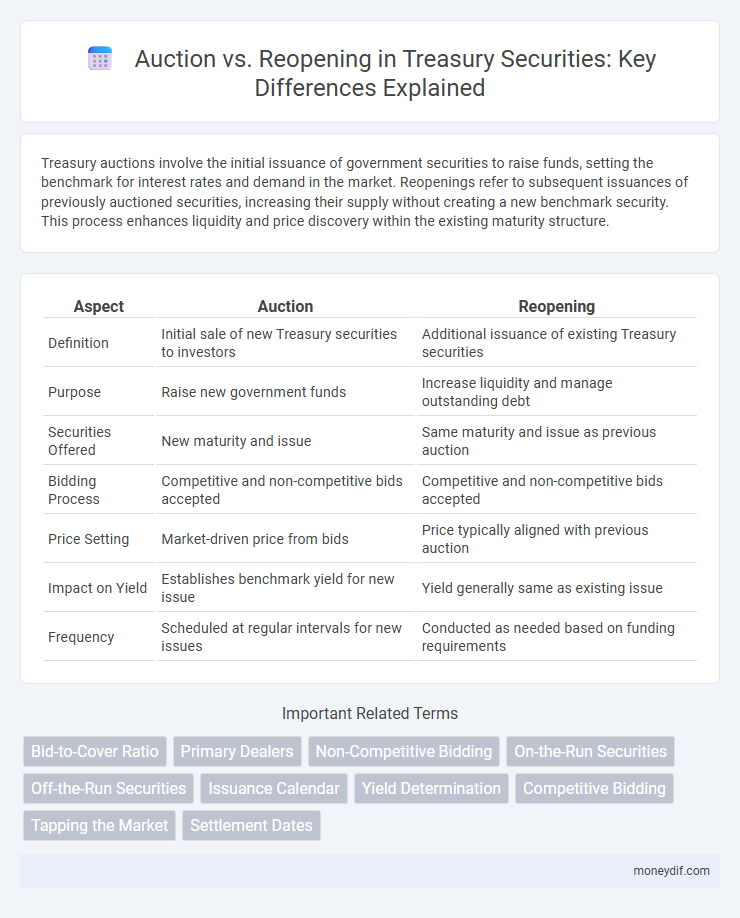
Treasury auctions involve the initial issuance of government securities to raise funds, setting the benchmark for interest rates and demand in the market. Reopenings refer to subsequent issuances of previously auctioned securities, increasing their supply without creating a new benchmark security. This process enhances liquidity and price discovery within the existing maturity structure.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Auction | Reopening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Initial sale of new Treasury securities to investors | Additional issuance of existing Treasury securities |
| Purpose | Raise new government funds | Increase liquidity and manage outstanding debt |
| Securities Offered | New maturity and issue | Same maturity and issue as previous auction |
| Bidding Process | Competitive and non-competitive bids accepted | Competitive and non-competitive bids accepted |
| Price Setting | Market-driven price from bids | Price typically aligned with previous auction |
| Impact on Yield | Establishes benchmark yield for new issue | Yield generally same as existing issue |
| Frequency | Scheduled at regular intervals for new issues | Conducted as needed based on funding requirements |
Understanding Treasury Auctions
Treasury auctions involve the initial issuance of government securities, establishing benchmark yields through competitive bidding by investors. Reopening refers to the issuance of additional amounts of an existing Treasury security, allowing the government to raise funds without creating a new series. Understanding the distinction between auctions and reopenings is essential for investors to assess market liquidity, price discovery, and yield implications in the fixed-income market.
What is Treasury Reopening?
Treasury reopening involves issuing additional new notes or bonds of an existing security to raise more funds without creating a new issue. This process helps maintain liquidity in the market and meets increased demand for specific maturities. By reopening, the Treasury efficiently manages its debt portfolio while supporting price stability and investor confidence in government securities.
Key Differences: Auction vs Reopening
Auctions involve the initial issuance of new Treasury securities to raise government funds, with competitive bidding determining the yield and price. Reopenings refer to subsequent issuances of existing Treasury securities, increasing the amount outstanding without affecting original auction terms or yields. Key differences include that auctions establish benchmark yields and supply, while reopenings provide liquidity and market depth by expanding prior issues.
How Treasury Auctions Work
Treasury auctions allocate government securities through a bidding process where competitive bidders specify their yield and non-competitive bidders accept the yield determined by the auction. Primary dealers and institutional investors typically participate in these auctions to purchase new debt instruments, ensuring liquidity and funding for government operations. Reopenings, on the other hand, involve issuing additional amounts of previously auctioned securities, allowing the Treasury to manage supply and investor demand efficiently.
The Process of Treasury Reopenings
Treasury reopenings involve issuing additional quantities of previously auctioned securities to meet ongoing government funding needs, enhancing liquidity and maintaining benchmark yield curves. The process includes announcing the reopening amount and date, followed by competitive bidding similar to initial auctions, allowing investors to submit bids for the additional securities. This approach efficiently manages debt issuance by leveraging existing maturities and market familiarity, reducing issuance costs and market disruption.
