A basis point represents one hundredth of a percentage point (0.01%) and is commonly used to measure changes in interest rates or bond yields. A pip, short for "percentage in point," is the smallest price movement in currency pairs in forex trading, typically equal to 0.0001. Understanding the difference between basis points and pips is crucial for accurately interpreting fluctuations in financial markets and managing risk effectively.
Table of Comparison
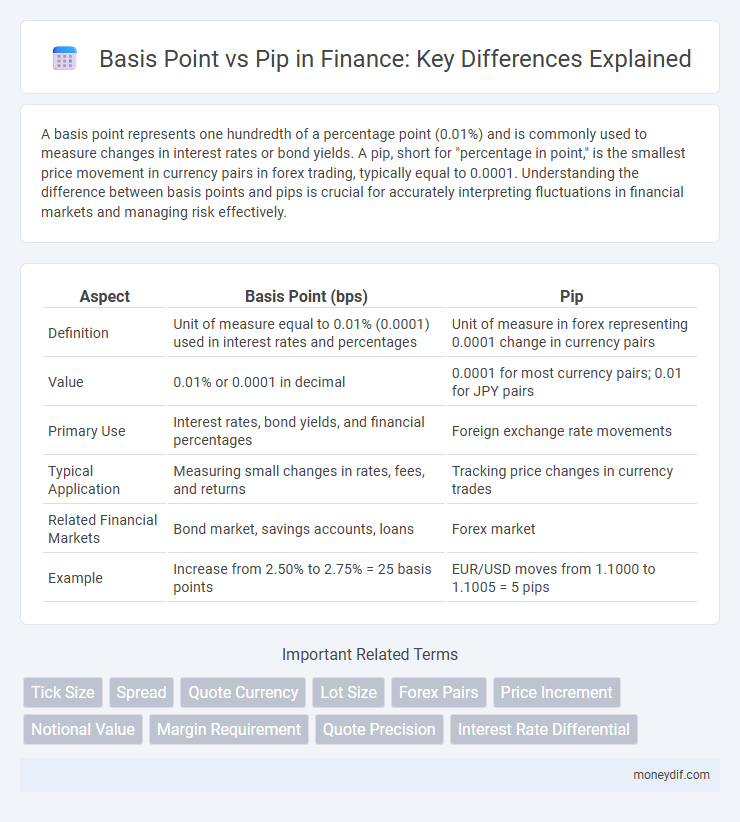
| Aspect | Basis Point (bps) | Pip |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unit of measure equal to 0.01% (0.0001) used in interest rates and percentages | Unit of measure in forex representing 0.0001 change in currency pairs |
| Value | 0.01% or 0.0001 in decimal | 0.0001 for most currency pairs; 0.01 for JPY pairs |
| Primary Use | Interest rates, bond yields, and financial percentages | Foreign exchange rate movements |
| Typical Application | Measuring small changes in rates, fees, and returns | Tracking price changes in currency trades |
| Related Financial Markets | Bond market, savings accounts, loans | Forex market |
| Example | Increase from 2.50% to 2.75% = 25 basis points | EUR/USD moves from 1.1000 to 1.1005 = 5 pips |
Understanding Basis Points: Definition and Importance
A basis point is a unit of measurement equal to 0.01% used to describe changes in interest rates, bond yields, and other financial percentages. It simplifies the communication of small fluctuations in financial metrics, preventing ambiguity in percentage change discussions. Understanding basis points is crucial for investors and financial analysts to accurately assess market movements, pricing, and risk evaluation.
What is a Pip? Key Concepts Explained
A pip, short for "percentage in point," measures the smallest price movement in forex trading, typically equal to 0.0001 for currency pairs like EUR/USD. It represents the unit used to express changes in exchange rates, allowing traders to quantify gains or losses accurately. Understanding pips is essential for calculating profit, risk management, and comparing currency pair movements in the foreign exchange market.
Basis Points vs Pips: Main Differences
Basis points measure interest rate changes or yield differences, where one basis point equals 0.01%, commonly used in bond markets and fixed income analysis. Pips quantify price movement in currency pairs in Forex trading, representing the smallest price increment, typically 0.0001 for most pairs. The key difference lies in application: basis points express rate changes in percentage terms, while pips denote discrete price fluctuations in currency trading.
How Basis Points Influence Interest Rates
Basis points represent the smallest unit of measure for interest rate changes, where one basis point equals 0.01%. Interest rates often move in basis points to indicate precise shifts in borrowing costs, affecting loan repayments, bond yields, and mortgage rates. Unlike pips, which primarily track currency price movements in forex trading, basis points directly influence financial instruments tied to interest rates and fixed-income markets.
