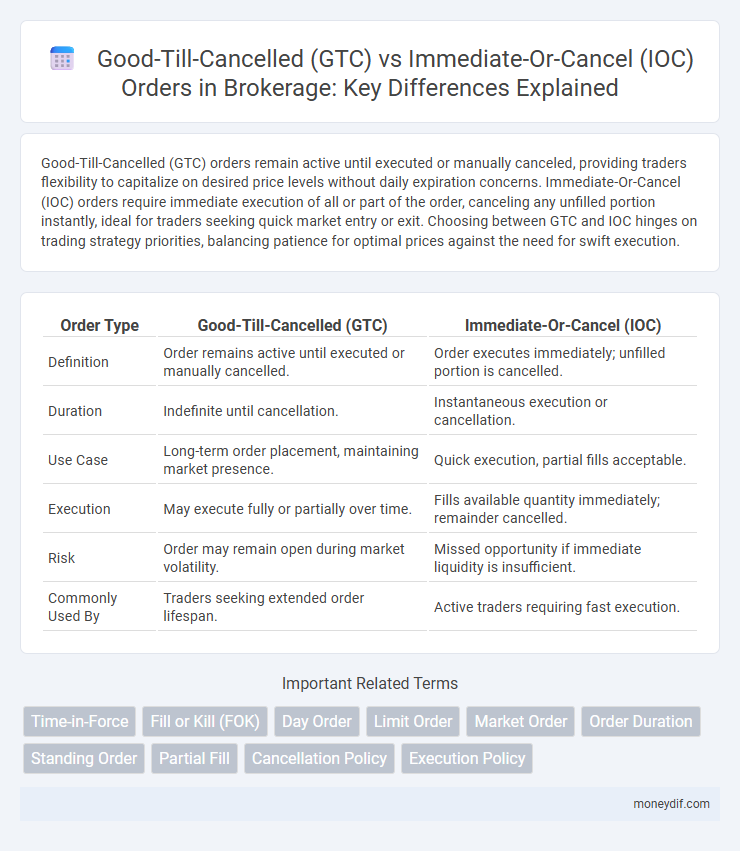
Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders remain active until executed or manually canceled, providing traders flexibility to capitalize on desired price levels without daily expiration concerns. Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders require immediate execution of all or part of the order, canceling any unfilled portion instantly, ideal for traders seeking quick market entry or exit. Choosing between GTC and IOC hinges on trading strategy priorities, balancing patience for optimal prices against the need for swift execution.
Table of Comparison
| Order Type | Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) | Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Order remains active until executed or manually cancelled. | Order executes immediately; unfilled portion is cancelled. |
| Duration | Indefinite until cancellation. | Instantaneous execution or cancellation. |
| Use Case | Long-term order placement, maintaining market presence. | Quick execution, partial fills acceptable. |
| Execution | May execute fully or partially over time. | Fills available quantity immediately; remainder cancelled. |
| Risk | Order may remain open during market volatility. | Missed opportunity if immediate liquidity is insufficient. |
| Commonly Used By | Traders seeking extended order lifespan. | Active traders requiring fast execution. |
Introduction to Order Types in Brokerage
Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders remain active in the market until the trader executes them or cancels explicitly, providing flexibility for longer-term strategies. Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders require instant execution of all or part of the order, with any unfilled portion cancelled immediately, optimizing speed and execution certainty. Understanding these order types is crucial in brokerage for managing trade timing, risk, and liquidity effectively.
What is a Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) Order?
A Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) order is a type of brokerage order that remains active in the market until the investor decides to cancel it or it gets executed. It allows traders to set a specific price for buying or selling securities without the pressure of the order expiring at the end of the trading day. GTC orders provide flexibility and convenience for investors aiming to execute trades over an extended period, avoiding the need to re-enter orders daily.
What is an Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) Order?
An Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) order is a type of brokerage order that requires all or part of the order to be executed immediately upon reaching the market; any portion that cannot be filled instantly is canceled. This order type is commonly used to prioritize speed and certainty in executions, minimizing exposure to price fluctuations. IOC orders are particularly useful in fast-moving markets or when seeking partial fills without leaving unexecuted orders on the order book.
