On-us transactions occur when both the payer and payee hold accounts within the same bank, enabling faster processing and reduced fees. Off-us transactions involve accounts at different banks, often leading to longer settlement times and additional intermediary charges. Understanding the distinction between on-us and off-us transactions helps optimize payment strategies and manage operational costs effectively.
Table of Comparison
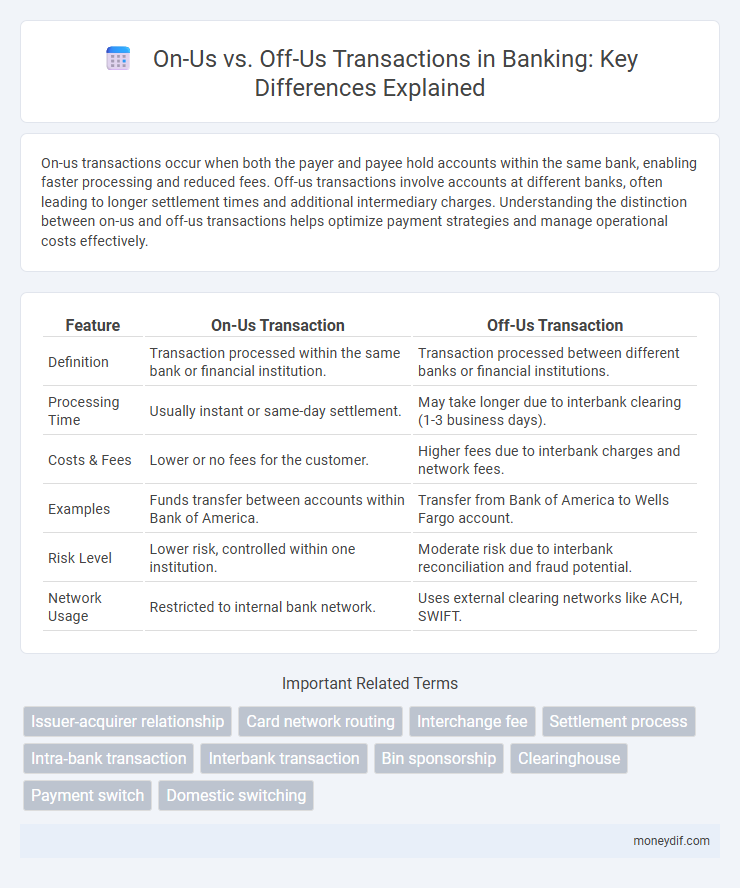
| Feature | On-Us Transaction | Off-Us Transaction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transaction processed within the same bank or financial institution. | Transaction processed between different banks or financial institutions. |
| Processing Time | Usually instant or same-day settlement. | May take longer due to interbank clearing (1-3 business days). |
| Costs & Fees | Lower or no fees for the customer. | Higher fees due to interbank charges and network fees. |
| Examples | Funds transfer between accounts within Bank of America. | Transfer from Bank of America to Wells Fargo account. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk, controlled within one institution. | Moderate risk due to interbank reconciliation and fraud potential. |
| Network Usage | Restricted to internal bank network. | Uses external clearing networks like ACH, SWIFT. |
Understanding On-Us and Off-Us Transactions in Banking
On-us transactions occur when both the payer and payee have accounts within the same bank, facilitating immediate fund transfers and reduced processing fees. Off-us transactions involve transferring funds between different banks, often requiring clearinghouses and incurring higher processing times and costs. Understanding these distinctions helps banks optimize transaction processing, manage settlement risks, and customize customer fee structures.
Key Differences Between On-Us and Off-Us Transactions
On-us transactions occur when both the payer and payee hold accounts within the same financial institution, enabling faster processing and lower transaction fees. Off-us transactions involve different banks, often requiring interbank networks and additional clearing time, which can increase costs and processing duration. Key differences include the transactional routing, settlement time, fee structures, and risk management protocols associated with same-bank versus interbank transfers.
How On-Us Transactions Work: A Closer Look
On-Us transactions occur when both the payer's and the payee's accounts are held within the same bank, enabling immediate fund transfers without the need for external clearing systems. These transactions streamline processing times and reduce transaction costs since the bank manages all account settlements internally. Real-time balance updates and instant payment confirmations enhance customer experience by providing faster access to transferred funds.
Off-Us Transactions: Definition and Process
Off-us transactions occur when a customer uses their payment card at a merchant or ATM outside their issuing bank's network. The process involves the merchant's bank sending the transaction details to the payment network, which then routes the information to the cardholder's issuing bank for authorization and settlement. This multi-step verification ensures secure processing and accurate fund transfer between different financial institutions.
