Governance risk arises from failures in organizational leadership, policies, or compliance processes that can lead to strategic missteps or reputational damage. Operational risk involves disruptions in day-to-day business activities due to system failures, human errors, or external events impacting efficiency and security. Effective risk management requires distinguishing governance risk from operational risk to allocate resources and implement controls tailored to each category's unique challenges.
Table of Comparison
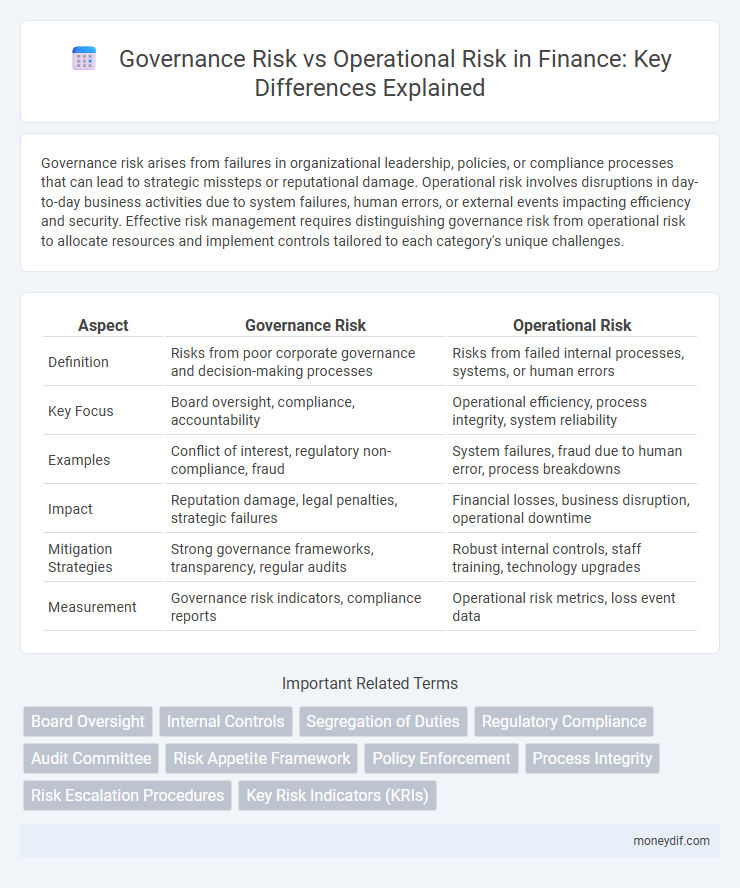
| Aspect | Governance Risk | Operational Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Risks from poor corporate governance and decision-making processes | Risks from failed internal processes, systems, or human errors |
| Key Focus | Board oversight, compliance, accountability | Operational efficiency, process integrity, system reliability |
| Examples | Conflict of interest, regulatory non-compliance, fraud | System failures, fraud due to human error, process breakdowns |
| Impact | Reputation damage, legal penalties, strategic failures | Financial losses, business disruption, operational downtime |
| Mitigation Strategies | Strong governance frameworks, transparency, regular audits | Robust internal controls, staff training, technology upgrades |
| Measurement | Governance risk indicators, compliance reports | Operational risk metrics, loss event data |
Defining Governance Risk in Financial Institutions
Governance risk in financial institutions refers to the potential for losses arising from inadequate leadership, poor decision-making, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, which can undermine organizational integrity and stakeholder trust. It encompasses risks related to board oversight, internal controls, and corporate ethics, directly impacting financial performance and regulatory standing. Effective management of governance risk ensures transparency, accountability, and alignment with legal standards, mitigating reputational damage and financial penalties.
Understanding Operational Risk in Finance
Operational risk in finance involves potential losses resulting from failed internal processes, people, systems, or external events, distinguishing it from governance risk, which centers on regulatory compliance and ethical standards. This risk type encompasses fraud, system failures, and human errors that directly impact financial institutions' day-to-day operations and resilience. Effective management of operational risk requires robust controls, continuous monitoring, and risk mitigation strategies tailored to dynamic financial environments.
Key Differences Between Governance Risk and Operational Risk
Governance risk primarily pertains to failures in leadership, board oversight, and compliance with laws and regulations, impacting an organization's strategic direction and ethical standards. Operational risk involves losses arising from failed internal processes, people, systems, or external events, affecting day-to-day business activities and operational efficiency. Key differences lie in governance risk influencing long-term organizational integrity, while operational risk directly impacts operational performance and financial losses.
Causes of Governance Risk: Structures and Systems
Governance risk arises primarily from ineffective organizational structures and inadequate systems that fail to enforce accountability and transparency. Weak board oversight, unclear roles and responsibilities, and poor compliance frameworks contribute significantly to governance failures. These structural deficiencies increase the likelihood of unethical behavior, regulatory breaches, and strategic misalignment within financial institutions.
Sources of Operational Risk: Processes and People
Operational risk arises primarily from internal processes and the actions of personnel, including procedural failures, human errors, and inadequate training. Flawed processes such as poor transaction handling, system failures, and insufficient controls increase vulnerability to financial loss and reputational damage. Human factors, including misconduct, lack of compliance awareness, and ineffective supervision, significantly contribute to the occurrence and magnitude of operational risk events.
