CUSIP and ISIN are both unique identifiers used in the financial industry to identify securities, with CUSIP primarily used in the United States and Canada, while ISIN is a global standard adopted internationally. CUSIPs consist of nine characters combining letters and numbers to specify the issuer and the specific issue, whereas ISINs are 12-character alphanumeric codes that include a country code, a security identifier, and a check digit. Understanding the differences between CUSIP and ISIN is essential for accurate treasury operations, ensuring precise trade settlements and compliance with regulatory reporting requirements.
Table of Comparison
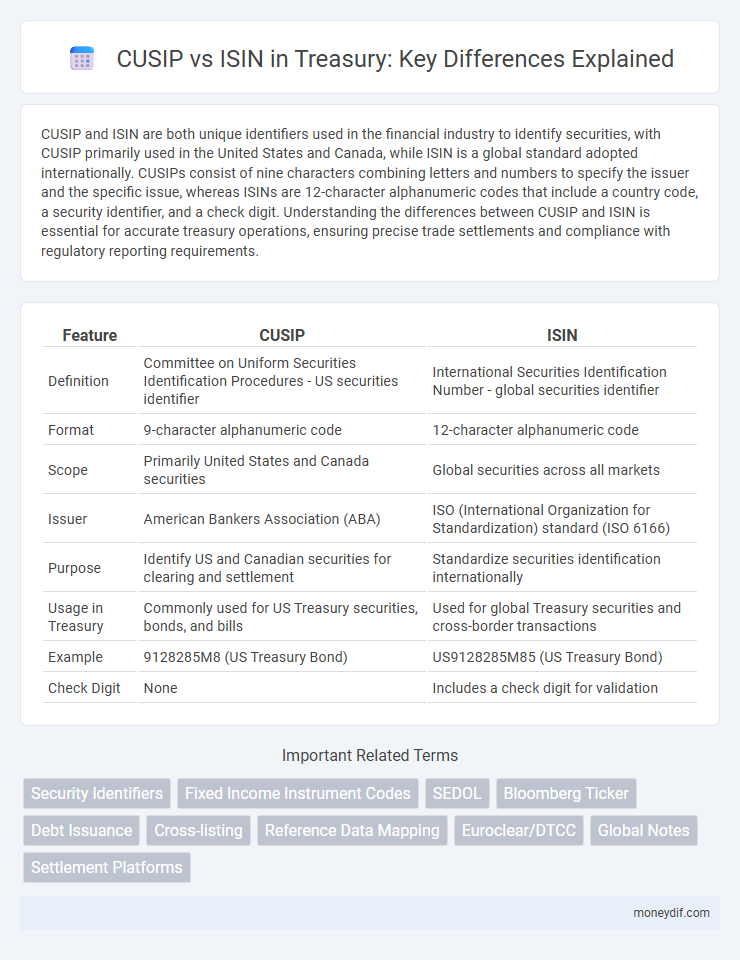
| Feature | CUSIP | ISIN |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Committee on Uniform Securities Identification Procedures - US securities identifier | International Securities Identification Number - global securities identifier |
| Format | 9-character alphanumeric code | 12-character alphanumeric code |
| Scope | Primarily United States and Canada securities | Global securities across all markets |
| Issuer | American Bankers Association (ABA) | ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standard (ISO 6166) |
| Purpose | Identify US and Canadian securities for clearing and settlement | Standardize securities identification internationally |
| Usage in Treasury | Commonly used for US Treasury securities, bonds, and bills | Used for global Treasury securities and cross-border transactions |
| Example | 9128285M8 (US Treasury Bond) | US9128285M85 (US Treasury Bond) |
| Check Digit | None | Includes a check digit for validation |
Overview of CUSIP and ISIN
CUSIP (Committee on Uniform Securities Identification Procedures) identifiers consist of nine alphanumeric characters uniquely identifying North American securities, facilitating efficient trade settlement and clearance. ISIN (International Securities Identification Number) is a 12-character alphanumeric code that standardizes security identification globally, integrating country codes with local identifiers like CUSIP. Both systems serve critical roles in financial markets by enabling precise security tracking, enhancing transparency, and reducing settlement risk in treasury operations.
History and Development of Security Identifiers
CUSIP was developed in 1964 by the American Bankers Association and stands as a key security identifier in the United States market, enabling efficient tracking of stocks and bonds. ISIN, introduced later in the 1980s by the International Organization for Standardization, serves as a global identifier to standardize securities across different countries, using a 12-character alphanumeric code. The evolution from CUSIP to ISIN reflects the increasing need for international harmonization in security identification amid growing cross-border investment activities.
Structure and Format of CUSIP Codes
CUSIP codes consist of nine alphanumeric characters uniquely identifying financial securities in the U.S. and Canada, with the first six characters representing the issuer, the next two identifying the security issue, and the final character serving as a checksum for error detection. Unlike ISINs, which are 12-character international identifiers including a country code prefix, CUSIPs are specific to North American markets and lack geographical indicators. The structured format of CUSIPs enables precise tracking and settlement of securities in domestic treasury operations.
Structure and Format of ISIN Codes
ISIN codes consist of a 12-character alphanumeric structure, beginning with a two-letter country code compliant with ISO 3166, followed by a nine-character national security identifier, and ending with a single check digit for validation. This standardized format enhances global interoperability and facilitates uniform security identification across international markets. In contrast to CUSIPs, which are primarily used within the United States and Canada, ISINs provide a universal framework for cross-border asset classification and settlement.