Impact of On-Us vs Off-Us Transactions on Clearing Time
On-us transactions, processed entirely within the same bank, typically have faster clearing times due to internal settlement mechanisms and reduced interbank reconciliation. Off-us transactions involve different banks, requiring the use of interbank networks or clearinghouses that inherently increase processing time and complexity. The distinction directly impacts both liquidity management and customer experience by influencing the speed of fund availability.
Fee Structures: On-Us Versus Off-Us Transactions
On-us transactions, where both the payer's and payee's accounts are held within the same bank, typically incur lower or no fees due to reduced processing costs. Off-us transactions involve accounts held at different financial institutions, leading to higher fees to cover interbank settlement and network charges. Banks often apply distinct fee structures reflecting these cost differences, impacting consumer costs and transaction routing strategies.
Security Considerations in On-Us and Off-Us Banking Transactions
Security considerations in On-Us transactions focus on internal controls within a single bank, ensuring robust authentication and fraud detection systems to prevent unauthorized access. Off-Us transactions require enhanced multi-institutional safeguards, including encryption protocols, cross-bank verification processes, and compliance with interbank security standards to mitigate risks of data breaches and fraudulent activities. Both transaction types demand continuous monitoring and real-time analytics to promptly identify and respond to suspicious behaviors.
Effects on Merchant Settlement: On-Us vs Off-Us Transactions
On-us transactions, where both the card issuer and acquirer belong to the same bank, result in faster merchant settlement due to streamlined processing and reduced clearance times. Off-us transactions involve multiple financial institutions, leading to longer settlement periods and potentially higher interchange fees, which can affect merchant cash flow. The efficiency of on-us transactions minimizes settlement risk and improves liquidity for merchants compared to off-us transactions.
Role of Payment Networks in On-Us and Off-Us Processing
Payment networks facilitate the routing and authorization of on-us and off-us transactions by connecting multiple financial institutions and enabling seamless fund transfers. In on-us transactions, where the issuer and acquirer are the same bank, the payment network's role is minimal, primarily handling transaction validation and security protocols. For off-us transactions, payment networks are critical, managing the communication between different banks, ensuring transaction integrity, and settling funds efficiently across diverse financial entities.
Future Trends: On-Us and Off-Us Transactions in Digital Banking
Future trends in digital banking show a significant shift towards enhanced processing efficiency for both on-us and off-us transactions, driven by advancements in blockchain technology and real-time payment systems. Banks are increasingly adopting AI-powered fraud detection to secure on-us transactions, while off-us transactions benefit from improved interoperability standards and open banking APIs that streamline cross-institution payments. The integration of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms also promises to redefine transaction settlements, reducing costs and increasing transparency for both transaction types.
Important Terms
Issuer-acquirer relationship
Issuer-acquirer relationships define transaction routing where on-us transactions occur within the same financial institution, while off-us transactions involve different institutions processing payment authorization and settlement.
Card network routing
Card network routing distinguishes between On-us transactions, where the issuer and acquirer are the same entity, and Off-us transactions, which involve different financial institutions, affecting processing paths and fees.
Interchange fee
Interchange fees for on-us transactions are typically lower or waived since the issuer and acquirer are the same entity, whereas off-us transactions incur higher interchange fees due to the involvement of different financial institutions.
Settlement process
The settlement process for On-us transactions is faster and involves internal account transfers within the same bank, while Off-us transactions require interbank clearing and reconciliation, resulting in longer processing times.
Intra-bank transaction
Intra-bank transactions, also known as On-us transactions, occur within the same bank's network, while Off-us transactions involve transfers between accounts held at different banks.
Interbank transaction
Interbank transactions involve Off-us transactions where funds are transferred between different banks, whereas On-us transactions occur within the same bank, enabling faster processing and lower fees.
Bin sponsorship
Bin sponsorship enables financial institutions to process On-us transactions internally while Off-us transactions require interbank network routing for settlement.
Clearinghouse
Clearinghouse processes On-us transactions internally within the same bank, while Off-us transactions involve multiple banks requiring interbank settlement.
Payment switch
Payment switches efficiently route on-us transactions within the same bank and off-us transactions between different banks, optimizing transaction processing speed and security.
Domestic switching
Domestic switching systems process On-us transactions within the same bank's network, while Off-us transactions involve cardholder and merchant accounts from different banks, requiring interbank settlement.
On-us transaction vs Off-us transaction Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com