Private equity involves investing in established companies to restructure and improve profitability, often taking a controlling interest and focusing on long-term value creation. Venture capital targets early-stage startups with high growth potential, providing funding in exchange for equity and accepting higher risk for the chance of significant returns. Both strategies play crucial roles in wealth generation but differ in investment horizon, risk profile, and company maturity.
Table of Comparison
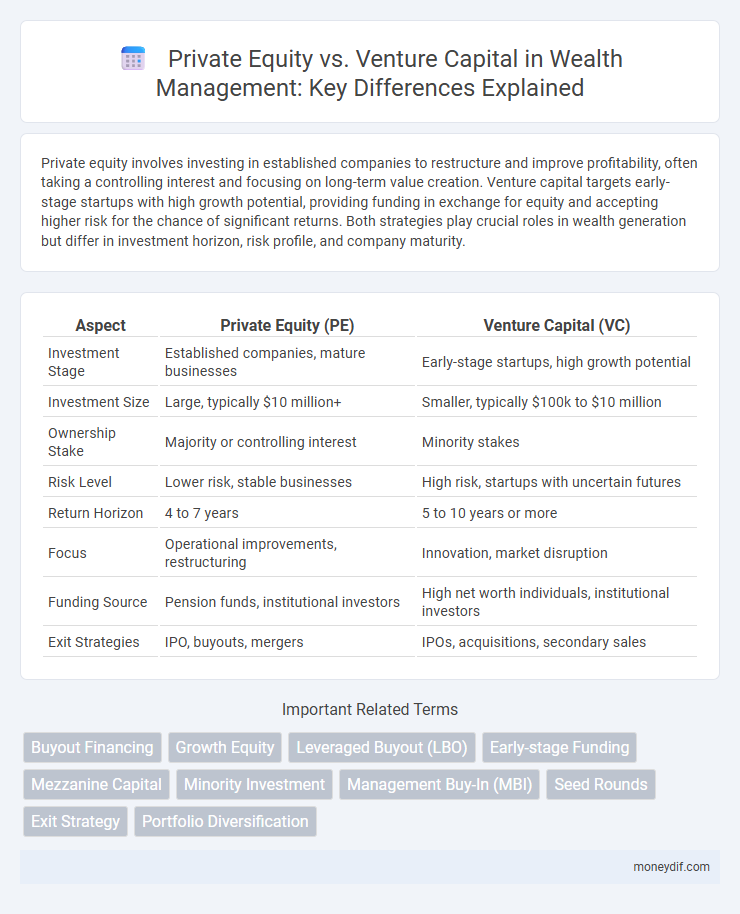
| Aspect | Private Equity (PE) | Venture Capital (VC) |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Stage | Established companies, mature businesses | Early-stage startups, high growth potential |
| Investment Size | Large, typically $10 million+ | Smaller, typically $100k to $10 million |
| Ownership Stake | Majority or controlling interest | Minority stakes |
| Risk Level | Lower risk, stable businesses | High risk, startups with uncertain futures |
| Return Horizon | 4 to 7 years | 5 to 10 years or more |
| Focus | Operational improvements, restructuring | Innovation, market disruption |
| Funding Source | Pension funds, institutional investors | High net worth individuals, institutional investors |
| Exit Strategies | IPO, buyouts, mergers | IPOs, acquisitions, secondary sales |
Understanding Private Equity and Venture Capital
Private equity involves investing in established companies through buyouts or direct acquisitions, aiming to improve their value over time before exiting via sales or public offerings. Venture capital focuses on funding early-stage startups with high growth potential, providing capital in exchange for equity and often active involvement in business development. Both investment types seek to generate substantial returns but differ in risk profiles, investment stages, and operational engagement.
Key Differences Between Private Equity and Venture Capital
Private equity primarily involves investing in mature companies through buyouts or significant stakes to improve profitability and achieve long-term value, while venture capital focuses on early-stage startups with high growth potential. Private equity deals typically require substantial capital and have lower risk compared to venture capital's higher-risk, high-reward investments in innovative, emerging businesses. The exit strategies also differ, with private equity favoring buy-and-build approaches and venture capital relying heavily on initial public offerings (IPOs) or acquisitions.
Investment Stages: Private Equity vs Venture Capital
Private equity primarily targets mature companies during later investment stages, often involving buyouts or significant equity stakes to drive operational improvements and growth. Venture capital focuses on early-stage startups and high-growth potential companies, providing funding in seed, Series A, and subsequent rounds to support product development and market expansion. The difference in investment stages reflects risk tolerance, deal structure, and expected return horizons unique to each asset class.
Sources of Funding in Private Equity and Venture Capital
Private equity primarily raises funds from institutional investors such as pension funds, insurance companies, and endowments, focusing on large-scale investments in mature companies. Venture capital sources funding mainly from high-net-worth individuals, family offices, and specialized VC funds targeting early-stage startups with high growth potential. Both funding sources structure capital through limited partnerships, but venture capital emphasizes risk capital from angel investors and seed funds, while private equity relies on more substantial commitments from institutional backers.
