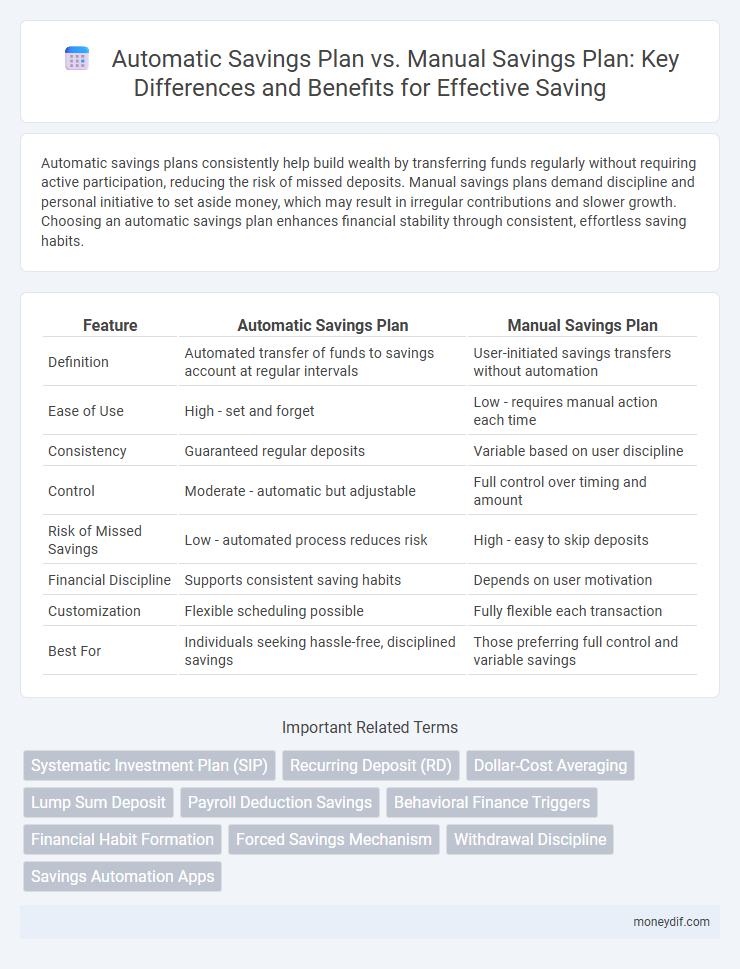
Automatic savings plans consistently help build wealth by transferring funds regularly without requiring active participation, reducing the risk of missed deposits. Manual savings plans demand discipline and personal initiative to set aside money, which may result in irregular contributions and slower growth. Choosing an automatic savings plan enhances financial stability through consistent, effortless saving habits.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Automatic Savings Plan | Manual Savings Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated transfer of funds to savings account at regular intervals | User-initiated savings transfers without automation |
| Ease of Use | High - set and forget | Low - requires manual action each time |
| Consistency | Guaranteed regular deposits | Variable based on user discipline |
| Control | Moderate - automatic but adjustable | Full control over timing and amount |
| Risk of Missed Savings | Low - automated process reduces risk | High - easy to skip deposits |
| Financial Discipline | Supports consistent saving habits | Depends on user motivation |
| Customization | Flexible scheduling possible | Fully flexible each transaction |
| Best For | Individuals seeking hassle-free, disciplined savings | Those preferring full control and variable savings |
Understanding Automatic Savings Plans
Automatic Savings Plans enable consistent and effortless contributions by scheduling regular transfers from checking to savings accounts, ensuring disciplined saving habits. These plans reduce the risk of forgetting to save and help build wealth over time through systematic deposits. Compared to manual savings, automatic plans leverage behavioral finance principles to promote financial stability and long-term goal achievement.
What Is a Manual Savings Plan?
A manual savings plan requires individuals to actively transfer funds into their savings account, offering greater control over the amount and timing of deposits. Unlike automatic savings plans, which deduct money on a set schedule, manual plans depend on personal discipline and regular effort to maintain consistent savings habits. This flexibility allows savers to adjust contributions based on fluctuating income or financial priorities.
Key Differences Between Automatic and Manual Savings
Automatic savings plans transfer fixed amounts directly from checking to savings accounts on set schedules, ensuring consistent contributions without user intervention. Manual savings plans require individuals to actively move funds, offering greater control but depend heavily on discipline and timely action. Key differences include automation level, consistency, and potential impact on saving habits and financial discipline.
Benefits of Automating Your Savings
Automating your savings ensures consistent contributions to your financial goals without the need for active decision-making, reducing the risk of impulsive spending. An automatic savings plan leverages scheduled transfers to build wealth efficiently, often benefiting from employer-linked programs like direct deposit or automated paycheck deductions. This method maximizes discipline, helping you accumulate emergency funds, retirement accounts, or investment portfolios faster than manual savings plans reliant on personal reminders.
Pros and Cons of Manual Savings Methods
Manual savings plans offer flexibility and full control over deposit amounts and timing, allowing savers to adjust contributions based on cash flow fluctuations. However, they require discipline and consistency, increasing the risk of missed deposits and slower accumulation of funds compared to automatic savings plans. The absence of automation can lead to procrastination, reducing overall savings efficiency and potentially delaying achieving financial goals.
Which Plan Boosts Savings Discipline?