Key Differences Between GTC and IOC Orders
Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders remain active until executed or manually cancelled, allowing investors to hold their buy or sell instructions indefinitely, while Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders require partial or full execution immediately, with any unfilled portion cancelled instantly. GTC orders provide long-term trading flexibility and reduce the need for constant monitoring, contrasted by IOC orders designed for rapid execution and minimizing exposure to price fluctuations. Understanding these key distinctions helps traders optimize order strategies based on market conditions and investment goals.
Advantages of Using GTC Orders
Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders offer the advantage of maintaining an active order until it is either executed or manually canceled, providing investors with continuous market presence without the need for repeated order placement. This order type enhances trading efficiency by allowing investors to set target prices and avoid missing opportunities in volatile markets. GTC orders are particularly beneficial for long-term investment strategies, as they help manage positions without constant monitoring.
Advantages of Using IOC Orders
Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders offer the advantage of swift execution by filling all or part of the order immediately and canceling the remainder, minimizing exposure to adverse price movements. This order type enhances trading efficiency during volatile markets by reducing the risk of unfilled or partially filled orders lingering in the order book. Brokers and traders benefit from improved liquidity management and rapid order fulfillment, making IOC orders ideal for time-sensitive trading strategies.
When to Use GTC vs IOC Orders
Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders are ideal for investors aiming to maintain a position over an extended period without frequent monitoring, as they remain active until executed or manually canceled. Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders suit traders seeking rapid execution of all or part of an order, with any unfilled portion canceled instantly, beneficial in volatile markets. Choosing between GTC and IOC depends on trading strategy, market conditions, and urgency of order execution in brokerage operations.
Impact on Trading Strategies
Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders maintain open positions until executed or manually canceled, providing traders the advantage of patient execution in volatile markets but increasing exposure to adverse price movements over time. Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders prioritize rapid execution by filling all or part of the order immediately and canceling any unfilled portion, benefiting day traders and scalpers seeking quick entry or exit with minimal market risk. Selecting between GTC and IOC directly impacts execution efficiency, trade timing, and risk management, essential factors in formulating robust trading strategies within brokerage platforms.
Risks Associated with Each Order Type
Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders carry the risk of unexecuted trades lingering indefinitely, exposing investors to market volatility and potential adverse price movements over time. Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders minimize exposure by requiring partial or full execution immediately, but risk partial fills or no execution at all, potentially resulting in missed trading opportunities. Both order types demand careful risk management to align with an investor's trading strategy and market conditions.
Choosing the Right Order Type for Your Brokerage Needs
Choosing the right order type in brokerage depends on your trading strategy and urgency. Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders remain active until executed or manually canceled, ideal for long-term positions seeking a specific price. Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders execute any available portion immediately and cancel the rest, perfect for traders needing fast execution without waiting for full order fulfillment.
Important Terms
Time-in-Force
Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders remain active until executed or manually cancelled, while Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders execute any available quantity immediately and cancel the remainder.
Fill or Kill (FOK)
Fill or Kill (FOK) orders require immediate execution of the entire order quantity or cancellation, unlike Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders that remain active until manually canceled and Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders that allow partial fills with the unfilled portion canceled instantly.
Day Order
Day orders expire at the end of the trading day if not executed, whereas Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders remain active until filled or cancelled and Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders require immediate execution of all or part and cancel any unfilled portion instantly.
Limit Order
A Limit Order with Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) duration remains active until executed or manually canceled, whereas an Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) Limit Order executes immediately for any available quantity and cancels the remaining unfilled portion.
Market Order
Market orders execute immediately at the best available price, with Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders remaining active until filled or canceled, while Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders execute all or part instantly and cancel any unfilled portion.
Order Duration
Order Duration options include Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC), which remains active until executed or canceled, and Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC), which executes any available portion immediately and cancels the remainder.
Standing Order
Standing orders can be set as Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) to remain active until executed or manually cancelled, unlike Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders which execute any available quantity immediately and cancel the remainder.
Partial Fill
Partial fill orders persist in Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) until fully filled or cancelled, whereas Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders execute only available quantities immediately and cancel any unfilled portion.
Cancellation Policy
The Cancellation Policy distinguishes Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) orders, which remain active until manually canceled, from Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) orders, which execute any portion immediately and cancel the rest if not filled.
Execution Policy
Execution policies dictate order fulfillment strategies, with Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) maintaining active orders until executed or cancelled, while Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) requires immediate execution of all or part of the order, canceling any unfilled portion instantly.
Good-Till-Cancelled (GTC) vs Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC) Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com