Wealth transfer involves the passing of assets and financial resources from one generation to another within families or close networks, ensuring continuity and preservation of wealth over time. Wealth migration refers to the movement of capital and high-net-worth individuals across borders to optimize tax strategies, investments, and lifestyle preferences. Understanding the distinctions between these concepts is crucial for effective wealth management and strategic financial planning in a globalized economy.
Table of Comparison
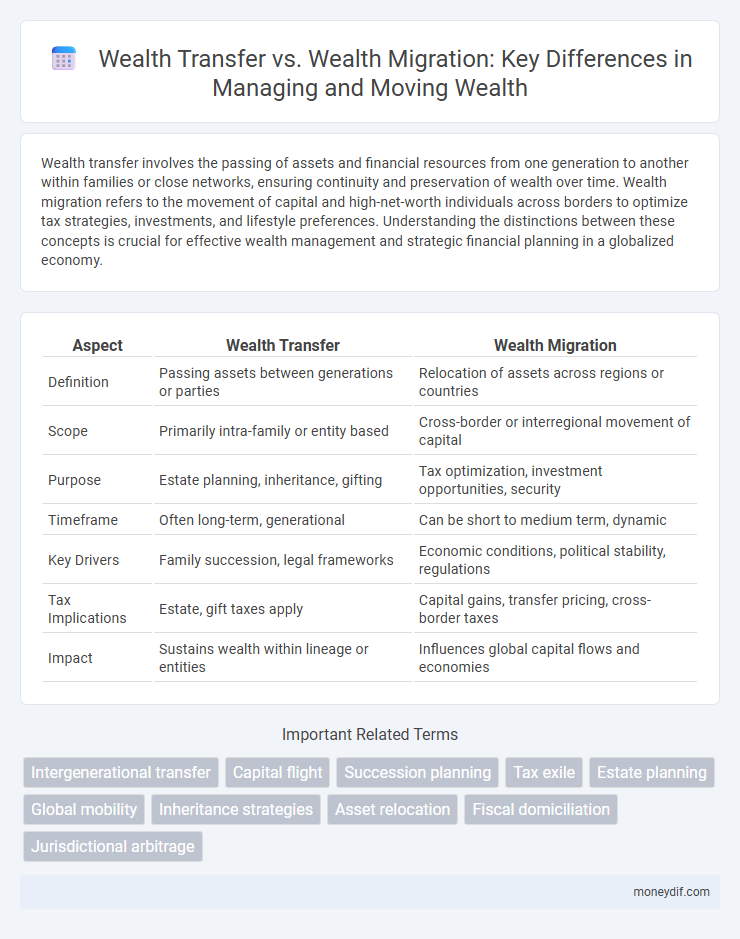
| Aspect | Wealth Transfer | Wealth Migration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Passing assets between generations or parties | Relocation of assets across regions or countries |
| Scope | Primarily intra-family or entity based | Cross-border or interregional movement of capital |
| Purpose | Estate planning, inheritance, gifting | Tax optimization, investment opportunities, security |
| Timeframe | Often long-term, generational | Can be short to medium term, dynamic |
| Key Drivers | Family succession, legal frameworks | Economic conditions, political stability, regulations |
| Tax Implications | Estate, gift taxes apply | Capital gains, transfer pricing, cross-border taxes |
| Impact | Sustains wealth within lineage or entities | Influences global capital flows and economies |
Understanding Wealth Transfer: Key Concepts
Wealth transfer involves the passing of assets and financial resources from one generation to another, typically through inheritance, trusts, or gifts, influencing family legacies and financial planning. Unlike wealth migration, which refers to the physical movement of individuals or capital to new locations for tax or lifestyle benefits, wealth transfer centers on the allocation and preservation of wealth within established relationships or legal frameworks. Understanding key concepts such as estate planning, tax implications, and generational wealth management is essential for optimizing wealth transfer strategies.
