Hypothecation involves pledging assets as collateral without transferring ownership, ensuring the borrower retains control while securing a loan. Rehypothecation occurs when a lender reuses those pledged assets to secure their own borrowing, potentially increasing liquidity but also risk exposure. Understanding the distinction is crucial for savers to assess the safety and leverage implications of their pledged securities.
Table of Comparison
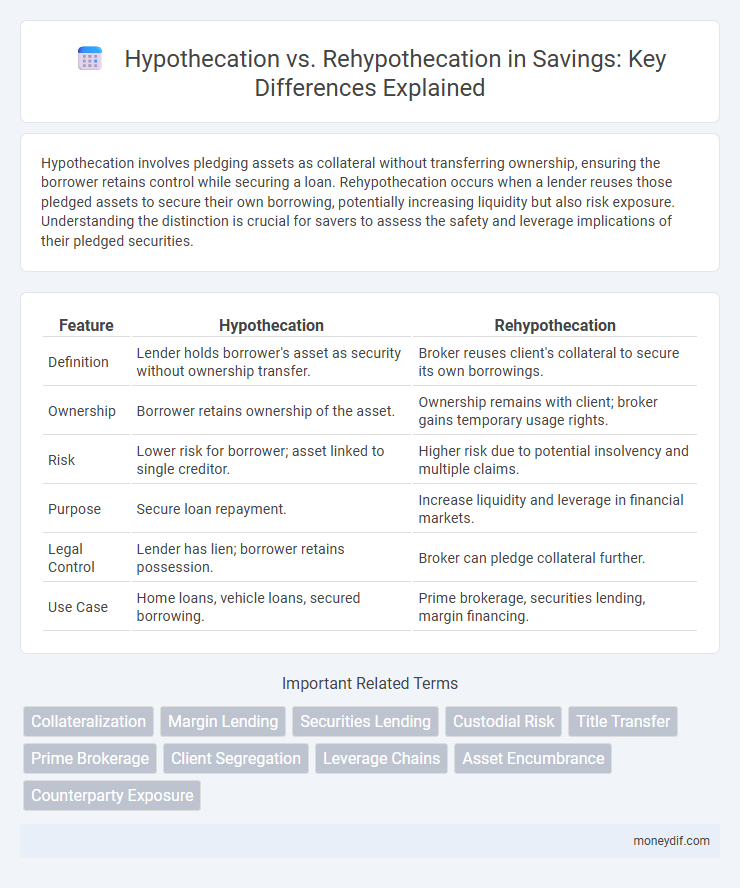
| Feature | Hypothecation | Rehypothecation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lender holds borrower's asset as security without ownership transfer. | Broker reuses client's collateral to secure its own borrowings. |
| Ownership | Borrower retains ownership of the asset. | Ownership remains with client; broker gains temporary usage rights. |
| Risk | Lower risk for borrower; asset linked to single creditor. | Higher risk due to potential insolvency and multiple claims. |
| Purpose | Secure loan repayment. | Increase liquidity and leverage in financial markets. |
| Legal Control | Lender has lien; borrower retains possession. | Broker can pledge collateral further. |
| Use Case | Home loans, vehicle loans, secured borrowing. | Prime brokerage, securities lending, margin financing. |
Understanding Hypothecation: Definition and Basics
Hypothecation is a financial arrangement where a borrower pledges an asset as collateral to secure a loan without transferring ownership, allowing them to retain possession while the lender holds a security interest. This mechanism is commonly used in secured loans, including mortgages and vehicle financing, ensuring lenders have a claim on the asset if the borrower defaults. Understanding hypothecation is crucial for savings strategy, as it affects risk management and the potential impact on personal assets during credit transactions.
What is Rehypothecation? Key Differences Explained
Rehypothecation refers to the practice where a financial institution uses assets pledged as collateral by clients to secure its own borrowing or obligations, effectively reusing the collateral beyond the original loan. Unlike hypothecation, where collateral is distinctly pledged to a creditor without transfer of ownership, rehypothecation allows the lender to leverage the asset multiple times, increasing liquidity but also risk exposure for the client. Key differences include ownership rights, risk levels, and regulatory constraints, with rehypothecation posing higher systemic risk and often subject to strict limits under financial regulations.
How Hypothecation Works in Savings and Loans
Hypothecation in savings and loans involves pledging an asset, such as a savings account or fixed deposit, as collateral without transferring ownership to the lender. This allows borrowers to access loans at lower interest rates while retaining the right to use or benefit from the asset. Banks use hypothecated assets to secure credit, reducing risk and facilitating easier loan approvals for savers.
The Mechanics of Rehypothecation in Financial Markets
Rehypothecation involves the re-use of collateral by financial institutions to secure their own borrowing, creating a chain of credit that enhances liquidity within markets. This process allows banks and brokers to lend client securities as collateral for their obligations without obtaining explicit client consent in many jurisdictions. Understanding the mechanics of rehypothecation is crucial for savings investors, as it affects the risk exposure of their assets and the overall stability of financial systems.
