamic savings plans offer flexibility by allowing adjustments in contribution amounts based on changing income levels, making them ideal for short-term goals or fluctuating financial situations. Static savings plans maintain fixed contributions and are better suited for long-term objectives requiring consistent funding, such as retirement or major purchases. Evaluating one's income stability and financial target timelines ensures the selection of the most effective savings strategy.
Case Studies: Dynamic vs Static Savings Performance
Case studies comparing dynamic savings to static savings reveal that dynamic strategies consistently outperform by adjusting contributions based on income fluctuations and market conditions, resulting in higher portfolio growth and improved financial resilience. Analysis of multiple datasets shows dynamic savers achieve annual returns 2-4% greater than static savers due to optimized allocation and adaptive risk management. These findings emphasize the effectiveness of dynamic savings models in maximizing long-term wealth accumulation compared to fixed, unchanging savings plans.
Choosing the Right Savings Strategy
Dynamic savings strategies adjust contribution amounts based on fluctuating income, offering flexibility and potentially higher growth during prosperous periods. Static savings involve fixed contributions, providing consistency and ease of budgeting but may limit growth opportunities when income increases. Selecting the right savings approach depends on individual financial stability, income variability, and long-term goals to balance flexibility and discipline.
Important Terms
Time-variant accumulation
Time-variant accumulation reflects fluctuations in savings growth influenced by changing interest rates and contribution patterns, contrasting with static savings that assume fixed rates and consistent deposits. Dynamic savings models incorporate real-world variability, optimizing investment strategies by accounting for market volatility and temporal changes in economic conditions.
Fixed rate savings
Fixed rate savings offer a predetermined interest rate locked for the savings term, providing predictable returns compared to dynamic savings, which fluctuate based on market conditions or interest rate changes. Static savings maintain a constant rate or balance without interest adjustments, differing from fixed rate savings by lacking guaranteed interest income stability over time.
Adaptive interest models
Adaptive interest models adjust savings rates based on real-time economic indicators and individual financial behavior, enhancing responsiveness compared to static savings models that rely on fixed rates regardless of market fluctuations. This dynamic approach optimizes returns by aligning interest calculations with changing inflation, income variability, and spending patterns.
Static principal
Static principal refers to the initial amount of money invested or saved without accounting for interest or growth over time, serving as a baseline in comparing static savings to dynamic savings. Dynamic savings incorporate interest rates or investment returns, leading to growth of the principal, whereas static savings maintain the original principal amount without fluctuations.
Compounding frequency
Compounding frequency significantly affects the growth of dynamic savings by allowing interest to be calculated and added to the principal more often, resulting in exponential growth compared to static savings where interest is typically compounded less frequently or calculated simply. Higher compounding frequencies, such as daily or monthly, amplify the benefits of regular contributions in dynamic savings plans, maximizing returns over time relative to static savings with fixed principal amounts and lower compounding rates.
Adjustable contribution
Adjustable contributions in dynamic savings plans allow for flexible payment amounts that adapt to changing financial goals, unlike static savings which require fixed, consistent deposits. This flexibility enhances the potential for higher returns and better alignment with individual cash flow variations over time.
Locked-in savings
Locked-in savings refer to funds that cannot be accessed until a certain period or specific condition is met, often associated with retirement accounts or fixed-term deposits. Dynamic savings involve flexible contributions and withdrawals adjusting to changing financial goals, whereas static savings consist of fixed contributions with minimal adjustments, typically resulting in locked-in funds for predetermined durations.
Responsive yield strategies
Responsive yield strategies leverage dynamic savings by continuously adjusting investment allocations based on market conditions, optimizing returns more effectively than static savings approaches that maintain fixed allocations. Dynamic savings enable higher yield potential through real-time rebalancing and risk management, contrasting with static savings which often result in missed opportunities during market fluctuations.
Predictive growth modeling
Predictive growth modeling evaluates future financial outcomes by comparing dynamic savings strategies, which adjust contributions based on income fluctuations and market conditions, against static savings plans with fixed contributions. Incorporating variables such as interest rates, inflation, and spending patterns, dynamic savings typically yield more accurate forecasts and higher long-term growth than static savings approaches.
Inflexible deposit plan
Inflexible deposit plans restrict withdrawals and adjustments, contrasting with dynamic savings options that allow flexible contributions and access, enabling better alignment with fluctuating financial goals. Static savings maintain fixed deposit terms and interest rates, providing predictable returns but limiting responsiveness to market changes or personal needs.
Dynamic savings vs Static savings Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com