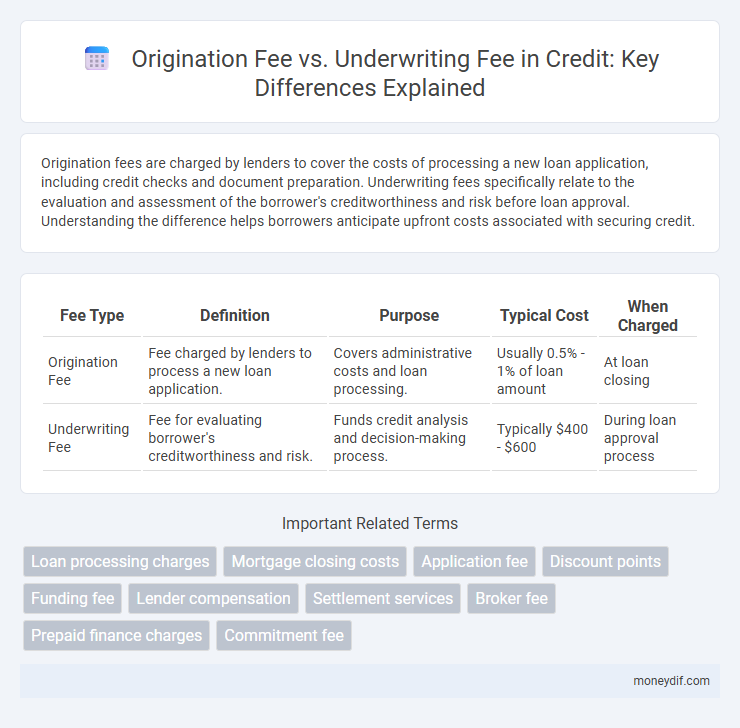
Origination fees are charged by lenders to cover the costs of processing a new loan application, including credit checks and document preparation. Underwriting fees specifically relate to the evaluation and assessment of the borrower's creditworthiness and risk before loan approval. Understanding the difference helps borrowers anticipate upfront costs associated with securing credit.
Table of Comparison
| Fee Type | Definition | Purpose | Typical Cost | When Charged |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origination Fee | Fee charged by lenders to process a new loan application. | Covers administrative costs and loan processing. | Usually 0.5% - 1% of loan amount | At loan closing |
| Underwriting Fee | Fee for evaluating borrower's creditworthiness and risk. | Funds credit analysis and decision-making process. | Typically $400 - $600 | During loan approval process |
Understanding Origination Fees in Credit Transactions
Origination fees in credit transactions represent a one-time charge by lenders for processing and evaluating a loan application, typically calculated as a percentage of the total loan amount. Unlike underwriting fees, which specifically cover the risk assessment and verification of borrower information, origination fees encompass a broader scope including administrative costs. Understanding these fees helps borrowers accurately anticipate upfront expenses and compare loan offers effectively.
What Are Underwriting Fees?
Underwriting fees are charges lenders impose to cover the cost of evaluating a borrower's creditworthiness and the risk associated with approving a loan. These fees differ from origination fees, which are charged for processing and initiating the loan application. Accurate underwriting ensures the lender assesses financial documents, credit history, and debt-to-income ratios, directly impacting loan approval and terms.
Key Differences: Origination Fee vs Underwriting Fee
Origination fees are charged by lenders to cover the costs of processing a new loan application, typically calculated as a percentage of the loan amount. Underwriting fees, on the other hand, specifically compensate the underwriter for assessing the borrower's creditworthiness and risk profile. The key difference lies in their purpose: origination fees encompass overall loan processing expenses while underwriting fees focus on credit evaluation and risk analysis.
Why Lenders Charge Origination Fees
Lenders charge origination fees to cover the administrative costs involved in processing and approving a loan application, including credit checks, document verification, and loan preparation. This fee compensates lenders for the resources and time spent evaluating borrower risk and ensuring compliance with lending criteria. Unlike underwriting fees that focus on risk assessment, origination fees primarily offset operational expenses, making them essential for maintaining efficient loan services.
The Role of Underwriting Fees in Loan Processing
Underwriting fees play a crucial role in loan processing by covering the costs associated with evaluating a borrower's creditworthiness and assessing risk. These fees compensate lenders for the detailed analysis, verification of income, employment, and credit history necessary to approve or deny a loan. Unlike origination fees, which are charged for loan creation and processing, underwriting fees specifically address the risk assessment and decision-making process in credit approval.
How Origination and Underwriting Fees Affect Borrowers
Origination fees and underwriting fees both impact the total cost of borrowing, with origination fees covering loan processing and underwriting fees relating to risk assessment and approval. Borrowers often face higher upfront expenses due to origination fees, which are typically a percentage of the loan amount, while underwriting fees can add to the overall charges depending on lender policies. Understanding these fees is crucial for borrowers to accurately compare loan offers and manage the financial burden of their credit agreements.