Key Differences Between CUSIP and ISIN
CUSIP and ISIN are both unique identifiers for financial securities, but CUSIP is a nine-character alphanumeric code used primarily in the United States and Canada, while ISIN is a twelve-character alphanumeric code with a global scope. CUSIP codes include a combination of letters and numbers to identify the issuer and specific security, whereas ISIN incorporates a country code, a unique security identifier, and a check digit. The key difference lies in their geographic usage and structure, with ISIN enabling cross-border trading and settlement, unlike the region-specific CUSIP system.
Geographic Usage: CUSIP vs ISIN
CUSIP numbers are primarily used within the United States and Canada for identifying securities, facilitating efficient trading and settlement processes in North American markets. ISIN codes serve as the international standard for securities identification, widely adopted across Europe, Asia, and other global markets to ensure consistent security referencing. Geographic usage differences highlight that CUSIP is dominant in North America, while ISIN provides a universal framework essential for cross-border financial transactions.
Regulatory Requirements for CUSIP and ISIN
CUSIP and ISIN serve as essential security identifiers in treasury operations, with CUSIP primarily used in the United States and ISIN recognized globally. Regulatory requirements mandate that CUSIP numbers comply with standards set by the American Bankers Association and vested authorities like the SEC for domestic transactions. ISINs adhere to ISO 6166 standards, often required by international regulators such as the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) to ensure cross-border regulatory compliance.
Importance of CUSIP and ISIN in Treasury Operations
CUSIP and ISIN numbers are essential identifiers in treasury operations, enabling precise tracking and management of financial securities across markets. CUSIP codes are primarily used in the United States to identify U.S. and Canadian securities, facilitating efficient settlement and clearing processes. ISIN codes serve as the global standard for cross-border securities identification, ensuring seamless international trading and compliance with regulatory requirements.
How to Obtain and Validate CUSIP/ISIN Codes
CUSIP codes, issued by the American Bankers Association and managed by CUSIP Global Services, can be obtained by contacting authorized organizations or accessing subscription-based databases, while ISIN codes are assigned by the respective country's national numbering agency or financial regulator. Validation of CUSIP and ISIN codes involves verifying the format, length, and check digit algorithm; CUSIP consists of nine alphanumeric characters, whereas ISIN codes have a 12-character alphanumeric structure with embedded country codes. Online validation tools and financial data providers offer reliable services to ensure the accuracy and legitimacy of both CUSIP and ISIN identifiers for treasury securities.
CUSIP and ISIN in Global Treasury Management
CUSIP and ISIN are essential identifiers in Global Treasury Management for accurately tracking and managing securities across markets. CUSIP, primarily used in the United States and Canada, provides a unique nine-character alphanumeric code identifying North American securities, facilitating efficient transaction processing and portfolio management. ISIN offers a 12-character international standard code crucial for cross-border trading and compliance, enabling treasury teams to seamlessly manage global asset portfolios and regulatory reporting.
Important Terms
Security Identifiers
Security Identifiers such as CUSIP, a nine-character alphanumeric code primarily used in North America, and ISIN, a 12-character international standard code, uniquely identify securities for accurate trading, settlement, and risk management.
Fixed Income Instrument Codes
Fixed Income Instrument Codes such as CUSIP and ISIN provide unique identifiers essential for global bond and debt security trading and settlement. While CUSIP codes are primarily used in North America to identify U.S. and Canadian fixed income securities, ISIN codes offer an international standard recognized worldwide, facilitating cross-border transactions and portfolio management.
SEDOL
SEDOL, a seven-character security identifier used in the UK, differs from CUSIP, a nine-character North American identifier, and ISIN, a 12-character global standard that incorporates both SEDOL and CUSIP codes for international securities classification.
Bloomberg Ticker
Bloomberg ticker codes provide a market-friendly identifier linked to comprehensive financial instruments, whereas CUSIP and ISIN are standardized identifiers used globally for securities identification, with CUSIP primarily used in the US and ISIN serving an international scope.
Debt Issuance
Debt issuance involves assigning unique identifiers such as CUSIP and ISIN to facilitate the tracking and trading of securities. CUSIP codes are primarily used in the United States and Canada, whereas ISINs serve as global identifiers, ensuring standardized recognition across international markets.
Cross-listing
Cross-listing allows a company's securities to be traded on multiple stock exchanges, utilizing identifiers such as CUSIP in the United States and ISIN internationally, enhancing global market access and investor reach. The CUSIP (Committee on Uniform Securities Identification Procedures) identifier is a nine-character alphanumeric code specific to North American securities, whereas the ISIN (International Securities Identification Number) is a 12-character code standardized globally, ensuring consistent security identification across markets.
Reference Data Mapping
Reference data mapping accurately links CUSIP identifiers to ISIN codes to ensure seamless security identification and data interoperability across global financial systems.
Euroclear/DTCC
Euroclear and DTCC serve as pivotal securities depositories facilitating global trading and settlement processes, with CUSIP numbers primarily utilized in the U.S. and Canada for identifying North American securities while ISIN codes provide a standardized global security identifier embraced by Euroclear and similar international platforms. The interoperability between CUSIP and ISIN supports cross-border investment and settlement by linking regional securities identification systems with international markets, ensuring efficient asset tracking and reduced settlement risk.
Global Notes
Global Notes streamline bond issuance by consolidating multiple securities into a single master note, reducing administrative complexity and enhancing liquidity. CUSIP identifies North American securities while ISIN provides a global standard, both critical for tracking and trading international financial instruments linked to these consolidated Global Notes.
Settlement Platforms
Settlement platforms streamline cross-border security transactions by integrating CUSIP identifiers for U.S. assets and ISIN codes for global securities, ensuring accurate trade matching and efficient settlement processing.
CUSIP vs ISIN Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com