Drag-along rights compel minority shareholders to join the sale of a company proposed by majority shareholders, ensuring a smooth and unified exit. Tag-along rights protect minority investors by allowing them to sell their shares alongside majority shareholders, preventing them from being left behind in unfavorable situations. Understanding the balance between drag-along and tag-along provisions is crucial for negotiating shareholder agreements and safeguarding investment interests.
Table of Comparison
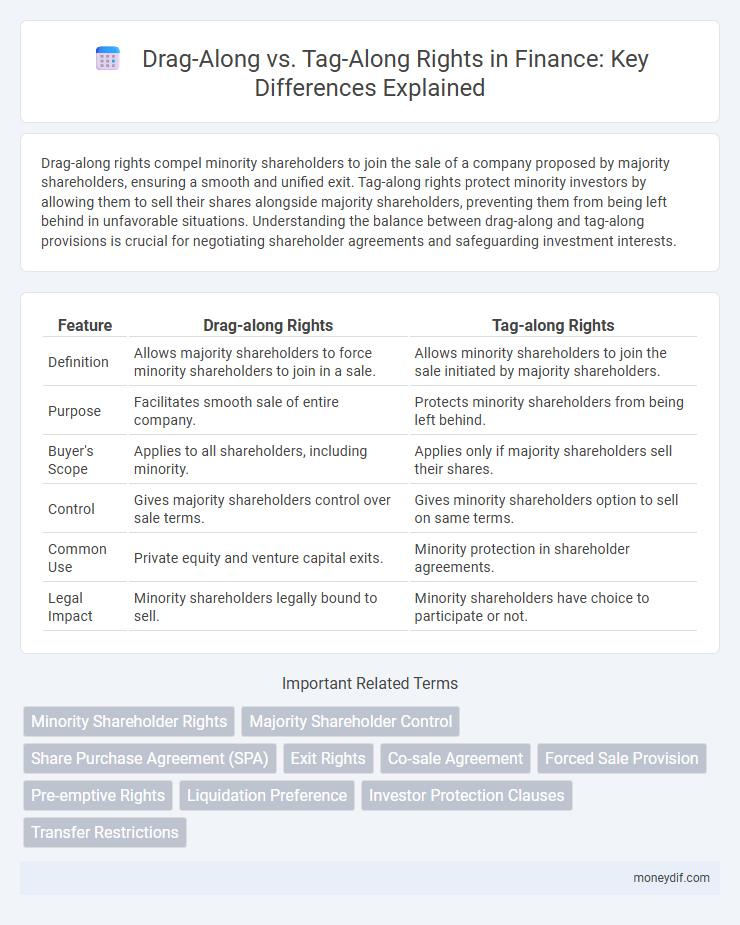
| Feature | Drag-along Rights | Tag-along Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allows majority shareholders to force minority shareholders to join in a sale. | Allows minority shareholders to join the sale initiated by majority shareholders. |
| Purpose | Facilitates smooth sale of entire company. | Protects minority shareholders from being left behind. |
| Buyer's Scope | Applies to all shareholders, including minority. | Applies only if majority shareholders sell their shares. |
| Control | Gives majority shareholders control over sale terms. | Gives minority shareholders option to sell on same terms. |
| Common Use | Private equity and venture capital exits. | Minority protection in shareholder agreements. |
| Legal Impact | Minority shareholders legally bound to sell. | Minority shareholders have choice to participate or not. |
Understanding Drag-along and Tag-along Rights
Drag-along rights enable majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring a streamlined exit process at the agreed terms. Tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by allowing them to sell their shares alongside majority shareholders, preventing them from being left behind during a buyout. Both rights are crucial in shareholder agreements to balance interests during mergers and acquisitions, offering protection and facilitating smooth ownership transitions.
Key Differences Between Drag-along and Tag-along
Drag-along rights enable majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring the sale proceeds smoothly without minority holdouts. Tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by allowing them to sell their shares alongside the majority, ensuring they receive the same exit terms. Key differences include enforcement power, with drag-along rights favoring majority control, while tag-along rights safeguard minority interests during ownership transfers.
Importance of Shareholder Agreements
Shareholder agreements are crucial in defining drag-along and tag-along rights, ensuring minority shareholders are protected during the sale of shares while enabling majority shareholders to enforce collective exit strategies. These clauses facilitate smoother transactions by clarifying conditions under which shareholders can be compelled or allowed to join a sale, minimizing disputes and preserving company value. Effective agreements balance control and protection, aligning interests between majority and minority stakeholders in complex financial arrangements.
How Drag-along Rights Protect Majority Shareholders
Drag-along rights enable majority shareholders to force minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring a smoother and more lucrative exit by preventing holdouts. This protection allows majority shareholders to maximize the sale price and maintain control over crucial transactional decisions. By compelling minority participation, drag-along rights safeguard the interests of majority owners and facilitate efficient liquidity events.
Safeguarding Minority Interests with Tag-along Rights
Tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by allowing them to join in on the sale of shares by majority shareholders, ensuring they receive proportional benefits and avoid being left with less valuable stakes. These rights prevent majority shareholders from selling their stakes without offering minorities the opportunity to exit under the same terms, safeguarding against potential exploitation. In contrast, drag-along rights compel minority shareholders to sell their shares when a majority agrees to a sale, potentially limiting minority control and benefits.
