Bankruptcy remote structures isolate assets to protect them from the bankruptcy of the originator, ensuring asset-backed securities remain unaffected by the originator's financial distress. Insolvency remote entities are designed to minimize the risk of insolvency by imposing strict operational and financial controls, thereby safeguarding cash flows and asset integrity. Understanding the distinction is crucial for investors seeking to mitigate credit risk in structured finance transactions.
Table of Comparison
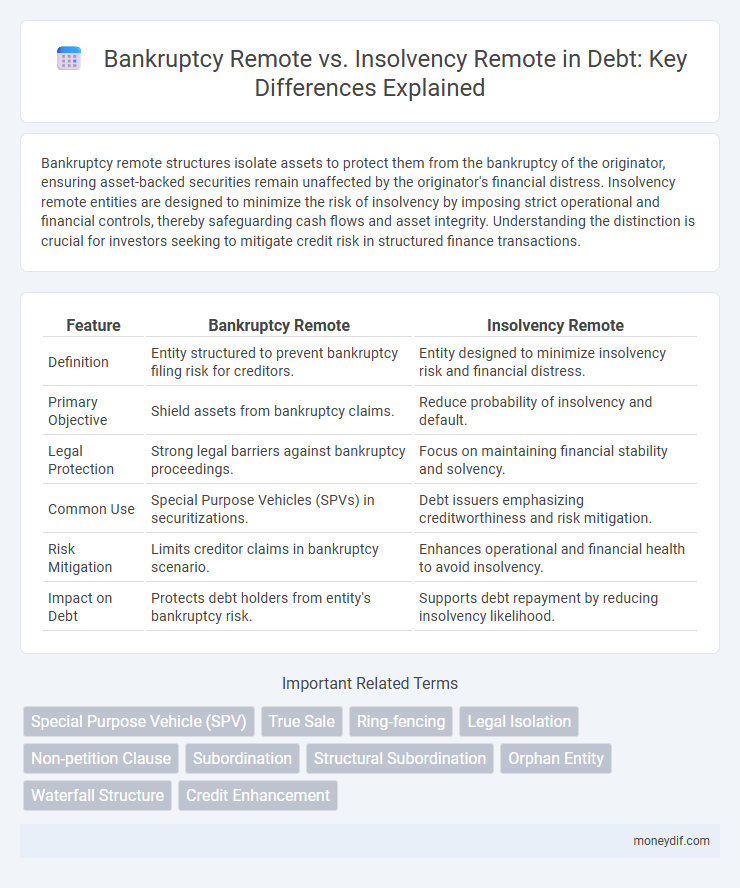
| Feature | Bankruptcy Remote | Insolvency Remote |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Entity structured to prevent bankruptcy filing risk for creditors. | Entity designed to minimize insolvency risk and financial distress. |
| Primary Objective | Shield assets from bankruptcy claims. | Reduce probability of insolvency and default. |
| Legal Protection | Strong legal barriers against bankruptcy proceedings. | Focus on maintaining financial stability and solvency. |
| Common Use | Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) in securitizations. | Debt issuers emphasizing creditworthiness and risk mitigation. |
| Risk Mitigation | Limits creditor claims in bankruptcy scenario. | Enhances operational and financial health to avoid insolvency. |
| Impact on Debt | Protects debt holders from entity's bankruptcy risk. | Supports debt repayment by reducing insolvency likelihood. |
Introduction to Bankruptcy Remote and Insolvency Remote Structures
Bankruptcy remote and insolvency remote structures are designed to protect assets from the financial risks and liabilities of affiliated entities by isolating them from claims in the event of default or bankruptcy. Bankruptcy remote structures ensure the entity holding assets is legally separated, making it less likely to be forced into bankruptcy due to parent company distress. Insolvency remote structures emphasize financial and operational independence to prevent insolvency by maintaining stringent restrictions on debt, cash flow, and ownership transfer.
Defining Bankruptcy Remoteness
Bankruptcy remoteness refers to a legal and structural framework designed to isolate an entity's assets from the risk of bankruptcy, ensuring creditor claims do not extend to those assets. Unlike insolvency remoteness, which primarily addresses the entity's financial stability and inability to pay debts, bankruptcy remoteness focuses on protecting assets through specific legal provisions such as true sale transfers and non-consolidation opinions. This structure enhances investor confidence by minimizing bankruptcy risk in securitizations and special purpose vehicles (SPVs).
Understanding Insolvency Remoteness
Insolvency remoteness ensures a special purpose entity (SPE) is structurally insulated from bankruptcy risks by legally separating its assets and liabilities from the parent company, minimizing the chance of creditor claims during financial distress. Unlike bankruptcy remote structures which emphasize protection from bankruptcy proceedings, insolvency remoteness specifically targets the SPE's financial independence and operational stability to prevent triggering insolvency events. Key legal mechanisms include non-consolidation opinions, asset segregation, and restrictions on SPE activities to maintain this financial isolation.
Key Differences Between Bankruptcy Remote and Insolvency Remote
Bankruptcy Remote entities are structured to isolate assets and liabilities to minimize the risk of being included in a bankruptcy filing, often used in securitization to protect investors. Insolvency Remote entities focus on maintaining financial and operational autonomy to prevent insolvency, ensuring obligations can be met without triggering default or liquidation. The key difference lies in bankruptcy remoteness targeting legal protection against bankruptcy proceedings, while insolvency remoteness emphasizes financial health and independence to avoid insolvency events.