Automatic Savings Plans boost savings discipline by enforcing regular, automatic transfers from checking to savings accounts, minimizing the temptation to spend. Manual Savings Plans rely on individual willpower and consistent action, often resulting in irregular contributions and less consistent growth. Data shows automatic plans increase savings rates by up to 30%, making them more effective for disciplined financial growth.
Flexibility: Automatic vs. Manual Approaches
Automatic savings plans provide consistent, scheduled transfers that help build savings effortlessly, reducing the risk of missed deposits. Manual savings plans offer greater flexibility, allowing savers to adjust amounts and timing based on fluctuating income or expenses. Choosing between automatic and manual approaches depends on the need for disciplined saving versus adaptable cash flow management.
Impact on Financial Goals Achievement
Automatic savings plans enhance the likelihood of achieving financial goals by ensuring consistent contributions directly from income, reducing the temptation to spend. Manual savings require disciplined self-control, often resulting in irregular deposits that may delay target attainment. Consistency and automation in savings significantly accelerate progress toward financial milestones.
Costs and Fees Comparison
Automatic savings plans often incur lower fees due to streamlined, automated transfers and reduced administrative costs, making them more cost-effective over time. Manual savings plans may involve higher fees or penalties related to transaction processing, increased risk of missed deposits, and potential bank charges for insufficient funds or overdrafts. Evaluating fee structures, such as monthly maintenance fees and service charges, is crucial when comparing the overall cost-efficiency of automatic versus manual savings plans.
Choosing the Right Savings Plan for You
Selecting the right savings plan depends on your financial goals and discipline; an Automatic Savings Plan ensures consistent contributions by deducting funds directly from your account, reducing the temptation to spend. A Manual Savings Plan offers flexibility, allowing you to decide when and how much to save, ideal for those with irregular income or fluctuating expenses. Evaluating your budgeting habits and income stability helps determine whether automated consistency or manual control best supports your long-term savings success.
Important Terms
Systematic Investment Plan (SIP)
Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs) enable disciplined investing by automating contributions into mutual funds, ensuring consistent wealth accumulation through an Automatic Savings Plan that deducts funds directly from your bank account. In contrast, a Manual Savings Plan requires investors to consciously transfer money, which can lead to irregular investments and potentially hinder long-term financial goals.
Recurring Deposit (RD)
Recurring Deposit (RD) offers consistent wealth accumulation through Automatic Savings Plans that debit fixed amounts periodically, ensuring disciplined savings without manual intervention. Manual Savings Plans grant flexibility to deposit varying amounts at the saver's discretion, catering to irregular income patterns but requiring active management to maximize returns.
Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging maximizes investment efficiency by consistently purchasing assets regardless of market fluctuations, which is more effectively executed through an automatic savings plan that schedules fixed contributions, reducing emotional decision-making and market timing risks. In contrast, manual savings plans require active participation and can lead to inconsistent investing patterns, increasing susceptibility to market timing errors and missed opportunities for disciplined dollar-cost averaging.
Lump Sum Deposit
A Lump Sum Deposit into an Automatic Savings Plan ensures consistent, disciplined contributions without manual intervention, maximizing compound interest benefits over time. In contrast, a Manual Savings Plan requires active participation for each deposit, which may lead to irregular saving patterns and potential missed opportunities for growth.
Payroll Deduction Savings
Payroll Deduction Savings leveraging an Automatic Savings Plan ensures consistent, hassle-free contributions directly from salary, fostering disciplined financial growth and reducing the risk of missed deposits compared to Manual Savings Plans that rely on individual initiative and timing. Automatic plans enhance saving efficiency by automating transfers during each pay period, promoting higher accumulation rates and financial security over manual approaches.
Behavioral Finance Triggers
Behavioral finance triggers such as mental accounting and loss aversion significantly influence the effectiveness of automatic savings plans by reducing decision fatigue and fostering consistent saving habits compared to manual savings plans. Automatic savings leverage behavioral cues like inertia and commitment devices, which enhance disciplined accumulation of wealth, whereas manual plans often suffer from procrastination and inconsistent contribution patterns.
Financial Habit Formation
Automatic savings plans significantly improve financial habit formation by promoting consistent contributions through scheduled transfers, reducing reliance on willpower and minimizing the risk of missed savings. Manual savings plans often face challenges such as inconsistent deposits and procrastination, which can hinder long-term wealth accumulation and financial discipline.
Forced Savings Mechanism
Forced Savings Mechanism improves financial discipline by automatically transferring a set amount into savings, contrasting with Manual Savings Plans that rely on individual initiative and often result in irregular contributions. Automatic Savings Plans leverage technology to ensure consistent deposits, significantly increasing the likelihood of achieving long-term financial goals compared to the variable nature of Manual Savings Plans.
Withdrawal Discipline
Withdrawal discipline significantly enhances the effectiveness of both Automatic Savings Plans and Manual Savings Plans by minimizing impulsive fund access and promoting consistent contributions. Automatic Savings Plans bolster withdrawal discipline through scheduled transfers that reduce temptations, whereas Manual Savings Plans require stronger self-control to resist withdrawals and maintain regular saving habits.
Savings Automation Apps
Savings automation apps streamline financial management by facilitating automatic savings plans that transfer fixed amounts regularly, minimizing the risk of missed contributions, while manual savings plans rely on user-initiated deposits, which can lead to inconsistent saving habits. Data shows automatic savings plans increase monthly savings by up to 30% compared to manual methods, making them more effective for achieving long-term financial goals.
Automatic Savings Plan vs Manual Savings Plan Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com