Practical Scenarios: When Rights Come into Play
Drag-along rights typically activate during acquisition offers where majority shareholders compel minority stakeholders to sell their shares, ensuring unified exit terms and maximizing deal attractiveness. Tag-along rights come into effect when majority shareholders decide to sell their stake, granting minority investors the option to join the sale on proportional terms, protecting their investment interests. Both rights play crucial roles in venture capital and private equity deals by balancing control and protection among shareholders during liquidity events.
Negotiation Strategies for Investors
Drag-along rights enable majority investors to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring a smoother exit and maximizing deal value. Tag-along rights protect minority investors by allowing them to participate in the sale under identical terms, preserving their interests during negotiations. Effective negotiation strategies balance these rights to align investor protections with exit flexibility, optimizing shareholder agreement outcomes.
Legal Implications of Drag-along and Tag-along
Drag-along rights legally obligate minority shareholders to sell their shares when majority shareholders decide to exit, ensuring cohesive transaction execution and preventing holdouts. Tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by granting them the option to join a sale on equal terms, safeguarding their investment against unfavorable exits. The enforceability of these provisions depends on their precise drafting within shareholder agreements and compliance with relevant securities laws.
Common Pitfalls in Drafting Rights Clauses
Common pitfalls in drafting drag-along and tag-along rights clauses include ambiguous definitions of triggering events, which can lead to disputes over when these rights apply. Overly broad or restrictive terms may either limit a minority shareholder's exit opportunities or unduly force minority participation in sales. Lack of clarity on procedural requirements, such as notice periods and valuation methods, often results in costly litigation and delays in transaction execution.
Best Practices for Implementing Shareholder Protections
Implementing shareholder protections through drag-along and tag-along rights requires clear drafting of agreements to ensure enforceability and prevent disputes. Best practices include defining triggering events precisely, establishing procedures for notice and sale execution, and balancing minority and majority shareholder interests to maintain trust. Regular legal reviews and aligning these rights with corporate governance frameworks optimize protection and enhance investment confidence.
Important Terms
Minority Shareholder Rights
Minority shareholder rights protect investors by allowing tag-along rights, which ensure minority shareholders can sell their shares alongside majority shareholders during a sale, preventing exclusion from exit opportunities. Drag-along rights enable majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale on the same terms, facilitating smooth transactions but potentially limiting minority autonomy.
Majority Shareholder Control
Majority shareholder control enables decision-making power to enforce drag-along rights, compelling minority shareholders to sell shares during a takeover, while tag-along rights protect minority investors by allowing them to join in the sale under the same terms. Understanding the dynamics between drag-along and tag-along clauses is essential for balancing control and minority shareholder protection in corporate governance.
Share Purchase Agreement (SPA)
A Share Purchase Agreement (SPA) often includes drag-along rights allowing majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in a sale, while tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by enabling them to sell their shares alongside majority shareholders.
Exit Rights
Exit rights balance shareholder power by granting drag-along rights to majority owners to compel minority sale, while tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by allowing them to join in a sale on equal terms.
Co-sale Agreement
A Co-sale Agreement ensures minority shareholders can sell their shares alongside majority shareholders during a sale, protecting their interests. Drag-along rights compel minority shareholders to join the sale under the same terms as majority holders, while Tag-along rights allow minorities to participate voluntarily, maintaining fair exit opportunities.
Forced Sale Provision
The Forced Sale Provision mandates shareholders to sell their shares under specific conditions, often triggered by a Drag-along right that compels minority shareholders to join a sale initiated by the majority. In contrast, Tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by allowing them to join a sale initiated by the majority, ensuring they can sell their shares on the same terms without being forced.
Pre-emptive Rights
Pre-emptive rights grant existing shareholders the option to purchase new shares before outsiders, preserving ownership percentage and control, which contrasts with drag-along rights that compel minority shareholders to join a sale initiated by majority owners. Tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by allowing them to sell their shares under the same terms as majority owners during a sale, complementing pre-emptive rights by safeguarding ownership interests.
Liquidation Preference
Liquidation preference protects investors by ensuring they receive their investment back before common shareholders during a company's liquidation event, influencing the payoffs during Drag-along and Tag-along rights executions. Drag-along rights compel minority shareholders to sell their shares alongside majority stakeholders, often prioritizing liquidation preferences, while Tag-along rights allow minority investors to join the sale, securing proportional returns after liquidation preferences are satisfied.
Investor Protection Clauses
Investor protection clauses such as drag-along and tag-along rights are critical in venture capital agreements to safeguard shareholder interests during a sale; drag-along rights compel minority shareholders to sell their shares if a majority shareholder approves a deal, ensuring deal completion. Tag-along rights protect minority investors by allowing them to join the sale under the same terms and conditions, preventing exclusion from profitable exit opportunities.
Transfer Restrictions
Transfer restrictions in shareholder agreements often include drag-along and tag-along rights to protect minority and majority shareholders. Drag-along rights compel minority shareholders to sell shares when the majority decides to sell, ensuring transaction completion, while tag-along rights allow minority shareholders to join a sale on the same terms, safeguarding their interests.
Drag-along vs Tag-along Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com