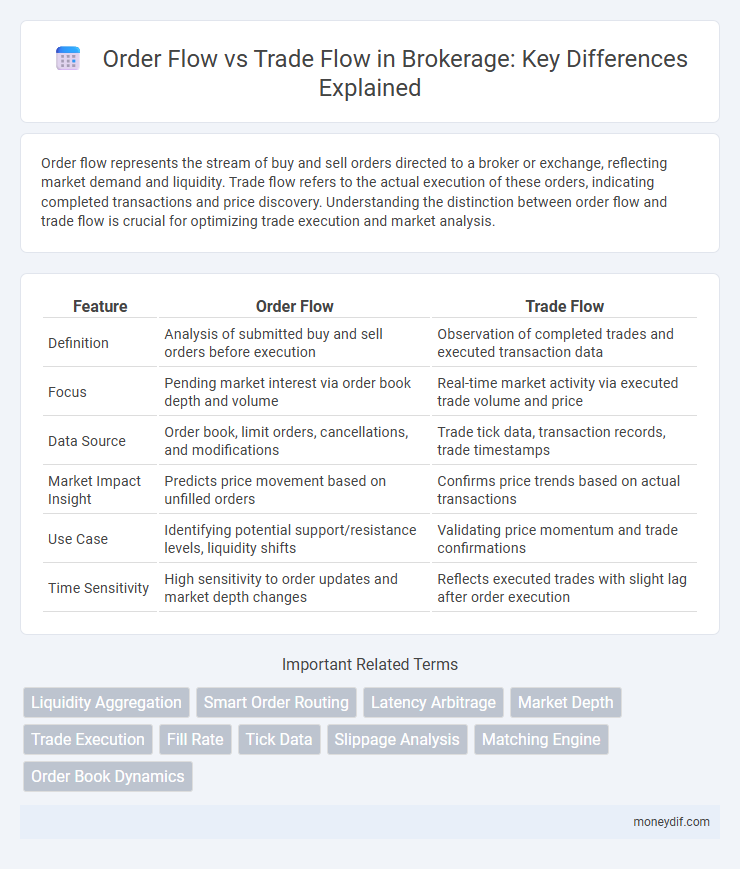
Order flow represents the stream of buy and sell orders directed to a broker or exchange, reflecting market demand and liquidity. Trade flow refers to the actual execution of these orders, indicating completed transactions and price discovery. Understanding the distinction between order flow and trade flow is crucial for optimizing trade execution and market analysis.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Order Flow | Trade Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analysis of submitted buy and sell orders before execution | Observation of completed trades and executed transaction data |
| Focus | Pending market interest via order book depth and volume | Real-time market activity via executed trade volume and price |
| Data Source | Order book, limit orders, cancellations, and modifications | Trade tick data, transaction records, trade timestamps |
| Market Impact Insight | Predicts price movement based on unfilled orders | Confirms price trends based on actual transactions |
| Use Case | Identifying potential support/resistance levels, liquidity shifts | Validating price momentum and trade confirmations |
| Time Sensitivity | High sensitivity to order updates and market depth changes | Reflects executed trades with slight lag after order execution |
Understanding Order Flow in Brokerage
Order flow in brokerage refers to the process by which brokers route client orders to various market makers or exchanges for execution, influencing trade execution quality and liquidity. Understanding order flow helps traders assess how brokers generate revenue through payment for order flow agreements while potentially affecting trade transparency and pricing. Efficient management of order flow ensures optimal execution speed, reduced slippage, and improved overall trading performance.
What is Trade Flow?
Trade flow refers to the actual execution of buy and sell orders in the financial markets, representing real-time transactions between traders and investors. It provides critical insights into market liquidity, price movements, and the behavior of market participants, influencing brokerage strategies and order execution quality. Understanding trade flow enables brokers to optimize routing decisions and enhance trade execution efficiency, impacting overall market transparency and investor outcomes.
Key Differences Between Order Flow and Trade Flow
Order flow represents the stream of buy and sell orders submitted to a broker before execution, while trade flow refers to the actual completed transactions or executed trades in the market. Order flow provides insight into market sentiment and potential price movements by revealing unfilled demand, whereas trade flow reflects real-time market liquidity and transaction volume. The key difference lies in order flow capturing intent and pre-trade interest, whereas trade flow confirms executed market activity and price discovery.
