A sweep account automatically transfers surplus funds into a savings account, maximizing interest earnings while maintaining liquidity for daily transactions. Unlike traditional savings accounts, sweep accounts optimize cash flow by dynamically balancing between checking and savings, reducing idle balances. This feature offers enhanced financial efficiency for individuals and businesses seeking to grow savings without sacrificing access to funds.
Table of Comparison
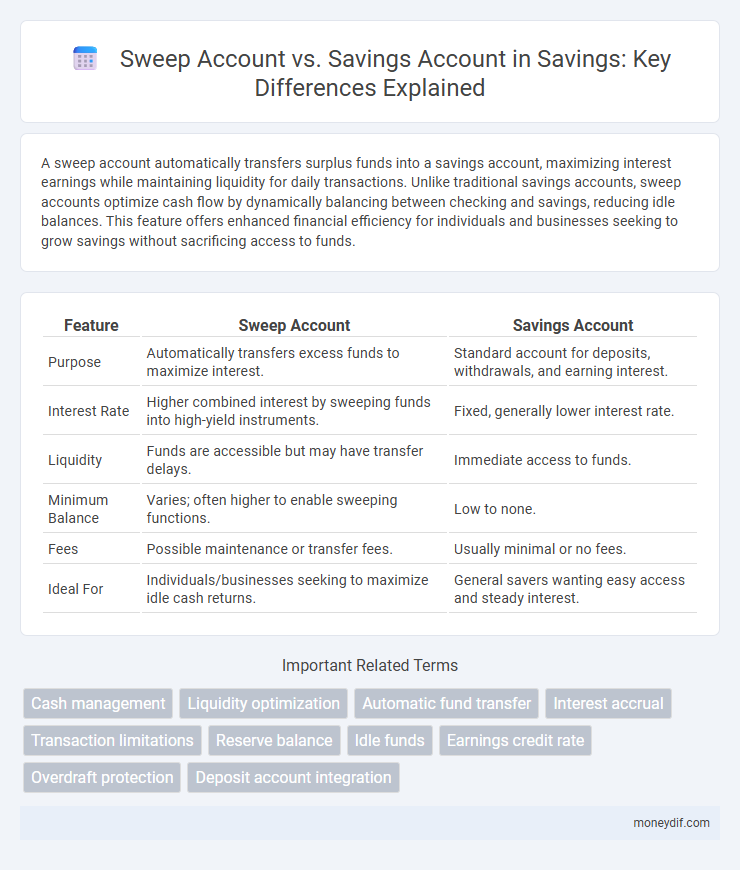
| Feature | Sweep Account | Savings Account |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Automatically transfers excess funds to maximize interest. | Standard account for deposits, withdrawals, and earning interest. |
| Interest Rate | Higher combined interest by sweeping funds into high-yield instruments. | Fixed, generally lower interest rate. |
| Liquidity | Funds are accessible but may have transfer delays. | Immediate access to funds. |
| Minimum Balance | Varies; often higher to enable sweeping functions. | Low to none. |
| Fees | Possible maintenance or transfer fees. | Usually minimal or no fees. |
| Ideal For | Individuals/businesses seeking to maximize idle cash returns. | General savers wanting easy access and steady interest. |
Overview: Sweep Account vs Savings Account
Sweep accounts automatically transfer excess funds from a checking account to a high-interest savings or investment account, optimizing cash flow and maximizing returns without manual intervention. Savings accounts offer a secure place to store money while earning interest, typically with easy access but lower interest rates compared to sweep accounts linked to investment options. Businesses and individuals use sweep accounts to efficiently manage liquidity, whereas savings accounts are ideal for personal savings goals with straightforward deposit and withdrawal processes.
Key Features Comparison
A sweep account automatically transfers excess funds from a checking account to a higher-interest savings or investment account, optimizing cash flow and maximizing returns. Savings accounts typically offer fixed interest rates with easy access to funds but lack automatic fund transfers, limiting earning potential on idle balances. Sweep accounts provide seamless liquidity management with higher interest rates, while savings accounts prioritize simplicity and accessibility.
How Sweep Accounts Work
Sweep accounts automatically transfer excess funds from a primary checking account to a higher-interest savings or investment account at the end of each business day. This process optimizes cash flow by ensuring idle funds earn interest while maintaining liquidity for daily expenses. Financial institutions use automated algorithms to monitor balances and execute these transfers, maximizing earnings without manual intervention.
