High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts, enabling your money to grow faster with minimal risk. While traditional savings accounts provide easy access and strong security, they typically yield lower returns, making them less effective for long-term growth. Opting for a high-yield savings account maximizes earning potential while maintaining liquidity and FDIC insurance protection.
Table of Comparison
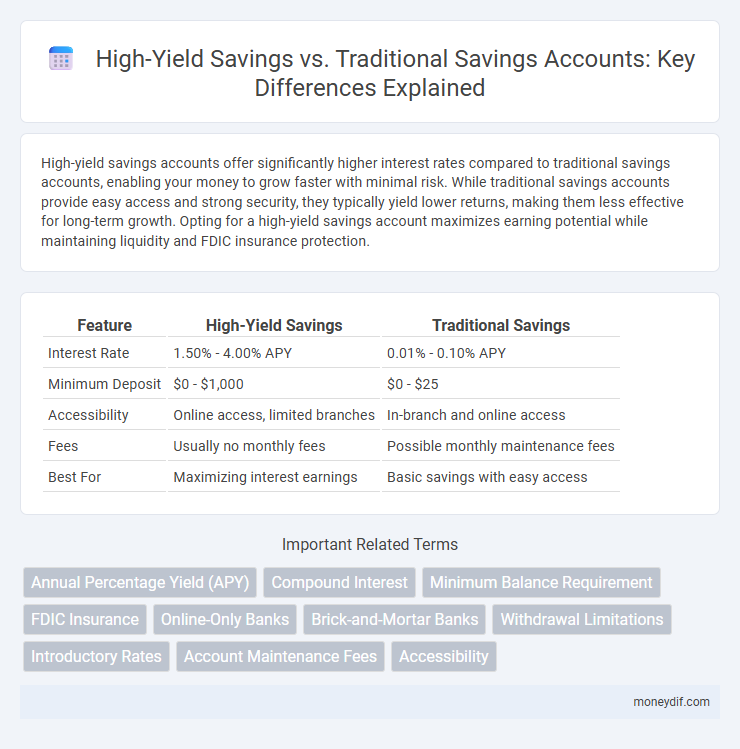
| Feature | High-Yield Savings | Traditional Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | 1.50% - 4.00% APY | 0.01% - 0.10% APY |
| Minimum Deposit | $0 - $1,000 | $0 - $25 |
| Accessibility | Online access, limited branches | In-branch and online access |
| Fees | Usually no monthly fees | Possible monthly maintenance fees |
| Best For | Maximizing interest earnings | Basic savings with easy access |
Understanding High-Yield vs Traditional Savings Accounts
High-yield savings accounts offer interest rates significantly higher than traditional savings accounts, often ranging from 1.5% to 4% APY compared to the typical 0.01% to 0.10% APY of traditional accounts. These accounts are typically offered by online banks with lower overhead costs, allowing them to pass on better rates to consumers while maintaining FDIC insurance protection. Traditional savings accounts provide easier access through physical branches but usually sacrifice higher returns, making high-yield accounts ideal for maximizing growth on emergency funds and short-term savings.
Key Features of High-Yield Savings Accounts
High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts, often yielding 10 to 20 times more in annual percentage yield (APY). These accounts typically require a higher minimum balance but provide faster growth on deposits due to compounded interest. Features such as limited monthly withdrawals and FDIC insurance ensure both liquidity and security while maximizing returns.
The Basics of Traditional Savings Accounts
Traditional savings accounts offer a secure way to store money with easy access and insured deposits up to $250,000 by the FDIC. These accounts typically have lower interest rates compared to high-yield savings, making them less effective for rapid growth. They are ideal for emergency funds and short-term savings goals due to their liquidity and minimal risk.
Interest Rates: High-Yield vs Traditional Savings
High-yield savings accounts typically offer interest rates that are 10 to 20 times higher than traditional savings accounts, often ranging from 3% to 5% APY compared to traditional rates below 0.5%. The higher interest rates in high-yield accounts result from online banks' lower overhead costs, enabling them to pass savings directly to customers. In contrast, traditional savings accounts at brick-and-mortar banks provide lower returns but greater accessibility and more physical branch options.
Accessibility and Account Management
High-yield savings accounts typically offer online access with intuitive mobile apps and digital tools, enabling easy account management and real-time monitoring of interest earnings. Traditional savings accounts often provide broader access through physical bank branches and ATMs, supporting in-person transactions and personalized banking services. While high-yield accounts prioritize digital convenience, traditional savings accounts excel in accessibility for customers preferring face-to-face support.
Fees and Minimum Balance Requirements
High-yield savings accounts typically offer higher interest rates but may require a higher minimum balance to avoid monthly fees, whereas traditional savings accounts often have lower or no minimum balance requirements and fewer fees. Many high-yield accounts charge maintenance fees if the balance falls below a set threshold, impacting overall savings growth. Traditional savings accounts generally provide more flexibility with fees, making them suitable for savers with fluctuating balances.