Defining Wealth Migration in a Global Context
Wealth migration refers to the movement of high net worth individuals or families across borders seeking favorable economic, political, or social conditions. This phenomenon differs from wealth transfer, which involves the passing of assets within generations or through inheritance. In a global context, wealth migration significantly impacts international financial markets, real estate, and tax policies as affluent individuals relocate to optimize wealth preservation and growth.
Major Drivers Behind Wealth Transfer
Wealth transfer primarily occurs due to intergenerational inheritance, estate planning strategies, and philanthropic contributions, significantly shaping asset distribution across families and communities. Tax policies, demographic shifts such as aging populations, and evolving economic landscapes act as major drivers facilitating or constraining the efficient transfer of wealth. Unlike wealth migration, which involves relocating assets across borders for legal or financial advantages, wealth transfer focuses on reallocating wealth within defined socio-economic groups to sustain or enhance financial legacies.
Factors Influencing Wealth Migration
Wealth migration is driven by factors such as favorable tax regimes, political stability, and quality of life, which attract high-net-worth individuals and their assets to new jurisdictions. Wealth transfer primarily involves the redistribution of existing assets within families or estates, influenced by inheritance laws and estate planning strategies. Economic opportunities, legal frameworks, and lifestyle preferences also play critical roles in shaping patterns of wealth migration across global regions.
Comparative Analysis: Wealth Transfer vs. Wealth Migration
Wealth transfer involves the redistribution of assets within families or communities across generations, typically through inheritance or gifts, ensuring long-term financial continuity and legacy preservation. Wealth migration, on the other hand, refers to the movement of high-net-worth individuals and their financial resources between countries or regions, driven by factors such as tax optimization, political stability, and lifestyle preferences. While wealth transfer emphasizes intra-family or intra-community wealth consolidation, wealth migration highlights the cross-border flow of capital seeking favorable economic or regulatory environments.
Legal and Tax Implications of Wealth Transfer
Wealth transfer involves passing assets directly through inheritance, trusts, or gifts, subject to estate and gift tax regulations that vary by jurisdiction and require careful legal structuring to minimize liabilities. Wealth migration refers to relocating high-net-worth individuals or families to jurisdictions with favorable tax laws, impacting residency status and triggering exit taxes or reporting obligations. Understanding the complex interplay of international tax treaties, estate laws, and compliance requirements is critical for optimizing tax outcomes and ensuring lawful wealth preservation.
Economic Effects of Wealth Migration on Home and Host Countries
Wealth migration significantly impacts both home and host countries by redistributing financial resources, often boosting economic growth and innovation in host nations while potentially leading to capital flight and reduced tax revenues in home countries. This flow of wealth can enhance investment opportunities, create jobs, and stimulate local markets in destination countries, whereas origin countries may experience challenges such as brain drain and diminished domestic investment. Understanding these economic effects helps policymakers create balanced strategies to harness the benefits of wealth migration while mitigating adverse outcomes.
Strategic Approaches to Managing Wealth Transfer
Strategic approaches to managing wealth transfer emphasize seamless succession planning, tax-efficient asset allocation, and leveraging trusts to preserve intergenerational wealth. Wealth transfer strategies optimize legal frameworks and financial instruments to minimize liabilities while ensuring long-term asset protection for beneficiaries. Integrating wealth migration considerations enhances cross-border asset management, aligning family goals with global economic opportunities.
The Role of Technology in Facilitating Wealth Migration
Technology accelerates wealth migration by enabling seamless global financial transactions and real-time asset management through digital platforms and blockchain solutions. Advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence provide personalized investment insights, optimizing cross-border wealth movement. Furthermore, fintech innovations reduce barriers to entry, allowing high-net-worth individuals to diversify assets and relocate wealth efficiently across international markets.
