FICO score and VantageScore are two primary credit scoring models used by lenders to evaluate creditworthiness. FICO scores typically range from 300 to 850 and are more widely used in mortgage, auto, and credit card lending decisions, while VantageScore, also ranging from 300 to 850, is gaining traction due to its use of more recent scoring technology and availability of credit history from multiple bureaus. Understanding the differences in their calculation methods and the impact of factors like payment history and credit utilization can help consumers better manage their credit profiles.
Table of Comparison
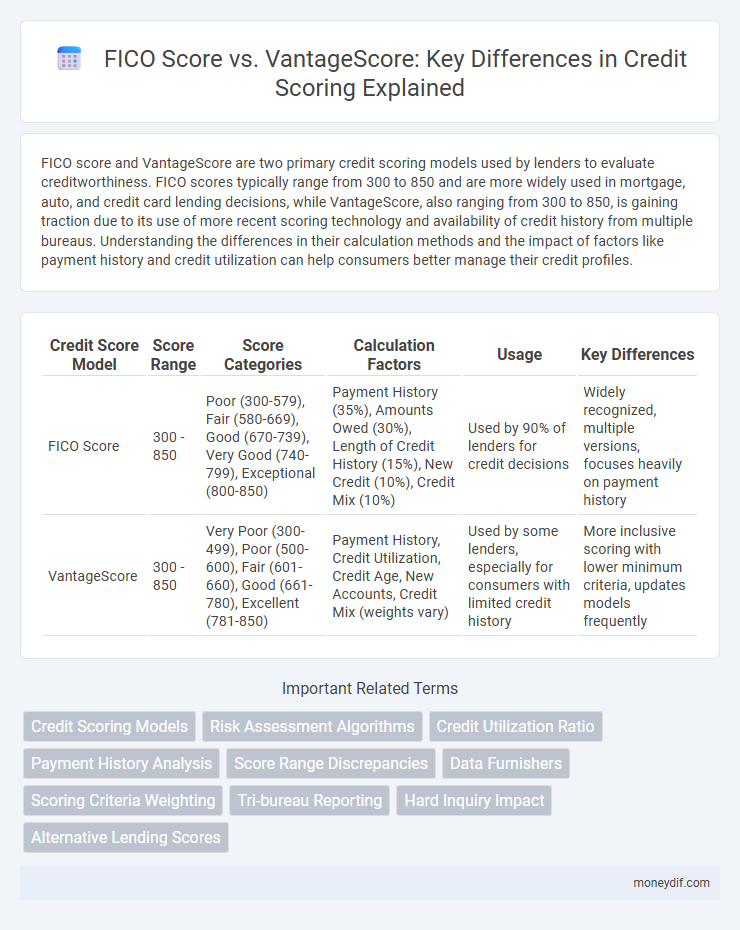
| Credit Score Model | Score Range | Score Categories | Calculation Factors | Usage | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FICO Score | 300 - 850 | Poor (300-579), Fair (580-669), Good (670-739), Very Good (740-799), Exceptional (800-850) | Payment History (35%), Amounts Owed (30%), Length of Credit History (15%), New Credit (10%), Credit Mix (10%) | Used by 90% of lenders for credit decisions | Widely recognized, multiple versions, focuses heavily on payment history |
| VantageScore | 300 - 850 | Very Poor (300-499), Poor (500-600), Fair (601-660), Good (661-780), Excellent (781-850) | Payment History, Credit Utilization, Credit Age, New Accounts, Credit Mix (weights vary) | Used by some lenders, especially for consumers with limited credit history | More inclusive scoring with lower minimum criteria, updates models frequently |
Understanding FICO Score and VantageScore
FICO Score and VantageScore are two primary credit scoring models used by lenders to evaluate creditworthiness, with FICO Score being developed by Fair Isaac Corporation and VantageScore created collaboratively by the three major credit bureaus: Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax. Both scoring models analyze credit report data such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, new credit inquiries, and credit mix but differ slightly in their weighting and methodology, resulting in potential score variations for the same individual. Understanding these differences is crucial for consumers aiming to improve their credit profiles, as certain lenders may prefer one model over the other when making lending decisions.
