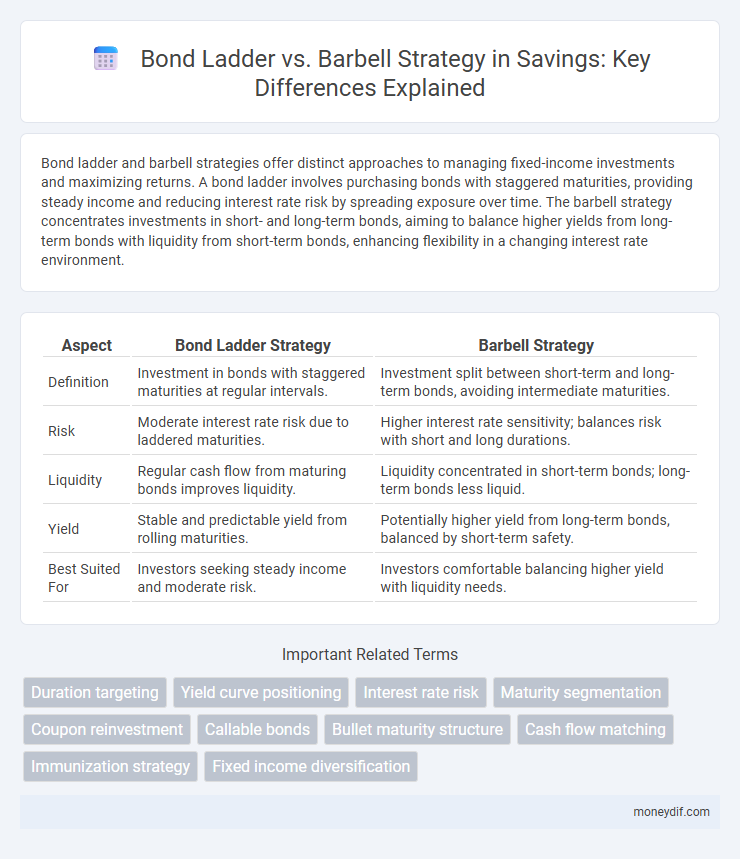
Bond ladder and barbell strategies offer distinct approaches to managing fixed-income investments and maximizing returns. A bond ladder involves purchasing bonds with staggered maturities, providing steady income and reducing interest rate risk by spreading exposure over time. The barbell strategy concentrates investments in short- and long-term bonds, aiming to balance higher yields from long-term bonds with liquidity from short-term bonds, enhancing flexibility in a changing interest rate environment.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bond Ladder Strategy | Barbell Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in bonds with staggered maturities at regular intervals. | Investment split between short-term and long-term bonds, avoiding intermediate maturities. |
| Risk | Moderate interest rate risk due to laddered maturities. | Higher interest rate sensitivity; balances risk with short and long durations. |
| Liquidity | Regular cash flow from maturing bonds improves liquidity. | Liquidity concentrated in short-term bonds; long-term bonds less liquid. |
| Yield | Stable and predictable yield from rolling maturities. | Potentially higher yield from long-term bonds, balanced by short-term safety. |
| Best Suited For | Investors seeking steady income and moderate risk. | Investors comfortable balancing higher yield with liquidity needs. |
Introduction to Bond Ladder and Barbell Strategies
Bond ladder strategy involves purchasing bonds with varying maturities to spread risk and ensure consistent returns as individual bonds mature periodically. Barbell strategy concentrates investments in short-term and long-term bonds, balancing high yield potential with liquidity. Both strategies aim to optimize income streams while managing interest rate risk in fixed-income portfolios.
Understanding the Basics of Bond Investing
A bond ladder strategy involves purchasing bonds with staggered maturities to manage interest rate risk and ensure consistent cash flow, while a barbell strategy concentrates investments in short- and long-term bonds, balancing yield and liquidity. Understanding the basics of bond investing, such as coupon rates, maturity dates, and credit risk, is essential to optimizing either strategy for stability and growth. Both methods aim to diversify bond portfolios but differ in risk tolerance and income timing preferences.
What Is a Bond Ladder Strategy?
A bond ladder strategy involves purchasing a series of bonds with staggered maturity dates to manage interest rate risk and provide consistent income. This approach allows investors to reinvest maturing bonds at current interest rates, enhancing liquidity and reducing market volatility impact. The structured maturity schedule helps balance income needs while preserving capital through diversified fixed-income investments.
Key Features of the Barbell Strategy
The Barbell strategy balances investments by allocating assets into short-term and long-term bonds, minimizing interest rate risk while maximizing returns during market volatility. Key features include flexibility in adjusting maturity dates, higher yield potential from long-term bonds, and liquidity retention through short-term bonds. This approach allows savers to capitalize on fluctuating interest rates and provides a hedge against economic uncertainty.
Risk and Return Profiles: Ladder vs Barbell
The bond ladder strategy mitigates interest rate risk by spreading maturities evenly, providing steady income and liquidity through staggered bond maturities. In contrast, the barbell strategy concentrates investments in short- and long-term bonds, enhancing yield potential but increasing exposure to interest rate volatility. Investors seeking a balanced risk-return profile often prefer the ladder for its stability, while those aiming for higher returns may opt for the barbell despite its greater price fluctuation risk.
Liquidity Considerations for Both Strategies
Bond ladder strategy enhances liquidity by staggering bond maturities at regular intervals, allowing investors to access funds periodically without penalty. In contrast, the barbell strategy concentrates investments in short-term and long-term bonds, offering quicker access to short-term funds while locking a portion in longer maturities for higher yields. Both strategies balance liquidity needs but require investor awareness of timing and market conditions to optimize cash flow and minimize reinvestment risk.
