Time deposits offer higher interest rates by requiring funds to be locked in for a fixed term, making them ideal for long-term savings goals. Demand deposits provide flexible access to funds without penalties but typically yield lower interest rates, suitable for everyday transactions and emergency needs. Choosing between them depends on balancing liquidity requirements against the desire for higher returns.
Table of Comparison
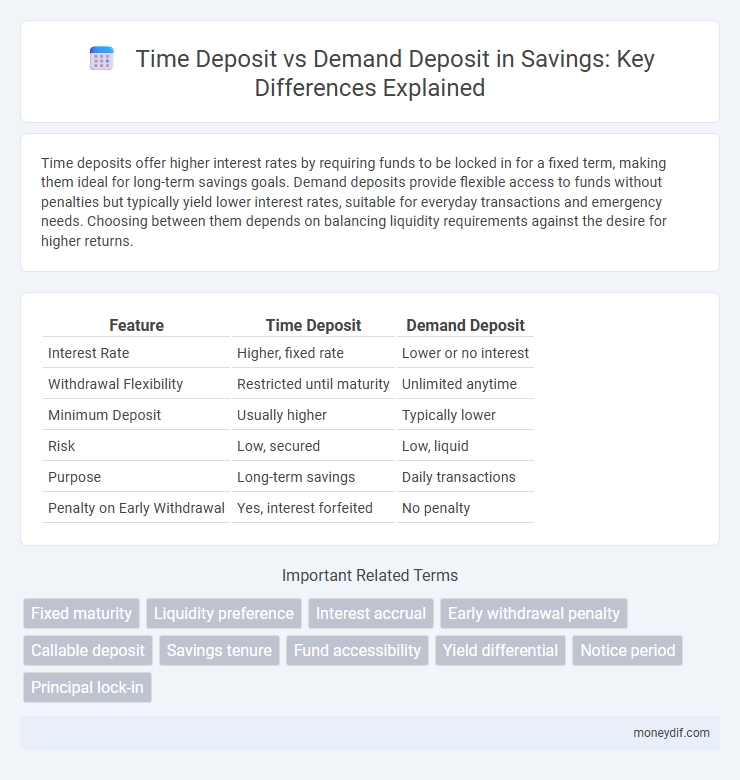
| Feature | Time Deposit | Demand Deposit |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Higher, fixed rate | Lower or no interest |
| Withdrawal Flexibility | Restricted until maturity | Unlimited anytime |
| Minimum Deposit | Usually higher | Typically lower |
| Risk | Low, secured | Low, liquid |
| Purpose | Long-term savings | Daily transactions |
| Penalty on Early Withdrawal | Yes, interest forfeited | No penalty |
Understanding Time Deposits and Demand Deposits
Time deposits, also known as certificates of deposit (CDs), require funds to be locked in for a fixed term, offering higher interest rates compared to demand deposits, which allow immediate access to funds without penalty. Demand deposits, typically held in checking or savings accounts, provide liquidity and convenience but usually yield lower interest returns. Understanding the trade-off between higher interest earnings with time deposits and the flexibility of demand deposits is crucial for effective savings management.
Key Differences Between Time Deposit and Demand Deposit
Time deposits require locking funds for a fixed term, offering higher interest rates compared to demand deposits, which allow immediate access to funds without penalties. Demand deposits provide liquidity and flexibility for daily transactions, whereas time deposits prioritize earning returns over short-term accessibility. The key difference lies in accessibility and interest rates: demand deposits favor convenience, time deposits favor growth.
Interest Rates: Time Deposit vs Demand Deposit
Time deposits generally offer higher interest rates compared to demand deposits due to fixed terms that allow banks to utilize funds longer. Demand deposits provide greater liquidity but typically yield lower or no interest, reflecting the ease of access for account holders. Investors seeking better returns often prefer time deposits for their guaranteed, higher interest earnings over predetermined periods.
Liquidity Comparison: Which is More Accessible?
Demand deposits offer superior liquidity with immediate access to funds anytime through withdrawals, transfers, or payments without penalties. Time deposits lock funds for a specified term, restricting access and often incurring early withdrawal penalties, reducing their accessibility. Therefore, demand deposits are more suitable for savers prioritizing quick and flexible access to their money.
Withdrawal Rules: Penalties and Flexibility
Time deposits impose strict withdrawal rules with penalties for early access, typically reducing interest earned or charging fees, which enforces commitment to a fixed term. Demand deposits offer high flexibility, allowing unlimited withdrawals without penalties, making them ideal for daily transactions and emergency funds. Understanding the trade-off between penalty risks of time deposits and the unrestricted access of demand deposits helps optimize savings strategies for liquidity needs.
Security and Risk Factors
Time deposits offer higher security due to fixed terms and insured principal, minimizing the risk of losing the initial investment, while demand deposits provide instant access but typically yield lower interest and expose funds to inflation risk. Time deposits are less vulnerable to market fluctuations, whereas demand deposits carry liquidity risk if funds are withdrawn during financial emergencies. Both deposit types benefit from Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) coverage up to $250,000, ensuring safety against bank failures.