The Role of Pips in Forex Trading
Pips play a crucial role in forex trading as the standard unit for measuring price movements, typically representing the smallest change a currency pair can make. Unlike basis points, which are primarily used to express interest rate changes or bond yields, pips quantify fluctuations in exchange rates, often valued at 0.0001 for most currency pairs. Accurate pip measurement enables traders to calculate profits, losses, and risks effectively, ensuring precise execution of trading strategies in the volatile forex market.
Calculating Changes Using Basis Points
Calculating changes using basis points is crucial in finance for expressing percentage changes with precision, especially in interest rates and bond yields. One basis point equals 0.01%, so a movement from 2.00% to 2.25% corresponds to a 25 basis point increase. Unlike pips, commonly used in forex trading to represent currency price changes, basis points provide a standardized way to quantify small but significant fluctuations in financial metrics.
Pip Value Calculation Across Currency Pairs
Pip value calculation varies significantly across currency pairs due to differing lot sizes and exchange rates, essential for precise risk management in forex trading. For major currency pairs with the USD as the quote currency, a standard pip usually equals a $10 value per standard lot, while cross-currency pairs require conversion to the trader's account currency to determine pip value accurately. Understanding pip value's impact on profit and loss enables forex traders to implement effective position sizing and hedge strategies across diverse currency markets.
Practical Examples: Basis Point vs Pip in Action
A basis point represents a 0.01% change in interest rates, commonly used to measure yield differences in bonds, such as a 25 basis point increase indicating a 0.25% rise in rates. A pip, used primarily in forex trading, stands for the smallest price move in currency pairs, typically 0.0001 for major pairs like EUR/USD, meaning a 50-pip gain translates to a $500 profit on a standard $100,000 position. Understanding basis points and pips through practical examples aids traders and investors in accurately assessing market movements and managing risk.
Why Investors Should Understand Both Metrics
Understanding both basis points and pips is crucial for investors to accurately evaluate financial instruments across different markets. Basis points measure interest rate changes and bond yields, providing clarity in fixed-income investments, while pips quantify price movements in forex trading, enabling precise risk management. Mastery of these metrics enhances decision-making, portfolio diversification, and effective performance tracking in global financial markets.
Choosing the Right Metric for Financial Analysis
Basis points measure changes in interest rates or yields, where one basis point equals 0.01%, making them ideal for fixed income and bond market analysis. Pips track price movements in forex trading, representing the smallest price increment, typically 0.0001 for most currency pairs, essential for currency traders assessing market volatility. Selecting the appropriate metric depends on the asset class and financial instrument, ensuring precise measurement and effective decision-making in portfolio management or risk assessment.
Important Terms
Tick Size
Tick size represents the minimum price movement of a trading instrument, often measured in basis points or pips depending on the market, with basis points typically used for bonds and interest rates, while pips are common in forex trading.
Spread
Spread represents the difference between the bid and ask prices, often measured in pips, while basis points quantify spread changes as 0.01% increments in financial metrics.
Quote Currency
Quote currency in forex trading determines the value of a pip and its impact measured in basis points, influencing precise profit and loss calculations.
Lot Size
A lot size of 100,000 units in forex trading equates a one pip movement to a 10 basis point change in the currency pair's value.
Forex Pairs
In Forex trading, a pip represents the smallest price move in currency pairs, typically 0.0001, while a basis point measures interest rate changes, equal to 0.01%, both crucial for accurate market analysis.
Price Increment
A price increment in financial markets is measured in basis points for interest rates and in pips for currency pairs, where one basis point equals 0.01% and one pip represents the smallest price move in forex trading, typically 0.0001 for most currency pairs.
Notional Value
Notional value represents the total value of a leveraged position and is crucial for calculating profit or loss expressed in basis points or pips in forex trading.
Margin Requirement
Margin requirement quantifies the collateral needed to open a trading position, where a basis point equals 0.01% price movement and a pip typically represents a 0.0001 price change in forex markets.
Quote Precision
Quote precision determines how accurately financial instruments are priced, with basis points measuring interest rate changes and pips quantifying forex price fluctuations at standardized decimal places.
Interest Rate Differential
Interest Rate Differential influences currency trading by affecting Basis Points, where one Basis Point equals 0.01%, and Pips measure currency price changes, with one Pip typically representing 0.0001 in most currency pairs.
Basis Point vs Pip Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com