Risks and Benefits of Hypothecation for Savers
Hypothecation allows savers to use their assets as collateral without transferring ownership, reducing borrowing costs and enhancing liquidity. The main risk involves the potential loss of collateral if loan conditions are not met, which could impact the saver's financial stability. However, the benefit lies in retaining asset control while accessing credit, making it a favorable option for savers seeking leverage without relinquishing asset rights.
The Implications of Rehypothecation for Investors
Rehypothecation allows financial institutions to use investors' collateral for their own purposes, increasing liquidity but also raising potential risks such as loss of asset control or exposure to counterparty default. Investors face the possibility that their collateralized assets may be rehypothecated multiple times, magnifying systemic risk during market stress. Regulatory measures and transparent disclosure are essential to protect investors from unintended consequences associated with rehypothecation practices.
Legal Framework: Hypothecation vs Rehypothecation
Hypothecation involves pledging an asset as collateral while retaining ownership, governed by specific legal frameworks such as the Indian Contract Act and secured transactions laws that protect the debtor's rights. Rehypothecation refers to the reuse of collateral by a bank or broker for its own borrowing, subject to regulatory oversight under securities laws like the U.S. Securities Exchange Act and European Market Infrastructure Regulation (EMIR). Legal distinctions emphasize borrower consent, collateral control, and risk exposure to ensure transparency and mitigate systemic financial risks.
Comparing Security: Which Is Safer for Your Savings?
Hypothecation involves pledging assets as collateral without transferring ownership, offering a clearer claim on your savings in case of default. Rehypothecation allows creditors to reuse pledged assets for their own borrowing, increasing the risk of loss or delayed recovery during financial distress. Choosing hypothecation provides stronger security for your savings by maintaining direct ownership and reducing counterparty risk.
Impact on Savings Accounts: What You Need to Know
Hypothecation involves pledging assets like savings accounts as collateral without transferring ownership, which keeps the account accessible but limits its use for other loans. Rehypothecation occurs when financial institutions re-use the pledged collateral, potentially increasing risk to the savings account holder if the institution faces insolvency. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for savers to assess the security and liquidity of their savings accounts when pledged for borrowing purposes.
Choosing the Right Option: Hypothecation or Rehypothecation
Choosing between hypothecation and rehypothecation depends on your risk tolerance and liquidity needs. Hypothecation allows you to retain ownership of your assets while securing a loan, minimizing counterparty risk. Rehypothecation involves your lender using your collateral for their own purposes, which can increase liquidity but also exposes you to additional counterparty risks.
Important Terms
Collateralization
Collateralization involves pledging assets to secure a loan, with hypothecation allowing borrowers to retain ownership while granting creditors a claim, whereas rehypothecation permits lenders to reuse the collateral for their own borrowing purposes. Differences between hypothecation and rehypothecation critically affect risk exposure and liquidity in financial markets, influencing asset control and potential insolvency scenarios.
Margin Lending
Margin lending involves borrowing funds using securities as collateral, where hypothecation grants the lender a right over the collateral without transfer of ownership, while rehypothecation allows the lender to reuse the collateral for their own borrowing purposes.
Securities Lending
Hypothecation in securities lending involves pledging collateral without transferring ownership, while rehypothecation allows the lender to reuse the same collateral for their own borrowing, increasing liquidity but also counterparty risk.
Custodial Risk
Custodial risk in hypothecation involves the lender holding the borrower's assets as collateral, whereas in rehypothecation, the lender reuses these assets for their own purposes, increasing counterparty risk.
Title Transfer
Title transfer in hypothecation involves the original owner retaining ownership while granting a security interest to the lender without transferring legal title, whereas rehypothecation allows the lender to reuse the collateral by transferring the security interest to a third party. Hypothecation limits title transfer to the borrower and lender, while rehypothecation extends it beyond the original parties, increasing liquidity but also risk in financial markets.
Prime Brokerage
Prime brokerage services enable hedge funds to use client assets as collateral through hypothecation while also permitting rehypothecation, where brokers re-pledge those assets to secure their own funding or leverage.
Client Segregation
Client segregation ensures customer assets are held separately from a broker's own holdings, reducing risk in transactions involving hypothecation where assets are pledged as collateral. Rehypothecation occurs when the broker reuses these pledged assets for their own purposes, potentially exposing clients to greater risk if segregation is not strictly enforced.
Leverage Chains
Leverage chains in finance involve the repeated use of hypothecation and rehypothecation, where hypothecation is the initial pledging of assets as collateral without transfer of ownership, while rehypothecation allows lenders to reuse those pledged assets for their own borrowing or trading activities, amplifying leverage but increasing systemic risk.
Asset Encumbrance
Asset encumbrance refers to the use of assets as collateral to secure debt, impacting a lender's claim priority. Hypothecation involves pledging assets without transferring ownership, while rehypothecation allows the lender to reuse these pledged assets to secure their own borrowing, increasing systemic risk.
Counterparty Exposure
Counterparty exposure increases in rehypothecation due to the lender's ability to reuse the collateral multiple times, amplifying credit risk compared to direct hypothecation where collateral is pledged without transfer of ownership. Effective risk management requires transparent tracking and limits on rehypothecation to mitigate compounded exposure across interconnected counterparties.
Hypothecation vs Rehypothecation Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com