Benefits of Auctions in Treasury Markets
Treasury auctions enhance price discovery by enabling competitive bidding that reflects real-time market demand, ensuring fair market value for government securities. They promote broad investor participation, increasing liquidity and enabling efficient allocation of capital in debt markets. Auctions also provide transparency and predictability in government borrowing costs, which stabilizes financial markets and strengthens investor confidence.
Advantages of Reopening Treasury Securities
Reopening Treasury securities allows the government to issue additional amounts of an existing bond, enhancing liquidity and market depth while reducing borrowing costs by leveraging established benchmark yields. This approach simplifies investor decisions by maintaining consistent terms and reduces issuance uncertainties compared to launching new auctions. As a result, reopening supports stable price discovery and efficient market functioning for Treasury instruments.
Impact on Investors: Auction vs Reopening
Auction events provide investors with direct access to newly issued Treasury securities, often offering competitive yields based on current market demand, which can enhance portfolio diversification. Reopenings, by contrast, involve the issuance of additional amounts of previously auctioned securities, potentially at yields influenced by prevailing secondary market conditions, allowing investors to acquire more of established maturities with known liquidity profiles. The choice between participating in auctions or reopenings affects portfolio strategy, yield optimization, and risk management, with auctions generally presenting fresh pricing dynamics and reopenings enabling scale in existing holdings.
Market Implications of Treasury Issuance Methods
Auction issuance of Treasury securities typically enhances price discovery and market liquidity by allowing competitive bidding from a broad investor base, reflecting current demand and supply dynamics. Reopening existing issues tends to stabilize secondary market trading by increasing the outstanding amount of benchmark securities, thereby reducing yield volatility. Market participants often prefer auctions for transparency, while reopenings support consistent benchmark curves and facilitate smoother portfolio management.
Choosing Between Auction and Reopening
Choosing between auction and reopening depends on market conditions and debt management objectives. Auctions establish new Treasury securities and determine initial pricing, while reopenings involve issuing additional amounts of existing securities to meet refinancing needs. Evaluating investor demand, yield curve implications, and cost efficiency guides the optimal selection between auction and reopening strategies.
Important Terms
Bid-to-Cover Ratio
Bid-to-Cover Ratio measures demand by comparing total bids to available supply in an auction, indicating investor interest and pricing efficiency. Reopenings can affect this ratio by expanding outstanding issues without fresh benchmarks, often leading to different demand dynamics compared to initial auctions.
Primary Dealers
Primary dealers act as key intermediaries in government securities markets, bidding at initial Treasury auctions to facilitate price discovery and market liquidity. During reopenings, these dealers support the issuance of additional amounts of previously auctioned securities, helping maintain consistent supply and market stability.
Non-Competitive Bidding
Non-Competitive Bidding allows investors to submit bids without specifying price, ensuring full allocation at the determined yield in Treasury auctions. In contrast, Auction Reopening enables the issuance of additional securities on an existing Treasury issue at the same yield, increasing supply without altering the original terms.
On-the-Run Securities
On-the-run securities represent the most recently issued U.S. Treasury bonds or notes, typically sold at primary auctions, while off-the-run securities are older issues reintroduced through reopenings to enhance market liquidity. Auctions establish the initial benchmark yield curve for on-the-run securities, whereas reopenings adjust supply without creating new benchmark instruments, influencing secondary market pricing and liquidity.
Off-the-Run Securities
Off-the-run securities refer to older issues of government bonds that are no longer the most recently issued (on-the-run) securities and typically trade with less liquidity and a wider bid-ask spread. In contrast to auctions, which are initial sales of new securities, reopenings involve issuing additional amounts of an existing off-the-run security to increase its outstanding supply and enhance market liquidity.
Issuance Calendar
The Issuance Calendar schedules bond auctions and reopenings to optimize market liquidity and investor demand timing.
Yield Determination
Yield determination in auctions is influenced by competitive bidding, often resulting in yields that reflect current market demand, while reopening methods rely on existing bond issues and typically produce yields aligned with previously established benchmarks. Auction yields tend to be more volatile and responsive to immediate investor sentiment, whereas reopening yields benefit from price discovery based on liquidity and secondary market conditions.
Competitive Bidding
Competitive bidding in auctions often involves a one-time offer process, whereas reopening allows bidders to submit revised bids, enhancing price discovery and competitive advantage.
Tapping the Market
Tapping the market through auctions typically ensures price discovery and competitive bidding, leading to optimal resource allocation, whereas reopening involves reissuing existing securities, often at predetermined terms, to efficiently meet additional funding needs without resetting market dynamics. Choosing between auction and reopening strategies depends on market liquidity, investor demand, and cost efficiency, impacting issuers' ability to raise capital effectively.
Settlement Dates
Settlement dates for auctions typically occur on a fixed timeline established at the time of issuance, ensuring regular liquidity and transaction finality. In contrast, reopenings settle on the original bond's established settlement date, maintaining continuity across multiple issuance tranches.
Auction vs Reopening Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com