Key Differences Between FICO and VantageScore
FICO scores range from 300 to 850 and are primarily used by lenders for credit decisions, while VantageScores also span 300 to 850 but incorporate trended credit data for more predictive insights. FICO models prioritize recent credit behavior and payment history, whereas VantageScore factors in broader credit usage patterns and weighs medical debt differently. Lenders predominantly rely on FICO scores in mortgage and auto lending, whereas VantageScore is increasingly used in credit card and personal loan approvals due to its quicker update cycle and more inclusive scoring of credit file activity.
How FICO and VantageScore Calculate Credit Scores
FICO scores are calculated using factors such as payment history (35%), amounts owed (30%), length of credit history (15%), new credit (10%), and credit mix (10%). VantageScore uses similar criteria but places greater emphasis on recent credit behavior, including total credit usage and balance trends over the past 24 months. Both models analyze credit report data from major credit bureaus but differ slightly in weighting and scoring ranges, impacting how lenders assess credit risk.
Factors Influencing FICO vs VantageScore
FICO scores rely heavily on payment history, amounts owed, length of credit history, new credit, and credit mix to determine creditworthiness. VantageScore places significant emphasis on recent credit behavior, such as utilization rate and recent inquiries, while also integrating public records and credit depth differently than FICO models. Both scoring systems utilize credit report data but weigh factors uniquely, impacting how lenders assess risk and eligibility.
Score Ranges: FICO Score vs VantageScore
FICO scores typically range from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating better creditworthiness, while VantageScore also spans from 300 to 850 but uses slightly different criteria to calculate the score. Both models categorize scores into segments such as poor, fair, good, and excellent, although the thresholds for these categories may differ, impacting credit decisions. Understanding the score ranges and their interpretations is vital for consumers seeking to improve their credit health and for lenders assessing risk.
Which Lenders Use FICO or VantageScore?
Most lenders use FICO scores when making credit decisions, as it remains the industry standard for mortgage, auto, and personal loans. VantageScore is increasingly accepted by some credit card issuers and newer fintech lenders due to its broader range of credit data and faster model updates. Understanding which scoring model a specific lender prefers can impact your loan approval chances and terms.
Impact of VantageScore and FICO on Loan Approval
FICO scores remain the dominant factor in loan approvals, with lenders relying heavily on its predictive analytics to assess credit risk and determine interest rates. VantageScore, gaining traction for its inclusive data usage and more frequent updates, increasingly influences loan decisions, especially for consumers with limited credit history. Both scoring models impact approval outcomes, but FICO's long-standing presence and lender preference often carry greater weight in underwriting processes.
How to Check Your FICO and VantageScore
To check your FICO and VantageScore credit scores, access the official websites of the major credit bureaus--Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax--or use authorized third-party platforms like myFICO and Credit Karma. Both FICO and VantageScore provide regular score updates, with FICO scores often available through lenders or paid services, while VantageScore is frequently offered for free by many credit monitoring websites. Regularly monitoring these scores helps identify errors and track improvements that impact loan approvals and interest rates.
Improving Your Credit: FICO vs VantageScore Tips
Improving your credit requires understanding the key differences between FICO and VantageScore models, as FICO emphasizes payment history and credit utilization, while VantageScore incorporates trends and recent credit behavior more heavily. To boost your FICO score, focus on timely payments, reducing credit card balances below 30%, and maintaining a long credit history. For VantageScore improvement, frequent low credit utilization and showing recent positive credit activity, such as new credit inquiries managed responsibly, can make a significant impact.
Common Myths About FICO and VantageScore
Common myths about FICO and VantageScore include the misconception that they use identical scoring models, when in reality each employs distinct algorithms and credit data considerations. Many believe that one score is universally accepted over the other, but lenders vary in their preference depending on business policies and credit types. Another widespread myth is that scores from both models are directly comparable, despite differences in range, emphasis on payment history, and treatment of credit inquiries.
