High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates compared to standard savings accounts, enabling faster growth of your savings through compound interest. While standard savings accounts provide easy access and lower risk, their interest rates often fail to keep pace with inflation, reducing the real value of money over time. Choosing a high-yield savings account can maximize earnings while still maintaining liquidity and safety.
Table of Comparison
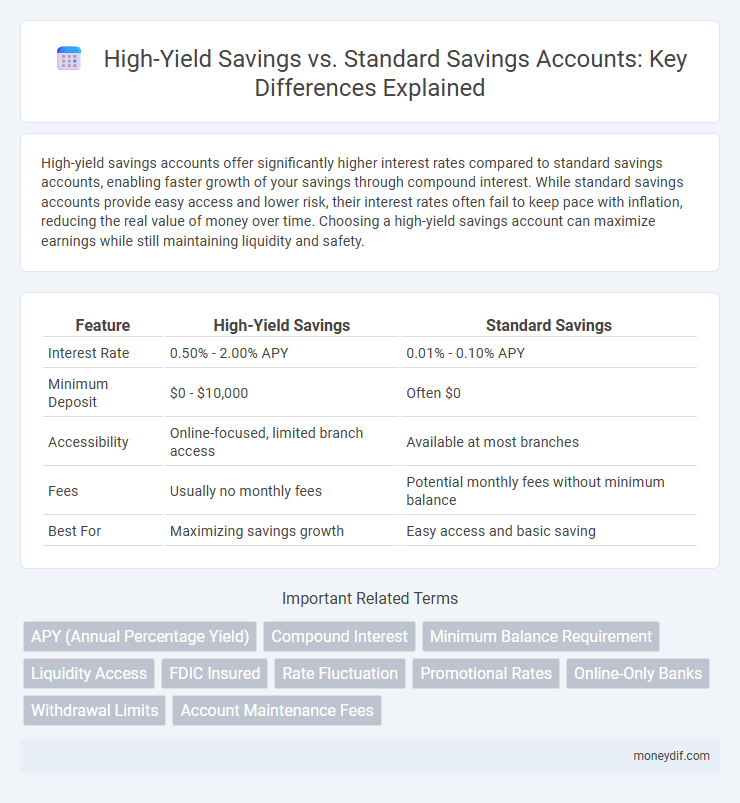
| Feature | High-Yield Savings | Standard Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | 0.50% - 2.00% APY | 0.01% - 0.10% APY |
| Minimum Deposit | $0 - $10,000 | Often $0 |
| Accessibility | Online-focused, limited branch access | Available at most branches |
| Fees | Usually no monthly fees | Potential monthly fees without minimum balance |
| Best For | Maximizing savings growth | Easy access and basic saving |
Understanding High-Yield Savings Accounts
High-yield savings accounts offer interest rates typically 10 to 20 times higher than standard savings accounts, significantly boosting your potential earnings. These accounts are often provided by online banks, which can afford to offer better rates due to lower operational costs. Understanding terms like APY (Annual Percentage Yield), minimum balance requirements, and withdrawal limits is crucial to maximizing the benefits of high-yield savings.
What Defines a Standard Savings Account
A standard savings account is defined by its low minimum balance requirements, easy access to funds, and relatively modest interest rates set by traditional banks. These accounts prioritize liquidity and security, often insured by the FDIC, but typically offer annual percentage yields (APYs) ranging from 0.01% to 0.10%. Unlike high-yield savings accounts, they lack competitive interest rates but provide a stable option for everyday savings needs.
Interest Rate Comparison: High-Yield vs Standard
High-yield savings accounts typically offer interest rates ranging from 3% to 5%, significantly outpacing the 0.01% to 0.10% rates found in standard savings accounts. This substantial difference in interest rates accelerates wealth growth through higher compound interest earnings over time. Choosing a high-yield account maximizes returns on savings without increased risk.
Accessibility and Withdrawal Limits
High-yield savings accounts often have limited accessibility compared to standard savings, typically offering online-only access without physical branches. Withdrawal limits on high-yield accounts are usually stricter, with federal regulations capping monthly transactions to six, similar to standard savings accounts. These restrictions can impact the ease of accessing funds when needed, making it crucial to consider how frequently withdrawals will be required.
Safety and FDIC Insurance
High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates while maintaining the same level of safety as standard savings accounts due to FDIC insurance coverage up to $250,000 per depositor, per institution. Both account types are federally insured, ensuring protection against bank failures and safeguarding principal funds. Choosing between high-yield and standard savings depends on interest earnings goals, but both provide secure, insured deposits.
Minimum Balance Requirements
High-yield savings accounts typically require a higher minimum balance to earn the advertised interest rates, often starting around $500 to $1,000. Standard savings accounts generally have lower or no minimum balance requirements, making them more accessible for everyday savers. Meeting the minimum balance in a high-yield account is crucial to maximize interest earnings and avoid monthly fees.