How Savings Accounts Work
Savings accounts function by allowing users to deposit money that earns interest over time, typically at variable rates set by financial institutions. These accounts provide liquidity while encouraging long-term savings through easy access to funds and periodic interest payments. Unlike sweep accounts, which automatically transfer excess funds between accounts to optimize returns or reduce fees, savings accounts primarily focus on growing funds through interest accrual without frequent automatic transfers.
Interest Rates Analysis
Sweep accounts typically offer higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts by automatically transferring excess funds into higher-yield investments. Savings accounts provide steady but generally lower interest rates with greater liquidity and easier access to funds. Analyzing interest yields, sweep accounts maximize earnings potential for balances exceeding set thresholds, while savings accounts prioritize safety and immediate accessibility.
Liquidity and Accessibility
Sweep accounts automatically transfer excess funds into higher-interest investments, offering less immediate liquidity but maximizing returns, whereas savings accounts provide easy access to funds with higher liquidity but typically lower interest rates. Savings accounts allow instant withdrawals via ATMs or online transfers, making them ideal for emergency funds and frequent access needs. Sweep accounts lock funds temporarily to optimize earnings, reducing accessibility but enhancing overall savings growth through automated money management.
Minimum Balance Requirements
Sweep accounts typically require a higher minimum balance compared to savings accounts, as they are designed for frequent fund transfers between checking and investment accounts. Savings accounts often have lower minimum balance requirements, making them more accessible for everyday savers aiming to earn interest. Meeting the minimum balance in a sweep account ensures automatic transfers, while savings accounts may charge fees if the balance falls below the threshold.
Fees and Charges
Sweep accounts typically involve higher fees and charges due to automatic fund transfers between accounts, which may incur transaction fees and minimum balance requirements. Savings accounts usually have lower or no maintenance fees, making them more cost-effective for straightforward savings purposes. Understanding the fee structures can help optimize your account choice based on transaction frequency and balance thresholds.
Suitability: Who Should Choose Which?
Sweep accounts are ideal for business owners or high-net-worth individuals who want to maximize liquidity by automatically transferring excess funds into higher-interest investments while maintaining easy access to cash. Traditional savings accounts suit individuals seeking simplicity, steady interest, and FDIC insurance for emergency funds or regular savings goals. Choosing between sweep and savings accounts depends on the need for active fund management versus straightforward savings with guaranteed security.
Pros and Cons Overview
Sweep accounts automatically transfer excess funds from a checking to a savings account, optimizing interest earnings and reducing idle cash, but may involve fees or minimum balance requirements. Savings accounts offer straightforward interest accrual and easy access to funds, though they often feature lower interest rates compared to sweep accounts. Choosing between the two depends on the need for liquidity versus maximizing interest income.
Important Terms
Cash management
A sweep account automatically transfers excess funds to a linked savings account to maximize interest earnings while maintaining liquidity for cash management.
Liquidity optimization
Sweep accounts automatically transfer excess funds into higher-interest savings accounts to optimize liquidity and maximize returns compared to standard savings accounts.
Automatic fund transfer
Automatic fund transfer in a sweep account dynamically moves excess funds into a savings account to optimize interest earnings and maintain liquidity.
Interest accrual
Interest accrual on sweep accounts occurs daily by automatically transferring excess funds into higher-yield savings, while traditional savings accounts accrue interest monthly based on average daily balances.
Transaction limitations
Sweep accounts automatically transfer excess funds to investment accounts for higher liquidity, while savings accounts have federal withdrawal limits of six transactions per month to comply with Regulation D.
Reserve balance
Reserve balances in a sweep account automatically transfer excess funds to optimize liquidity, whereas savings accounts maintain fixed balances with limited withdrawal flexibility.
Idle funds
Idle funds in a sweep account are automatically transferred into higher-yield interest-bearing instruments when the balance exceeds a predetermined threshold, maximizing returns without manual intervention. Conversely, a savings account holds idle funds with fixed interest rates and limited automatic transfers, often resulting in less efficient fund utilization compared to sweep accounts.
Earnings credit rate
The earnings credit rate on a sweep account typically be higher than that of a traditional savings account, optimizing cash management by automatically transferring excess funds to interest-bearing accounts.
Overdraft protection
Overdraft protection through a sweep account automatically transfers funds from a linked savings account to cover shortfalls, minimizing fees and maintaining account balance continuity.
Deposit account integration
Deposit account integration enables seamless fund transfers between Sweep accounts and Savings accounts, optimizing liquidity management by automatically moving excess balances to higher-yield Savings accounts. This integration enhances cash flow efficiency and maximizes interest earnings while maintaining daily transactional accessibility through Sweep accounts.
Sweep account vs Savings account Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com