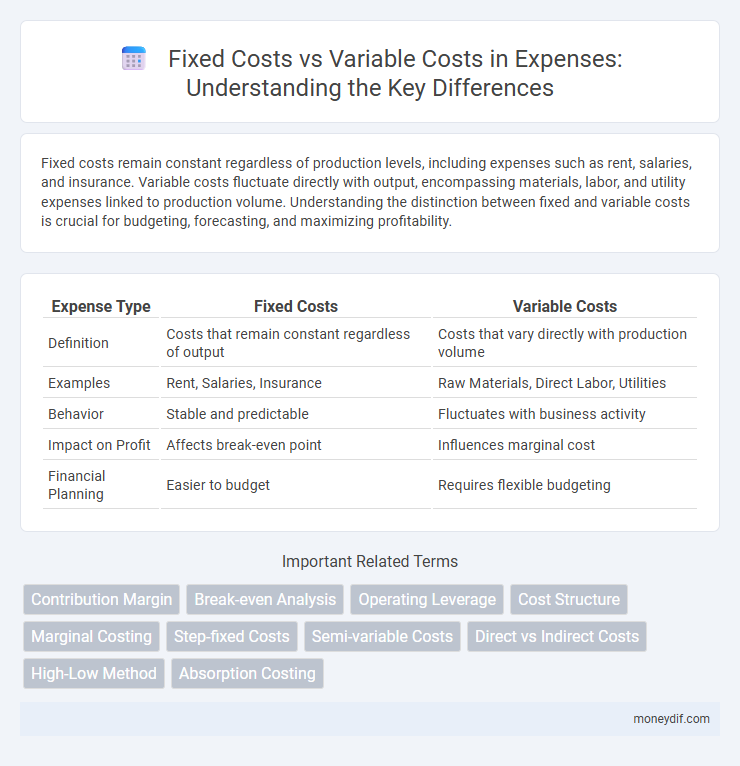
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production levels, including expenses such as rent, salaries, and insurance. Variable costs fluctuate directly with output, encompassing materials, labor, and utility expenses linked to production volume. Understanding the distinction between fixed and variable costs is crucial for budgeting, forecasting, and maximizing profitability.
Table of Comparison
| Expense Type | Fixed Costs | Variable Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Costs that remain constant regardless of output | Costs that vary directly with production volume |
| Examples | Rent, Salaries, Insurance | Raw Materials, Direct Labor, Utilities |
| Behavior | Stable and predictable | Fluctuates with business activity |
| Impact on Profit | Affects break-even point | Influences marginal cost |
| Financial Planning | Easier to budget | Requires flexible budgeting |
Understanding Fixed Costs: Definition and Examples
Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant regardless of production levels, such as rent, salaries, and insurance premiums. These costs do not fluctuate with business activity, making them predictable and essential for budgeting and financial planning. Understanding fixed costs helps businesses determine their break-even point and manage long-term financial stability effectively.
What are Variable Costs? Key Characteristics
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume or sales activity, such as raw materials, direct labor, and utility expenses tied to manufacturing. These costs increase as output rises and decrease when production slows, making them highly sensitive to business activity levels. Key characteristics include their proportional behavior to production changes, short-term variability, and direct impact on profit margins.
Fixed Costs vs Variable Costs: Core Differences
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production levels, including expenses like rent, salaries, and insurance, while variable costs fluctuate with output volume, such as raw materials and direct labor. Understanding the core differences between fixed and variable costs is essential for budgeting, forecasting, and decision-making in business finance. Effective cost management hinges on accurately distinguishing these expenses to optimize profitability and operational efficiency.
Impact of Fixed and Variable Costs on Budgeting
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production levels, providing predictability and stability in budgeting, which simplifies long-term financial planning. Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume, requiring dynamic adjustments in budgeting to accommodate changes in operational activity. Effective budgeting balances fixed cost commitments with variable cost flexibility to optimize cost control and profit margins.