Suitability: Who Should Choose Time Deposit?
Time deposits are ideal for savers seeking higher interest rates and who do not need immediate access to their funds, making them suitable for long-term financial goals such as emergency funds or future expenses. Individuals with stable income and risk-averse preferences benefit from the fixed returns and protection against market volatility offered by time deposits. Conversely, those requiring liquidity and flexibility should consider demand deposits for easy access to their money without penalties.
Suitability: Who Should Choose Demand Deposit?
Demand deposits best suit individuals and businesses needing frequent access to funds without withdrawal restrictions, such as for daily expenses or emergency liquidity. These accounts provide flexibility with unlimited withdrawals and no fixed maturity, contrasting time deposits that lock funds for higher interest rates. Choosing a demand deposit aligns with priorities on accessibility and cash flow management rather than maximizing interest earnings.
Tax Implications and Benefits
Time deposits usually offer higher interest rates compared to demand deposits, resulting in greater tax liabilities on earned interest income. Interest from demand deposits is often more accessible but typically yields lower taxable income due to lower interest rates. Both accounts have tax benefits, but time deposits may provide better long-term growth potential despite delayed access to funds.
Making the Right Choice for Your Savings
Time deposits offer higher interest rates compared to demand deposits, making them ideal for savers seeking growth over a fixed period. Demand deposits provide easy access to funds without penalties, suitable for emergency savings or frequent transactions. Assessing your liquidity needs and financial goals ensures making the right choice for maximizing your savings potential.
Important Terms
Fixed maturity
Fixed maturity time deposits offer a predetermined term with a higher interest rate compared to demand deposits, which allow immediate access but typically yield lower returns. Time deposits lock funds until maturity, minimizing liquidity, while demand deposits provide flexible access without fixed terms.
Liquidity preference
Liquidity preference theory explains that individuals favor demand deposits for their immediate accessibility, while time deposits offer higher interest rates as compensation for reduced liquidity. The trade-off between liquidity in demand deposits and the fixed-term commitment in time deposits influences consumer saving and investment choices.
Interest accrual
Interest accrual on time deposits typically occurs at a fixed rate over a predetermined term, resulting in predictable earnings that compound periodically or at maturity, whereas demand deposits generally offer lower or no interest accrual and allow immediate access to funds without penalties. Time deposits maximize interest income by locking funds for a set duration, while demand deposits prioritize liquidity with flexible withdrawals but minimal interest growth.
Early withdrawal penalty
Early withdrawal penalties for time deposits, such as certificates of deposit (CDs), often involve forfeiting a portion of the interest earned, reflecting the fixed-term commitment, while demand deposits like savings or checking accounts allow immediate access to funds without penalties but typically offer lower interest rates. The rigid structure of time deposits contrasts with the liquidity of demand deposits, influencing investors' choice based on their need for access versus return.
Callable deposit
Callable deposits combine features of time deposits and demand deposits by allowing banks to recall funds before maturity while typically offering higher interest rates than demand deposits. Unlike traditional time deposits, callable deposits provide liquidity options for banks, balancing fixed-term commitments with flexibility.
Savings tenure
Savings tenure for time deposits typically ranges from 7 days to several years, offering higher interest rates locked in for the agreed period, while demand deposits have no fixed tenure and allow flexible withdrawals with lower or no interest. The commitment period of a time deposit influences the interest earned, whereas demand deposits prioritize liquidity and immediate access to funds.
Fund accessibility
Fund accessibility differs significantly between time deposits and demand deposits, as demand deposits provide immediate withdrawal options without penalties, making them ideal for daily transactions. Time deposits, however, offer higher interest rates but restrict access until the maturity date, often imposing penalties for early withdrawal, which limits liquidity.
Yield differential
Yield differential between time deposits and demand deposits reflects the higher interest rates offered by time deposits due to fixed terms and reduced liquidity, incentivizing longer-term savings. This spread compensates depositors for the opportunity cost and limited access to funds compared to the typically lower-yield, highly liquid demand deposits.
Notice period
Notice period for time deposits requires customers to inform the bank before withdrawing funds, typically ranging from 7 to 90 days, ensuring penalty-free access while maintaining interest benefits. Demand deposits offer immediate access without notice, prioritizing liquidity over interest earnings, making them ideal for everyday transactions.
Principal lock-in
Principal lock-in in time deposits ensures the invested amount remains fixed for a specified term, preventing early withdrawal without penalties, unlike demand deposits which allow flexible access to funds but offer lower interest rates due to the absence of fixed tenure. Time deposits optimize returns by securing principal amounts over fixed periods, while demand deposits prioritize liquidity over interest earnings.
Time deposit vs Demand deposit Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com