Important Terms
Credit Scoring Models
FICO Score utilizes proprietary analytics based on payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, new credit, and credit mix to determine credit risk, influencing over 90% of lending decisions in the United States. VantageScore, developed collaboratively by the three major credit bureaus, employs a similar scoring range but incorporates alternative data such as trended credit usage and recent credit behavior, aiming for broader consumer inclusion, especially for thin-file borrowers.
Risk Assessment Algorithms
Risk assessment algorithms evaluate creditworthiness using distinct models like FICO Score and VantageScore, where FICO relies heavily on payment history and credit utilization, while VantageScore incorporates trended data and considers credit behavior across multiple bureaus. FICO scores range from 300 to 850 and are widely used by lenders, whereas VantageScore also spans 300 to 850 but provides faster score updates and better performance for consumers with limited credit history.
Credit Utilization Ratio
Credit utilization ratio critically impacts both FICO and VantageScore credit scoring models, with the ideal utilization rate being below 30% to maintain a strong credit profile. While FICO places significant emphasis on utilization as a major factor, VantageScore also considers it essential but integrates additional data points like recent credit behavior for a more dynamic scoring approach.
Payment History Analysis
Payment history analysis significantly impacts both FICO Score and VantageScore models, as timely payments can improve creditworthiness while late payments lower scores. FICO places heavier emphasis on payment history, accounting for approximately 35% of the score, whereas VantageScore also considers recent payment behavior but integrates additional factors like credit utilization and age more flexibly.
Score Range Discrepancies
Score range discrepancies between FICO Score and VantageScore arise because FICO scores typically range from 300 to 850, whereas VantageScore uses the same 300 to 850 scale but calculates scores differently, leading to variations in borrower credit assessment. These differences impact credit risk evaluation as lenders may interpret creditworthiness distinctly based on the scoring model applied.
Data Furnishers
Data furnishers such as banks, credit card companies, and lenders play a crucial role in reporting accurate and timely credit information that impacts both FICO Score and VantageScore models. While FICO Score relies heavily on payment history and credit utilization data furnished by these entities, VantageScore incorporates similar data but utilizes a slightly different scoring algorithm that can lead to variations in credit assessments for the same consumer information.
Scoring Criteria Weighting
Scoring criteria weighting differs between FICO Score and VantageScore models, with FICO placing approximately 35% emphasis on payment history and 30% on amounts owed, while VantageScore assigns similar but slightly varied weights, prioritizing credit utilization and recent credit behavior. Both models integrate factors like length of credit history and new credit inquiries but differ in their scoring algorithms and factor emphasis, impacting credit risk assessments and borrower profiles.
Tri-bureau Reporting
Tri-bureau reporting integrates credit data from Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax, providing a comprehensive view of consumer credit used by both FICO and VantageScore models. While FICO scores tend to prioritize payment history and credit utilization, VantageScore incorporates trended credit data and weighs recent credit behavior more heavily, resulting in slight variations in scores from identical tri-bureau reports.
Hard Inquiry Impact
Hard inquiries typically lower FICO scores by 5-10 points and remain on credit reports for up to two years, influencing credit risk assessment more heavily than VantageScore models, which generally treat multiple inquiries occurring within a short period as a single inquiry to reduce impact. FICO scores emphasize the frequency and recency of hard inquiries in credit scoring, while VantageScore incorporates them more flexibly to better reflect consumer credit behavior.
Alternative Lending Scores
Alternative lending scores incorporate non-traditional data sources such as utility payments and rental history to assess creditworthiness, offering a more inclusive evaluation compared to traditional FICO and VantageScore models. Both FICO and VantageScore emphasize credit card usage and payment history but differ in weighting criteria, with VantageScore leveraging trended data to predict future behavior more dynamically.
FICO score vs VantageScore Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com