Interest Rate Risk: How Each Strategy Responds
A bond ladder mitigates interest rate risk by staggering maturities, ensuring consistent reinvestment opportunities and reducing exposure to rate fluctuations. In contrast, the barbell strategy concentrates investments in short- and long-term bonds, balancing income generation with capital preservation amid volatile rates. Both strategies offer unique responses to interest rate changes, with ladders providing stability and barbells leveraging rate shifts for potential gains.
Diversification Benefits Compared
Bond ladder and barbell strategies both enhance diversification by spreading investments across multiple maturities, reducing interest rate risk. A bond ladder evenly staggers bond maturities over time, providing consistent liquidity and reducing reinvestment risk, while a barbell strategy concentrates on short- and long-term bonds, balancing yield potential with risk management. Diversification benefits are maximized in a ladder by stable cash flow, whereas a barbell captures rate movements at both ends of the maturity spectrum, offering flexibility during market shifts.
Suitability for Different Investor Profiles
Bond ladder strategy suits conservative investors seeking steady income and reduced interest rate risk through staggered maturities. Barbell strategy appeals to risk-tolerant investors aiming to capitalize on both short- and long-term interest rate fluctuations by balancing bonds at opposite ends of the maturity spectrum. Moderate investors may combine elements of both to optimize yield while managing risk according to their financial goals.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Savings Goals
Choosing the right strategy for your savings goals depends on your risk tolerance, income needs, and market outlook. A bond ladder provides steady income and reduces reinvestment risk by staggering maturities, ideal for conservative savers aiming for predictable cash flow. In contrast, the barbell strategy balances short and long-term bonds to capitalize on interest rate changes, suited for investors seeking higher yield potential with moderate risk.
Important Terms
Duration targeting
Duration targeting in fixed income portfolios focuses on managing interest rate risk by aligning bond maturities with specific time horizons, enhancing predictability in cash flow and portfolio sensitivity. The bond ladder strategy staggers maturities evenly across intervals to maintain steady reinvestment opportunities, while the barbell strategy concentrates investments in short and long maturities to balance yield and duration exposure.
Yield curve positioning
Yield curve positioning involves strategically allocating bond investments along different maturities to optimize risk and return. Bond ladder strategies spread holdings evenly across multiple maturities to reduce interest rate risk, while barbell strategies concentrate investments in short- and long-term bonds, aiming to balance yield and liquidity preferences.
Interest rate risk
Interest rate risk affects bond ladder and barbell strategies differently; the bond ladder mitigates this risk by staggering maturities to reinvest at varying rates over time, while the barbell strategy concentrates investments in short- and long-term bonds, balancing reinvestment and price sensitivity. Investors seeking to manage interest rate fluctuations should consider the bond ladder's steady cash flow against the barbell's potential for higher yield through strategic maturity extremes.
Maturity segmentation
Maturity segmentation in fixed-income investing involves dividing bonds into distinct time segments to manage interest rate risk and cash flow needs, which is central to both bond ladder and barbell strategies. The bond ladder strategy evenly spaces maturities to generate steady income and reduce reinvestment risk, while the barbell strategy concentrates investments in short- and long-term maturities to balance liquidity and yield opportunities.
Coupon reinvestment
Coupon reinvestment plays a crucial role in enhancing returns within bond ladder and barbell strategies by systematically reallocating interest payments to purchase additional bonds, thereby compounding income and optimizing portfolio yield. The bond ladder strategy benefits from regular coupon reinvestment at staggered maturities to maintain consistent liquidity and reduce interest rate risk, whereas the barbell strategy reinvests coupons predominantly in short- and long-term bonds to balance income stability and capital appreciation potential.
Callable bonds
Callable bonds offer issuers the option to redeem before maturity, posing reinvestment risk that can impact bond ladder strategies by disrupting predictable cash flows; in contrast, barbell strategies balance short-term callable bonds with long-term non-callable securities to manage yield and interest rate risk effectively. Investors utilize callable bond features within barbell approaches to optimize income while maintaining flexibility against interest rate fluctuations.
Bullet maturity structure
Bullet maturity structure focuses on bonds maturing at a single point in time, providing a concentrated payoff and reducing reinvestment risk compared to the Barbell strategy, which involves investing in short- and long-term maturities to balance risk and return. Unlike the Bond ladder strategy that staggers maturities evenly over time for steady income, the Bullet strategy targets a specific timeframe to optimize for particular financial needs or interest rate expectations.
Cash flow matching
Cash flow matching focuses on aligning bond maturities precisely with future liabilities to ensure predictable cash inflows, contrasting with bond ladder and barbell strategies which prioritize diversification of maturity dates for risk management and yield optimization. While bond ladder spreads investments evenly across multiple maturities and barbell concentrates on short and long-term bonds, cash flow matching targets exact timing of cash needs to reduce reinvestment risk and guarantee liquidity.
Immunization strategy
The immunization strategy in fixed-income portfolio management focuses on minimizing interest rate risk by matching asset durations with liability durations, often aligned with a bond ladder approach that staggers maturities to ensure steady cash flows. In contrast, the barbell strategy concentrates investments in short- and long-term bonds to balance yield and duration, offering flexibility but potentially higher interest rate exposure compared to the structured cash flow matching of a bond ladder.
Fixed income diversification
Fixed income diversification enhances risk management by spreading investments across various maturities, with bond ladder strategies providing steady cash flow through evenly spaced maturities while barbell strategies concentrate holdings in short and long-term bonds to capitalize on yield curve movements. Bond ladders reduce reinvestment risk and interest rate volatility, whereas barbell portfolios offer higher potential returns by balancing income from short-term bonds and price appreciation from long-term bonds.
Bond ladder vs Barbell strategy Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com