Risk and Return Profiles: A Comparative Analysis
Private equity typically involves investing in mature companies with established cash flows, offering lower risk but moderate returns compared to venture capital, which targets early-stage startups with high growth potential and significantly higher risk. The return profile of venture capital is more volatile, often driven by successful exits through initial public offerings or acquisitions, whereas private equity aims for steady appreciation via operational improvements and financial restructuring. Investors seeking risk-adjusted returns balance their portfolios by allocating capital based on these distinct risk and reward dynamics inherent in private equity and venture capital markets.
Ownership and Control Dynamics
Private equity investments typically acquire a majority ownership stake, granting firms significant control over portfolio companies' strategic decisions and operations. Venture capital usually involves minority stakes, providing investors with influence rather than outright control, as the focus is on high-growth startups requiring operational autonomy. This fundamental difference in ownership structures shapes the level of governance and decision-making authority between private equity and venture capital investors.
Exit Strategies in Private Equity and Venture Capital
Private equity exit strategies primarily include leveraged buyouts, secondary sales, and initial public offerings (IPOs), focusing on maximizing returns through long-term ownership and operational improvements. Venture capital tends to exit via IPOs or acquisitions, aiming for rapid growth and market disruption to achieve high multiples on invested capital. Both utilize strategic timing and market conditions to optimize returns, but private equity often seeks more control and steady value realization compared to venture capital's higher-risk, high-reward approach.
Impact on Portfolio Companies
Private equity firms typically invest in more mature companies, driving operational improvements and strategic growth to enhance cash flow and profitability, which often leads to significant influence over management decisions and governance structures. Venture capital focuses on early-stage startups, providing not only capital but also mentorship, industry connections, and support to accelerate innovation and market penetration, though with less control over day-to-day operations. The impact on portfolio companies varies as private equity usually seeks value creation through restructuring and efficiency, while venture capital aims at scaling high-growth potential ventures rapidly.
Role in Wealth Creation and Preservation
Private equity focuses on acquiring established companies to optimize operations, driving long-term wealth preservation and steady returns through strategic management and restructuring. Venture capital invests in early-stage startups with high growth potential, aiming for exponential wealth creation through innovation and scalability. Both private equity and venture capital play distinct but complementary roles in wealth strategies by balancing risk, growth, and capital preservation.
Choosing Between Private Equity and Venture Capital Investments
Private equity investments typically target mature companies with stable cash flows, offering lower risk and steady returns, while venture capital focuses on early-stage startups with high growth potential but increased risk. Investors must evaluate their risk tolerance, investment horizon, and desired involvement level before choosing, as private equity often requires significant capital and longer lock-up periods compared to venture capital's faster exit opportunities. Strategic alignment with portfolio goals and industry expertise can optimize returns when selecting between private equity and venture capital investment options.
Important Terms
Buyout Financing
Buyout financing in private equity involves acquiring majority stakes in mature companies to improve operations and generate returns, whereas venture capital focuses on minority investments in early-stage startups with high growth potential.
Growth Equity
Growth equity focuses on investing in established companies with proven revenue streams seeking capital for expansion, bridging the risk-return profile between high-risk venture capital and more mature private equity buyouts.
Leveraged Buyout (LBO)
Leveraged Buyouts (LBOs) primarily involve private equity firms acquiring mature companies using significant debt, while venture capital focuses on investing equity in early-stage startups with high growth potential.
Early-stage Funding
Early-stage funding primarily involves venture capital, which targets high-growth startups with innovative business models, while private equity typically focuses on later-stage investments in more mature companies. Venture capital provides not only capital but also strategic guidance and networking opportunities, whereas private equity emphasizes operational improvements and scaling established enterprises.
Mezzanine Capital
Mezzanine capital is a hybrid financing option that bridges the gap between private equity and venture capital by providing subordinated debt with equity conversion features to fund mature companies seeking growth or buyouts.
Minority Investment
Minority investment in private equity typically involves acquiring a non-controlling stake in established companies, whereas venture capital focuses on minority investments in early-stage startups with high growth potential.
Management Buy-In (MBI)
Management Buy-In (MBI) typically involves experienced external managers acquiring a significant stake in a company, often supported by private equity firms focused on mature businesses, contrasting with venture capital's emphasis on funding early-stage startups with high growth potential.
Seed Rounds
Seed rounds are early-stage funding events where venture capital often plays a critical role in providing capital to startups, whereas private equity typically focuses on later-stage investments with established companies. Venture capital seed funding targets high-growth potential startups, while private equity invests in more mature businesses seeking expansion or restructuring.
Exit Strategy
Exit strategies in private equity typically involve leveraged buyouts, secondary sales, or IPOs to maximize returns, while venture capital exits focus more on high-growth IPOs or acquisitions to capitalize on early-stage investments.
Portfolio Diversification
Portfolio diversification in private equity and venture capital reduces investment risk by balancing stable, mature assets with high-growth, early-stage opportunities.
private equity vs venture capital Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com