Safety and FDIC Insurance Comparison
High-yield savings accounts and traditional savings accounts both offer FDIC insurance, protecting deposits up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank, which ensures the safety of your funds. High-yield savings accounts typically provide higher interest rates without sacrificing FDIC protection, making them a secure option for maximizing returns. Traditional savings accounts offer liquidity and low risk but generally yield lower returns compared to the FDIC-insured, higher-rate alternatives provided by high-yield savings accounts.
Best Uses for High-Yield Savings Accounts
High-yield savings accounts are best used for emergency funds and short-to-medium term savings goals due to their significantly higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts. They maximize earnings on idle cash while maintaining liquidity, making them ideal for building financial buffers without risking principal. The key benefit lies in achieving greater compound interest growth while retaining easy access to funds.
When to Choose a Traditional Savings Account
Traditional savings accounts are ideal for individuals seeking maximum liquidity and easy access to their funds without risking market fluctuations. They offer minimal balance requirements and are typically insured by the FDIC up to $250,000, ensuring security for short-term savings or emergency funds. These accounts suit those prioritizing safety and convenience over higher interest returns found in high-yield savings options.
Which Savings Account Is Right for You?
High-yield savings accounts typically offer interest rates several times higher than traditional savings accounts, making them ideal for maximizing returns on emergency funds or short-term goals. Traditional savings accounts usually provide easier access and fewer minimum balance requirements, which suits individuals prioritizing liquidity and lower fees. Comparing interest rates, accessibility, and account terms helps determine the savings account that best aligns with your financial objectives and risk tolerance.
Important Terms
Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
Annual Percentage Yield (APY) quantifies the real rate of return on savings by accounting for compound interest, making it a critical metric when comparing high-yield savings accounts to traditional savings accounts. High-yield savings accounts typically offer APYs several times greater than traditional savings accounts, enabling faster growth of savings due to higher interest accrual compounded daily or monthly.
Compound Interest
Compound interest accelerates growth in high-yield savings accounts due to their significantly higher interest rates compared to traditional savings, resulting in greater earnings over time. The effect of compounding interest in high-yield accounts maximizes returns by frequently adding earned interest to the principal, outperforming the slower accumulation in traditional savings accounts with lower rates.
Minimum Balance Requirement
High-yield savings accounts typically require a higher minimum balance, often ranging from $500 to $1,000, compared to traditional savings accounts that may have no minimum balance or as low as $25. Maintaining the required minimum balance in high-yield accounts is essential to earn the advertised annual percentage yield (APY) and avoid fees that can reduce overall interest gains.
FDIC Insurance
FDIC insurance protects deposits up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank, for both high-yield and traditional savings accounts, ensuring the safety of principal regardless of interest rate differences. High-yield savings accounts typically offer higher returns with the same FDIC insurance coverage as traditional savings, combining increased earnings potential with federal protection.
Online-Only Banks
Online-only banks offer high-yield savings accounts with interest rates significantly higher than traditional savings accounts, often exceeding 4% APY compared to the typical 0.01%-0.10% APY found at brick-and-mortar banks. These digital banks reduce overhead costs, enabling them to provide more competitive rates, no monthly fees, and easy online access to funds, making them an attractive alternative for savers seeking greater returns.
Brick-and-Mortar Banks
Brick-and-mortar banks typically offer traditional savings accounts with lower interest rates compared to high-yield savings accounts often found online. High-yield savings accounts provide significantly higher annual percentage yields (APYs), allowing savers to grow their funds faster while maintaining FDIC insurance protection.
Withdrawal Limitations
High-yield savings accounts often have withdrawal limitations similar to traditional savings accounts, typically restricting transactions to six per month due to federal Regulation D. Exceeding these limits in either account type may result in fees or account conversion to a checking account, impacting the benefits of higher interest rates found in high-yield savings.
Introductory Rates
Introductory rates on high-yield savings accounts often start significantly higher than traditional savings accounts, sometimes offering APYs above 4%, compared to the typical 0.01% to 0.10% APY of traditional accounts. These promotional rates usually last from 3 to 12 months before reverting to a lower ongoing yield, making it essential to compare long-term benefits and fees.
Account Maintenance Fees
High-yield savings accounts typically charge lower or no account maintenance fees compared to traditional savings accounts, which often have monthly fees that can erode interest earnings. Choosing a high-yield savings account can maximize returns by minimizing fees and offering significantly higher interest rates, sometimes up to 20 times greater than those of conventional savings options.
Accessibility
High-yield savings accounts typically offer online-only access, making it essential to have digital literacy and internet connectivity, while traditional savings accounts often provide easier in-person access via local bank branches and ATMs. The accessibility differences impact how quickly and conveniently users can manage funds, with high-yield accounts favoring tech-savvy customers seeking higher interest rates.
High-yield savings vs Traditional savings Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com