Origination and Underwriting Fees: What’s Included?
Origination fees typically cover the lender's costs for processing a new loan application, including credit checks, document preparation, and administrative expenses. Underwriting fees specifically relate to the evaluation of creditworthiness, income verification, and risk assessment conducted by the underwriter to approve the loan. Both fees are crucial components of the loan closing costs but target different stages and aspects of the credit approval process.
Which Fee Is Higher: Origination or Underwriting?
Origination fees are typically higher than underwriting fees because they cover the lender's costs for processing and initiating a loan, often ranging from 0.5% to 1% of the loan amount. Underwriting fees, which compensate lenders for assessing the creditworthiness and risk of the borrower, usually fall between $400 and $600. Borrowers should compare both fees as part of the total loan costs to understand the overall expense associated with credit origination.
Tips to Minimize Origination and Underwriting Fees
To minimize origination and underwriting fees, borrowers should shop around and compare loan offers from multiple lenders, as fees can vary significantly. Improving credit scores and providing complete, accurate documentation upfront can reduce lender risk assessments, leading to lower fees. Negotiating fees directly with lenders and opting for loans with discounted or waived fees based on promotional offers can also decrease overall borrowing costs.
Choosing the Best Loan: Considering All Fees
When choosing the best loan, it is crucial to compare the origination fee and underwriting fee, as both impact the overall cost. Origination fees, typically 0.5% to 1% of the loan amount, cover administrative expenses, while underwriting fees compensate for the lender's risk assessment. Evaluating these fees alongside interest rates and loan terms ensures a comprehensive understanding of the loan's true cost.
Important Terms
Loan processing charges
Loan processing charges commonly include origination fees, which cover the lender's administrative costs for evaluating and preparing the loan, and underwriting fees, which specifically compensate the underwriter for assessing the borrower's creditworthiness and risk. Differentiating these fees helps borrowers understand the cost breakdown and ensures transparency in the overall loan expense structure.
Mortgage closing costs
Mortgage closing costs typically include both origination fees and underwriting fees, where the origination fee covers the lender's expenses for processing the loan application, often ranging from 0.5% to 1% of the loan amount. The underwriting fee compensates for the evaluation of the borrower's creditworthiness and risk assessment, usually a smaller, fixed amount within the total closing costs.
Application fee
Application fees cover the initial processing costs of a loan request, while origination fees specifically compensate the lender for evaluating and preparing the loan. Underwriting fees focus on the risk assessment and verification of borrower information to determine loan eligibility.
Discount points
Discount points are prepaid fees that borrowers pay to lower their mortgage interest rate, directly impacting the loan's overall cost and monthly payments. Unlike the underwriting fee, which covers the lender's cost of evaluating and approving the loan application, discount points are primarily financial tools used to reduce interest rates rather than administrative expenses.
Funding fee
The funding fee, often associated with loan origination, covers the lender's costs for processing and funding a mortgage, whereas the underwriting fee specifically pays for the evaluation and risk assessment of the borrower's creditworthiness and loan eligibility. Both fees are common in mortgage transactions but differ in purpose, with the origination fee addressing loan creation and the underwriting fee focusing on loan approval criteria.
Lender compensation
Lender compensation primarily consists of origination fees, charged for processing loan applications, while underwriting fees cover the evaluation of borrower creditworthiness and risk assessment. Origination fees are typically calculated as a percentage of the loan amount, whereas underwriting fees are often fixed or variable based on loan complexity.
Settlement services
Settlement services encompass a range of processes involved in finalizing a real estate transaction, where origination fees represent charges by lenders for processing new loan applications, and underwriting fees cover the cost of evaluating the borrower's creditworthiness and loan risk. Differentiating between origination fees and underwriting fees is crucial for understanding the specific costs associated with loan approval and closing procedures in real estate settlements.
Broker fee
Broker fees typically cover the origination fee, which is charged for processing and initiating a loan application, while underwriting fees are distinct charges assessed for evaluating the risk and creditworthiness of the borrower during loan approval. Origination fees are usually a percentage of the loan amount, whereas underwriting fees are fixed or variable costs related to risk assessment and documentation verification.
Prepaid finance charges
Prepaid finance charges often include origination fees charged by lenders for processing a new loan application, which are typically disclosed upfront and added to the loan balance. Underwriting fees, however, represent the cost of evaluating the borrower's creditworthiness and risk assessment, and may be either prepaid or included in the lender's overall fees without being classified as prepaid finance charges.
Commitment fee
A commitment fee is a charge paid by a borrower to a lender for reserving funds, distinct from an origination fee that covers the cost of processing a loan application and establishing the loan. Unlike an underwriting fee, which compensates the lender for evaluating and assuming the risk of the loan, the commitment fee ensures the lender's promised funds remain available during the loan approval period.
origination fee vs underwriting fee Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com