Fees and Maintenance Costs
High-yield savings accounts typically offer higher interest rates while maintaining low or no monthly maintenance fees, maximizing returns on deposits. Standard savings accounts often have lower fees but correspondingly lower interest rates, which can diminish growth potential over time. Evaluating fee structures and maintenance costs is crucial to ensure the savings account aligns with financial goals for cost-effective growth.
Digital vs Traditional Banking Options
High-yield savings accounts offered by digital banks typically provide interest rates two to four times higher than standard savings accounts from traditional banks, boosting growth potential for depositors. Digital banking platforms allow users to access and manage high-yield savings with lower fees, enhanced mobile features, and 24/7 online access, compared to limited branch visits and reduced accessibility associated with traditional banks. Security measures such as FDIC insurance cover deposits up to $250,000 in both digital and traditional banks, making high-yield savings accounts via digital banks a competitive, convenient choice for maximizing savings returns.
Best Uses for Each Account Type
High-yield savings accounts are ideal for individuals seeking to maximize interest earnings on emergency funds or short-term savings with minimal effort and low risk. Standard savings accounts provide easy access and stability, making them suitable for everyday savings, bill payments, and maintaining minimum balance requirements. Selecting the right account depends on prioritizing higher returns with limited withdrawals versus accessibility and liquidity.
Choosing the Right Savings Account for Your Needs
High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates than standard savings accounts, making them ideal for maximizing growth on emergency funds and short-term savings. Standard savings accounts provide easier access and typically lower minimum balance requirements, which suits those prioritizing liquidity and simplicity. Evaluating factors such as interest rate, access frequency, fees, and minimum deposit ensures selecting the right savings account tailored to your financial goals.
Important Terms
APY (Annual Percentage Yield)
High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher APY compared to standard savings, often ranging from 0.40% to over 4.00%, maximizing interest earnings through compound interest. Standard savings accounts typically have APYs below 0.10%, resulting in much slower growth and lower returns over time.
Compound Interest
High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher compound interest rates compared to standard savings accounts, enabling faster growth of your principal through more frequent and substantial interest accrual. Choosing a high-yield savings account can dramatically increase your earnings over time due to the power of compound interest compounding daily or monthly on larger interest rates.
Minimum Balance Requirement
High-yield savings accounts typically require higher minimum balance requirements, often ranging from $1,000 to $5,000, compared to standard savings accounts that may have minimal or no minimum balance constraints. Maintaining the minimum balance in high-yield accounts is crucial to earn the advertised interest rates, whereas standard savings accounts offer more flexibility but with lower interest yields.
Liquidity Access
Liquidity access in high-yield savings accounts often matches that of standard savings, allowing easy withdrawals and transfers, but higher interest rates in high-yield accounts maximize earnings during idle periods. Standard savings accounts typically offer lower APYs, making high-yield savings optimal for maintaining emergency funds without sacrificing liquidity.
FDIC Insured
FDIC insured High-Yield Savings Accounts offer significantly higher interest rates compared to Standard Savings Accounts while maintaining federal protection on deposits up to $250,000 per account holder. This combination ensures both enhanced growth potential and secure federal insurance coverage through the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
Rate Fluctuation
Rate fluctuctuation in high-yield savings accounts typically exceeds that of standard savings, directly impacting potential interest earnings due to their variable rates often tied to market benchmarks like the Federal Reserve's rates. Standard savings accounts offer more stable but lower interest rates, making them less sensitive to market shifts but yielding less growth over time compared to the more volatile high-yield options.
Promotional Rates
Promotional rates on high-yield savings accounts often exceed standard savings interest rates by several percentage points, significantly enhancing potential earnings. These elevated APYs typically apply for a limited introductory period before reverting to the lower, standard savings rates.
Online-Only Banks
Online-only banks typically offer high-yield savings accounts with interest rates significantly above traditional standard savings accounts, leveraging lower operational costs to pass savings onto customers. These high-yield accounts provide better inflation protection and faster balance growth, making them an advantageous choice for maximizing savings returns.
Withdrawal Limits
High-yield savings accounts often impose stricter withdrawal limits compared to standard savings accounts, typically allowing up to six transactions per month to comply with federal Regulation D. Standard savings accounts may offer more flexible withdrawal options without stringent monthly caps, making them suitable for frequent access but usually with lower interest rates.
Account Maintenance Fees
High-yield savings accounts typically have higher interest rates with minimal or no account maintenance fees, maximizing your earnings compared to standard savings accounts, which often charge monthly maintenance fees that can erode interest gains. Choosing a high-yield savings account helps reduce unnecessary expenses while optimizing your savings growth through significantly better annual percentage yields (APY).
High-Yield Savings vs Standard Savings Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com