Impact of Governance Failures on Financial Performance
Governance failures significantly undermine financial performance by eroding investor confidence and increasing the cost of capital, often leading to stock price declines and reduced market valuation. Ineffective governance mechanisms result in strategic missteps, compliance breaches, and misallocation of resources, directly impacting profitability and cash flow stability. Empirical studies show firms with poor governance structures face higher volatility in earnings and greater exposure to regulatory penalties, ultimately diminishing shareholder value.
Operational Risk Events: Case Studies and Lessons
Operational risk events, such as system failures, fraud, and human errors, reveal critical vulnerabilities in financial institutions' processes and controls. Case studies highlight how inadequate risk management frameworks exacerbate losses and undermine regulatory compliance. Lessons emphasize the need for robust employee training, real-time monitoring systems, and contingency planning to mitigate operational disruptions effectively.
Mitigation Strategies for Governance Risk
Effective governance risk mitigation in finance centers on establishing robust internal controls, enforcing transparent decision-making processes, and ensuring board accountability through regular audits and compliance checks. Implementing clear policies for risk management, fostering a culture of ethical behavior, and providing continuous training for leadership further reduce governance failures. Leveraging technology like automated compliance monitoring systems enhances real-time risk detection and supports timely corrective actions.
Best Practices for Managing Operational Risk
Implementing robust internal controls and comprehensive risk assessment frameworks are essential best practices for managing operational risk in finance. Regular staff training combined with advanced technology such as real-time monitoring systems enhances early detection and mitigation of potential operational failures. Establishing a clear governance structure with defined roles ensures accountability and continuous improvement in operational risk management processes.
Integrating Governance and Operational Risk Frameworks
Integrating governance and operational risk frameworks enhances organizational resilience by aligning risk management processes with strategic objectives and regulatory requirements. A unified framework enables real-time risk identification, controls monitoring, and comprehensive reporting, reducing silos and improving decision-making efficiency. Leveraging advanced analytics and automated workflows supports continuous risk assessment, ensuring proactive mitigation of governance and operational risks across business units.
Important Terms
Board Oversight
Board oversight ensures governance risk is mitigated by establishing robust policies and aligning risk appetite with organizational objectives, while operational risk is managed through continuous monitoring of internal processes and controls. Effective board involvement fosters transparency and accountability, reducing the likelihood of compliance breaches and operational failures.
Internal Controls
Internal controls are essential mechanisms designed to mitigate governance risk by ensuring compliance with policies, regulations, and ethical standards, thereby promoting transparent decision-making and accountability. These controls also address operational risk by safeguarding assets, enhancing process efficiency, and preventing errors or fraud within day-to-day business activities.
Segregation of Duties
Segregation of Duties (SoD) minimizes governance risk by ensuring no single individual has control over all critical stages of a process, thereby preventing fraud and errors. Operational risk is reduced through SoD by distributing responsibilities, which enhances process integrity and internal controls within organizations.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance involves adhering to laws and regulations to mitigate governance risk, which stems from failures in corporate decision-making and oversight. Operational risk, related to internal processes, technology, or human errors, is managed through compliance frameworks that ensure consistent risk identification and control measures.
Audit Committee
Audit Committees play a critical role in governance risk by overseeing financial reporting, compliance, and internal control frameworks to ensure accurate disclosures and regulatory adherence. Their focus on operational risk includes evaluating risk management processes and controls to mitigate disruptions, fraud, and inefficiencies within organizational operations.
Risk Appetite Framework
A Risk Appetite Framework delineates the acceptable levels of risk an organization is willing to assume, balancing governance risk linked to regulatory compliance and strategic oversight with operational risk arising from internal processes and systems failures. Effective implementation ensures that governance risk is mitigated through clear policies and oversight, while operational risk is controlled via robust procedures and risk monitoring mechanisms.
Policy Enforcement
Policy enforcement strengthens governance by mitigating compliance risks and ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements, while simultaneously reducing operational risks through standardized procedures and consistent controls. Effective enforcement mechanisms align organizational objectives with risk management frameworks, enhancing overall risk resilience.
Process Integrity
Process integrity ensures accurate and reliable execution of business operations, directly impacting governance risk by maintaining compliance with policies and regulatory requirements. It also mitigates operational risk by preventing errors, fraud, and inefficiencies within organizational workflows.
Risk Escalation Procedures
Risk Escalation Procedures ensure timely identification and reporting of governance risks, such as policy compliance failures, and operational risks, including process disruptions, by establishing clear thresholds and communication channels. These procedures enable organizations to mitigate potential impacts by facilitating swift decision-making and accountability across management levels.
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) for governance risk typically focus on metrics like board meeting frequency, policy compliance rates, and internal audit findings, reflecting oversight and decision-making effectiveness. In contrast, KRIs for operational risk emphasize quantitative data such as system downtime, error rates, and incident reports, highlighting vulnerabilities in day-to-day business processes and controls.
governance risk vs operational risk Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com