ECN (Electronic Communication Network) platforms offer transparent order books and facilitate direct trading between market participants, ensuring price discovery and reduced spreads. Dark pools provide off-exchange trading venues where large orders can be executed anonymously, minimizing market impact but sacrificing transparency. Choosing between ECN and dark pools depends on a trader's priority for transparency versus anonymity and order size management.
Table of Comparison
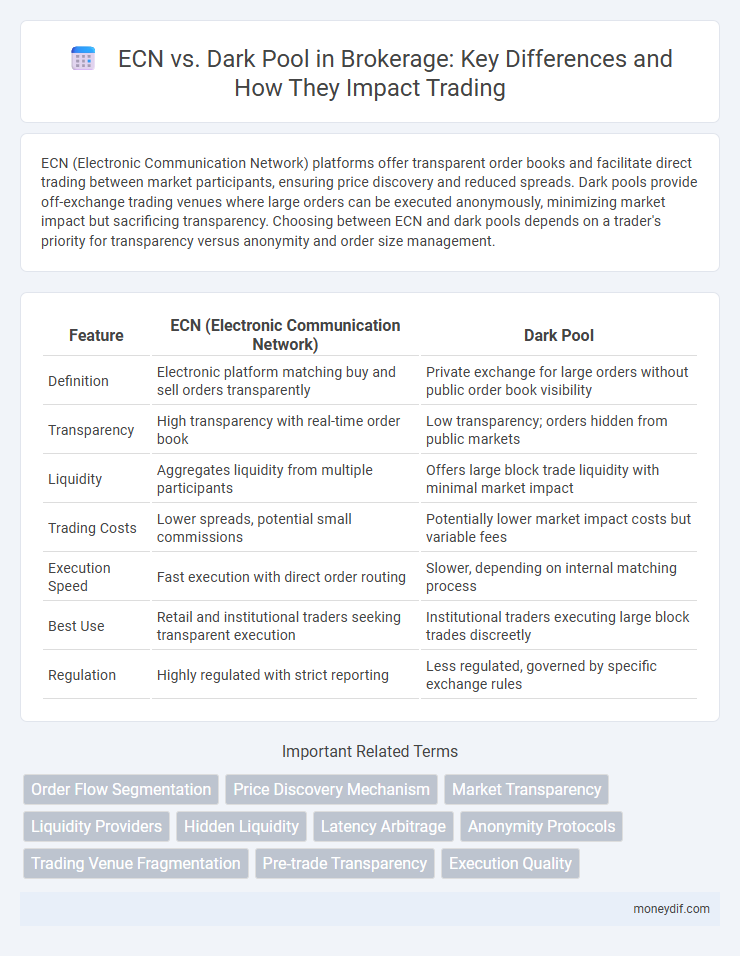
| Feature | ECN (Electronic Communication Network) | Dark Pool |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electronic platform matching buy and sell orders transparently | Private exchange for large orders without public order book visibility |
| Transparency | High transparency with real-time order book | Low transparency; orders hidden from public markets |
| Liquidity | Aggregates liquidity from multiple participants | Offers large block trade liquidity with minimal market impact |
| Trading Costs | Lower spreads, potential small commissions | Potentially lower market impact costs but variable fees |
| Execution Speed | Fast execution with direct order routing | Slower, depending on internal matching process |
| Best Use | Retail and institutional traders seeking transparent execution | Institutional traders executing large block trades discreetly |
| Regulation | Highly regulated with strict reporting | Less regulated, governed by specific exchange rules |
Understanding ECN and Dark Pool: Key Concepts
ECN (Electronic Communication Network) operates as an automated system that matches buy and sell orders in real-time, providing transparent pricing and increased market liquidity. Dark pools are private trading venues where large institutional investors execute orders anonymously, reducing market impact and minimizing information leakage. Understanding these platforms' distinct mechanisms is crucial for traders seeking optimal execution strategies within the brokerage ecosystem.
How ECNs Operate in Brokerage Trading
ECNs (Electronic Communication Networks) operate by matching buy and sell orders directly between market participants, ensuring transparent and real-time price discovery in brokerage trading. These platforms provide access to multiple liquidity sources by aggregating orders from various brokers and institutions, enhancing market efficiency and reducing spreads. Unlike dark pools, ECNs maintain transparency by displaying order books publicly, enabling traders to see available liquidity before executing trades.
Mechanisms Behind Dark Pools Explained
Dark pools operate through private trading venues where buy and sell orders are matched without public visibility, allowing large institutional investors to execute sizable trades with minimal market impact. These venues utilize sophisticated algorithms and midpoint pricing to conceal order sizes and intentions, preventing price slippage commonly observed in traditional exchanges or ECNs. The opaque nature of dark pools provides anonymity and reduced transaction costs, contrasting with ECNs that offer transparent order books and public order matching.