Future Trends in Wealth Transfer and Migration
Future trends in wealth transfer indicate a significant increase in intergenerational asset redistribution, with estimates suggesting over $84 trillion will shift from baby boomers to millennials by 2040. Wealth migration is increasingly influenced by geopolitical stability, tax policies, and the rise of digital nomadism, prompting affluent individuals to relocate to countries offering favorable economic and regulatory environments. Emerging markets and tech hubs are expected to see substantial inflows of high-net-worth individuals, reshaping global wealth distribution patterns in the coming decades.
Important Terms
Intergenerational transfer
Intergenerational transfer involves passing assets within families, primarily focusing on wealth transfer which denotes the direct inheritance or gifting of financial resources to descendants. Wealth migration differs as it entails the strategic relocation of assets or individuals across jurisdictions to optimize tax benefits, legal protections, and investment opportunities, often influencing how and where wealth is transferred between generations.
Capital flight
Capital flight refers to the rapid outflow of financial assets from a country, often triggered by economic instability or unfavorable policies, severely impacting domestic investment and economic growth. Wealth transfer involves the redistribution of assets between generations or entities, whereas wealth migration specifically denotes the relocation of wealth across borders, highlighting differences in scale and intent within global financial dynamics.
Succession planning
Succession planning focuses on the strategic transfer of wealth within families or organizations to ensure continuity and preserve financial legacy, while wealth migration involves the movement of assets across borders influenced by taxation, legal frameworks, and economic opportunities. Effective succession planning minimizes risks associated with wealth migration by aligning estate laws and wealth preservation strategies to maintain asset integrity across generations.
Tax exile
Tax exile status significantly impacts wealth transfer strategies by enabling high-net-worth individuals to minimize tax liabilities when relocating assets internationally, while wealth migration focuses on the physical relocation of individuals or families to optimize fiscal benefits. Strategic tax planning for exiles often involves structured trusts and offshore accounts to preserve wealth during migration, ensuring efficient intergenerational transfer across jurisdictions with favorable tax regimes.
Estate planning
Estate planning involves strategic decisions to facilitate wealth transfer, ensuring assets pass efficiently to heirs and beneficiaries, minimizing taxes and legal complications. Wealth migration, in contrast, refers to relocating assets or individuals to different jurisdictions for favorable tax treatment or legal benefits, influencing estate planning by altering the regulatory environment governing wealth distribution.
Global mobility
Global mobility significantly influences wealth transfer by enabling high-net-worth individuals to relocate assets across borders, optimizing tax benefits and estate planning. Wealth migration drives this phenomenon as affluent individuals physically move to jurisdictions with favorable economic policies, impacting global capital flows and investment landscapes.
Inheritance strategies
Inheritance strategies focus on efficient wealth transfer through wills, trusts, and estate planning to minimize tax liabilities and preserve assets for future generations. Wealth migration, driven by cross-border relocation or investments, often alters these strategies by introducing international tax laws, residency considerations, and compliance requirements that impact asset distribution.
Asset relocation
Asset relocation involves transferring financial holdings or properties to new jurisdictions to optimize tax benefits, legal protections, or investment opportunities. Wealth transfer focuses on passing assets between generations, whereas wealth migration emphasizes moving assets across borders to leverage favorable economic or regulatory environments.
Fiscal domiciliation
Fiscal domiciliation determines the legal tax residency used to assess wealth transfer taxes, directly influencing estate planning and inheritance liabilities. Wealth migration involves relocating assets or individuals to jurisdictions with favorable fiscal domiciliation rules, optimizing tax efficiency and preserving wealth across generations.
Jurisdictional arbitrage
Jurisdictional arbitrage involves strategically relocating assets or wealth to jurisdictions with favorable tax laws, regulations, or privacy protections to optimize wealth transfer efficiency. This practice contrasts with wealth migration, which focuses on the physical movement of individuals to countries that offer better economic or lifestyle benefits, affecting wealth distribution across borders.
Wealth transfer vs wealth migration Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com