Importance in Structured Finance and Securitization
Bankruptcy Remote structures isolate assets from the originator's bankruptcy risks, ensuring investor protection and enhancing credit ratings in securitization transactions. Insolvency Remote entities are designed to minimize insolvency risk by restricting access to the entity's assets and operational decisions, maintaining financial stability critical for structured finance. These mechanisms are vital for mitigating counterparty risk, preserving asset integrity, and attracting investment in structured finance and securitization markets.
Legal Frameworks Governing Bankruptcy Remote Entities
Bankruptcy remote entities are structured to isolate assets from the parent company's financial risks, ensuring creditors have limited claims in the event of bankruptcy under laws such as the U.S. Bankruptcy Code Section 101(9). Legal frameworks mandate strict separateness, independent governance, and restrictions on activities to maintain the entity's bankruptcy-remote status, reducing the risk of consolidation or substantive consolidation during insolvency proceedings. Insolvency remote structures, while similar, focus more on preventing financial distress through covenants and operational constraints rather than relying solely on legal separateness to shield assets.
Insolvency Remote Entities: Protections and Limitations
Insolvency remote entities are structured to minimize financial distress risks by isolating assets and liabilities, protecting stakeholders from insolvency-related claims. These entities typically have legal safeguards such as non-consolidation clauses, restricted transfers, and operational covenants to maintain separation from parent company bankruptcy risks. However, insolvency remote status does not guarantee immunity from bankruptcy if the entity itself faces financial failure or if courts pierce the corporate veil.
Common Use Cases in Debt Markets
Bankruptcy remote structures are commonly used in asset-backed securities and project finance to isolate assets from the originator's creditors, reducing bankruptcy risk and enhancing investor confidence. Insolvency remote entities are often employed in structured finance and securitization to ensure that the entity remains solvent and operational, preventing insolvency proceedings that could disrupt cash flows. Both structures are critical in debt markets for mitigating counterparty risk and facilitating access to capital at favorable terms.
Risks and Challenges Associated with Each Structure
Bankruptcy remote structures minimize the risk of the sponsor's bankruptcy affecting the project by isolating assets, but they face challenges such as complex legal frameworks and higher transaction costs. Insolvency remote structures focus on protecting assets from the insolvency of specific parties, yet they encounter risks related to enforcement uncertainty and limited creditor access. Both structures must carefully balance asset protection with operational flexibility to mitigate risks of default and maximize recoverability.
Best Practices for Structuring Bankruptcy and Insolvency Remote Vehicles
Structuring bankruptcy remote vehicles involves isolating assets and liabilities to protect investors by legally separating the entity from the parent company's financial risks. Insolvency remote structures focus on maintaining operational independence and liquidity thresholds to reduce the likelihood of insolvency, often through covenants and control mechanisms. Best practices include the use of non-consolidation opinions, third-party guarantees, and strict governance protocols to enhance creditworthiness and minimize cross-default risks.
Important Terms
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)
A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) structured as bankruptcy remote ensures legal separation from the parent company's financial distress, preventing the SPV's assets from being included in the parent's bankruptcy estate. Insolvency remote focuses on operational independence and contractual arrangements to minimize the risk of the SPV becoming insolvent, thereby protecting investors and creditors from the originating entity's insolvency risks.
True Sale
True Sale ensures asset transfers are bankruptcy remote by legally isolating assets from the seller's liabilities, whereas insolvency remote refers to structures minimizing insolvency risk but may not fully isolate assets from the seller's creditors.
Ring-fencing
Ring-fencing ensures asset protection by creating Bankruptcy Remote entities shielded from parent company bankruptcy risks, while Insolvency Remote structures minimize the chance of entity insolvency through contractual restrictions and governance controls.
Legal Isolation
Legal isolation ensures bankruptcy remote entities are structurally separated from parent company liabilities, whereas insolvency remote structures focus on maintaining solvency through operational and financial safeguards.
Non-petition Clause
A Non-petition Clause prevents parties from filing bankruptcy against each other, crucial for maintaining Bankruptcy Remote status by limiting insolvency risk, which differs from Insolvency Remote structures that focus on safeguarding assets from creditors without prohibiting bankruptcy filings.
Subordination
Subordination in bankruptcy remote structures prioritizes creditor claims to isolate asset risks, contrasting with insolvency remote frameworks that focus on legal separation to prevent entity insolvency implications.
Structural Subordination
Structural subordination occurs when debt is secured by assets of a subsidiary, ranking senior to the parent company's obligations, affecting bankruptcy remote structures by isolating creditor claims within separate legal entities to minimize risk exposure. Insolvency remote entities are specifically designed to remain operational and solvent under financial distress, enhancing creditor protection by restricting subsidiaries' ability to incur debt that could jeopardize the parent company's financial stability.
Orphan Entity
An orphan entity is a bankruptcy remote structure designed to isolate liabilities by ensuring the entity has no direct ownership links to the parent company, enhancing insolvency remote characteristics for asset protection.
Waterfall Structure
Waterfall structure prioritizes the order of payment distributions in bankruptcy remote entities to protect investors, while insolvency remote structures focus on preventing the entity's insolvency through legal and operational safeguards.
Credit Enhancement
Credit enhancement mechanisms improve the creditworthiness of financial instruments by reducing risk exposure through structural features like bankruptcy remote and insolvency remote entities. Bankruptcy remote structures isolate assets from the parent company's insolvency proceedings, while insolvency remote designs ensure operational continuity and asset protection even during financial distress, enhancing investor confidence and debt recovery prospects.
Bankruptcy Remote vs Insolvency Remote Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com