Benefits of Using ECNs for Investors
ECNs (Electronic Communication Networks) provide investors with transparent trade execution by displaying real-time bid and ask prices, allowing access to a broad range of market participants and enhancing price discovery. They offer lower transaction costs and faster execution speeds compared to traditional dark pools, enabling investors to capitalize on market opportunities efficiently. ECNs also reduce market manipulation risks by eliminating hidden order books, promoting fairer and more competitive trading environments.
Advantages of Dark Pool Trading in Brokerage
Dark pool trading in brokerage offers significant advantages such as enhanced privacy, allowing large institutional investors to execute sizable trades without revealing their intentions to the public market. This reduces market impact and price slippage, preserving trade value and minimizing adverse effects on stock prices. Dark pools also provide access to liquidity that is not available on traditional exchanges, facilitating more efficient block trading.
ECN vs Dark Pool: Comparing Liquidity and Transparency
ECN (Electronic Communication Network) offers direct access to multiple liquidity providers, ensuring higher transparency and real-time order book visibility, which enhances price discovery and execution quality. Dark Pools match large orders anonymously away from public exchanges, providing reduced market impact but limited transparency and delayed reporting. Comparing liquidity, ECNs aggregate visible bids and offers, whereas Dark Pools conceal order details to protect anonymity, impacting how traders assess market depth and price fairness.
Regulatory Differences Between ECN and Dark Pool Platforms
ECN (Electronic Communication Network) platforms operate under stricter regulatory oversight, requiring transparent order books and real-time trade reporting to ensure market fairness and liquidity. Dark pools, by contrast, are subject to less stringent regulations, allowing anonymous trading and limited disclosure to protect large institutional orders from market impact. The regulatory divergence aims to balance transparency in ECNs with privacy and reduced market disturbance in dark pools.
Execution Speed and Costs: ECN vs Dark Pool
ECN (Electronic Communication Network) offers faster execution speeds due to its transparent matching engine connecting multiple liquidity providers, resulting in competitive bid-ask spreads and lower transaction costs. Dark Pools facilitate large block trades anonymously, potentially reducing market impact and slippage, but often at the expense of slower execution and higher hidden costs due to limited transparency. Traders prioritize ECN for rapid order fulfillment and cost efficiency, while Dark Pools suit institutional investors seeking discretion over immediate speed.
Risks Associated with ECN and Dark Pool Trading
ECN trading carries risks such as reduced liquidity during volatile markets, leading to wider spreads and potential slippage. Dark pool trading poses concerns about transparency, as limited pre-trade information can increase the likelihood of adverse selection and market manipulation. Both trading venues demand robust risk management to mitigate potential execution and information asymmetry issues.
Choosing the Right Brokerage Platform: ECN or Dark Pool?
Choosing the right brokerage platform depends on your trading goals: ECN (Electronic Communication Network) platforms offer greater transparency and faster trade execution by connecting buyers and sellers directly across multiple markets, ideal for active traders seeking liquidity and price discovery. Dark Pools provide anonymity and reduced market impact by allowing large orders to be executed privately, suitable for institutional investors aiming to avoid price slippage. Evaluate factors such as trade size, need for transparency, and execution speed to determine whether ECN or Dark Pool services align with your investment strategy.
Important Terms
Order Flow Segmentation
Order flow segmentation distinguishes ECN markets, which offer transparent, real-time order books, from dark pools that execute large trades privately to minimize market impact.
Price Discovery Mechanism
Price discovery in Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) offers transparent, real-time market data contrasting with dark pools, where limited visibility can obscure true asset valuation.
Market Transparency
Market transparency improves significantly in ECNs compared to dark pools due to real-time public order book visibility and regulated trading environments.
Liquidity Providers
Liquidity providers in ECN markets offer transparent, real-time bid-ask prices enhancing price discovery, while in dark pools they execute large block trades anonymously to minimize market impact and slippage.
Hidden Liquidity
Hidden liquidity in ECNs offers transparent order book access unlike dark pools where trade intentions remain concealed to reduce market impact.
Latency Arbitrage
Latency arbitrage exploits speed advantages by routing orders through faster ECN networks instead of slower dark pools, capturing price discrepancies before dark pool trades are reflected in market prices.
Anonymity Protocols
Anonymity protocols in financial markets enhance privacy by masking trader identities, with Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) offering transparent order books while dark pools provide private trade execution to minimize market impact.
Trading Venue Fragmentation
Trading venue fragmentation intensifies as Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) enhance transparency and liquidity, while dark pools offer anonymous, off-exchange trading that impacts price discovery and market efficiency.
Pre-trade Transparency
Pre-trade transparency in ECNs provides visible order books enhancing price discovery, whereas dark pools obscure orders to minimize market impact and maintain confidentiality.
Execution Quality
Execution quality on ECNs typically offers greater transparency and faster trade confirmation compared to dark pools, which provide improved price improvement opportunities through non-displayed orders but may have less market visibility.
ECN vs Dark Pool Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com