How to Identify Fixed and Variable Expenses
Fixed expenses remain constant regardless of production volume, such as rent, salaries, and insurance premiums, making them easier to identify through consistent, recurring payments. Variable expenses fluctuate with operational activity levels, including costs like raw materials, direct labor, and utilities tied to production output, often tracked by analyzing their correlation with sales or production data. Distinguishing these costs involves reviewing financial statements and expense patterns to classify costs that vary directly with business activity versus those that do not.
The Role of Costs in Break-Even Analysis
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production volume, while variable costs fluctuate directly with output levels. In break-even analysis, understanding the distinction between these costs is crucial for determining the sales volume needed to cover total expenses and achieve profitability. Accurately categorizing fixed and variable costs enables businesses to set pricing strategies and forecast financial performance effectively.
Managing Fixed Costs for Financial Stability
Managing fixed costs, such as rent, salaries, and insurance, is crucial for maintaining financial stability in any business. These expenses remain constant regardless of production levels, making it essential to optimize and reduce them where possible to improve cash flow and profitability. Strategic negotiation of long-term contracts and periodic review of fixed cost components can help businesses sustain financial resilience during market fluctuations.
Strategies to Control Variable Costs
Controlling variable costs involves implementing effective strategies such as negotiating supplier contracts to secure better rates, optimizing production processes to reduce waste, and closely monitoring consumption patterns for timely adjustments. Utilizing technology like inventory management software enhances real-time tracking and demand forecasting, which minimizes overstocking and stockouts. Empowering employees through training and performance incentives encourages cost-conscious behaviors that directly impact variable expenses.
Real-World Examples: Fixed vs Variable Costs in Business
Rent for office space and salaried employee wages are prime examples of fixed costs, remaining constant regardless of production volume. In contrast, raw materials and hourly labor costs fluctuate directly with the level of business activity, representing variable costs. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses forecast expenses and optimize budgeting strategies effectively.
Choosing the Right Cost Structure for Your Organization
Choosing the right cost structure is crucial for optimizing financial performance and maintaining profitability in any organization. Fixed costs, such as rent and salaries, provide stability and predictability, while variable costs like raw materials and hourly wages allow for greater flexibility in response to production levels. Analyzing business goals and industry conditions helps determine the ideal balance between fixed and variable expenses to enhance operational efficiency and support scalable growth.
Important Terms
Contribution Margin
Contribution Margin represents the revenue remaining after deducting Variable Costs, which contributes directly to covering Fixed Costs and generating profit.
Break-even Analysis
Break-even analysis determines the sales volume at which total revenues equal total costs, distinguishing between fixed costs--expenses that remain constant regardless of production levels--and variable costs, which fluctuate directly with output. Understanding this relationship helps businesses set pricing strategies and control cost structures to achieve profitability.
Operating Leverage
Operating leverage measures the impact of fixed costs on a company's earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by amplifying profit changes relative to sales fluctuations compared to variable costs.
Cost Structure
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production volume, while variable costs fluctuate directly with the level of output, defining the overall cost structure and impacting profit margins.
Marginal Costing
Marginal costing focuses on variable costs per unit to determine product profitability while treating fixed costs as period expenses that do not vary with production volume.
Step-fixed Costs
Step-fixed costs remain constant within specific activity ranges but increase in fixed increments once those ranges are exceeded, distinguishing them from fixed costs that remain constant regardless of activity level and variable costs that change proportionally with activity.
Semi-variable Costs
Semi-variable costs combine fixed costs that remain constant regardless of output and variable costs that fluctuate directly with production levels.
Direct vs Indirect Costs
Direct costs typically align with variable costs as they fluctuate with production levels, while indirect costs often correspond to fixed costs, remaining constant regardless of output.
High-Low Method
The High-Low Method estimates fixed and variable costs by analyzing the highest and lowest activity levels and their total costs to determine the variable cost per unit and total fixed costs. This approach separates mixed costs into fixed costs, which remain constant regardless of activity, and variable costs, which fluctuate directly with production volume.
Absorption Costing
Absorption costing allocates both fixed and variable manufacturing costs to product units, ensuring fixed overhead costs are included in inventory valuation.
Fixed costs vs Variable costs Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com