How Order Flow Impacts Market Liquidity
Order flow represents the stream of buy and sell orders submitted by traders, directly influencing market liquidity by indicating the actual demand and supply at different price levels. High order flow activity enhances liquidity by creating tighter bid-ask spreads and facilitating faster execution of trades. Brokers and market makers utilize detailed order flow data to optimize pricing strategies and improve market depth, ensuring more efficient trading environments.
The Role of Trade Flow in Execution Quality
Trade flow plays a critical role in execution quality by directly impacting market liquidity and price discovery, enabling brokers to execute orders at optimal prices. Order flow aggregates client intentions, but trade flow reflects actual transaction data, providing real-time insights into market dynamics and improving fill rates. Efficient analysis of trade flow allows brokers to minimize slippage and price impact, enhancing overall execution performance and client satisfaction.
Order Flow Analysis for Traders
Order flow analysis provides traders with real-time insights into market liquidity by tracking the number and size of buy and sell orders, enabling precise entry and exit points. Unlike trade flow, which records executed transactions, order flow reveals upcoming market pressure before trades are confirmed, offering a predictive advantage. Advanced order flow tools such as the depth of market (DOM) and footprint charts enhance decision-making by visualizing order book dynamics and identifying support and resistance levels.
Trade Flow Tracking for Brokerages
Trade flow tracking provides brokerages with granular insights into executed transactions, enabling enhanced analysis of buying and selling behaviors across different markets and asset classes. By monitoring real-time trade data, brokerages can optimize liquidity management, improve pricing strategies, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Advanced trade flow analytics supports better client servicing by identifying execution patterns and potential market impacts, leading to more informed decision-making and competitive advantage.
Technological Advances in Order and Trade Flow
Technological advances in order flow leverage algorithmic trading platforms and advanced data analytics to optimize the routing and execution of buy and sell orders, enhancing market efficiency and transparency. In contrast, trade flow technologies focus on real-time trade reporting and settlement systems that ensure accuracy, reduce latency, and streamline post-trade processes. Both innovations utilize machine learning and high-frequency trading infrastructure to minimize slippage and improve overall liquidity in brokerage environments.
Risks Associated with Order Flow and Trade Flow
Risks associated with order flow include potential conflicts of interest where brokers may prioritize order flow payments over best execution, leading to suboptimal trade prices for clients. Trade flow risks involve delayed or inaccurate trade execution, which can cause price slippage and increased market exposure. Both order flow and trade flow risks can impact the transparency and fairness of brokerage services, affecting client trust and regulatory compliance.
Optimizing Brokerage Strategies with Flow Data
Order flow data provides detailed insights into the intentions behind client trades, enabling brokers to anticipate market movements and optimize execution strategies. Trade flow reflects actual completed transactions, offering real-time confirmation of liquidity and price levels essential for adjusting brokerage algorithms. Leveraging both order flow and trade flow enhances predictive accuracy and execution efficiency, driving improved brokerage performance and client satisfaction.
Important Terms
Liquidity Aggregation
Liquidity aggregation consolidates order flow from multiple sources to enhance trade flow efficiency and execution quality in financial markets.
Smart Order Routing
Smart Order Routing optimizes trade execution by dynamically directing order flow to multiple venues based on real-time trade flow data and market liquidity.
Latency Arbitrage
Latency arbitrage exploits the time gap between order flow information reaching different market participants and the subsequent trade flow execution to gain risk-free profits.
Market Depth
Market depth provides a detailed visualization of order flow by displaying pending buy and sell orders at various price levels, whereas trade flow represents the actual executed transactions within the market.
Trade Execution
Trade execution efficiency improves significantly when integrating real-time order flow analysis with trade flow data to optimize price impact and minimize market slippage.
Fill Rate
Fill rate measures the percentage of executed orders relative to submitted order flow, indicating the efficiency of matching against actual trade flow in financial markets.
Tick Data
Tick Data provides granular insights essential for analyzing Order Flow, which captures market participant actions, versus Trade Flow, reflecting executed transactions and price changes.
Slippage Analysis
Slippage analysis compares order flow and trade flow to identify disparities between expected and executed prices, optimizing trade execution strategies.
Matching Engine
Matching Engine optimizes trade execution by accurately reconciling order flow, which represents submitted orders, with trade flow, the completed transactions reflected in market data.
Order Book Dynamics
Order book dynamics reveal that order flow represents the submission and cancellation of limit orders influencing market depth, while trade flow reflects executed transactions impacting price movement and liquidity.
Order Flow vs Trade Flow Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com