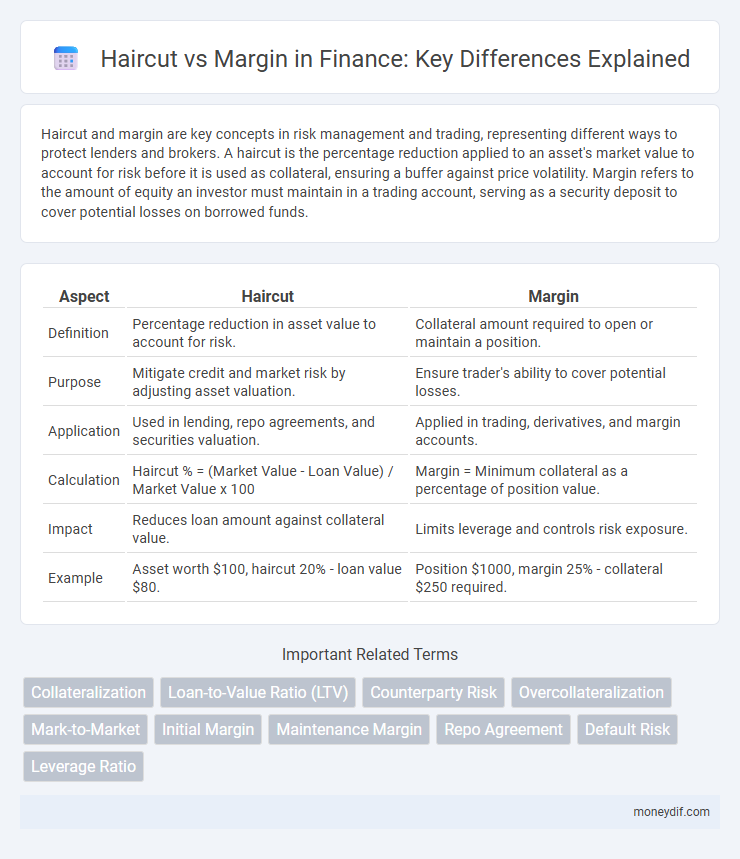
Haircut and margin are key concepts in risk management and trading, representing different ways to protect lenders and brokers. A haircut is the percentage reduction applied to an asset's market value to account for risk before it is used as collateral, ensuring a buffer against price volatility. Margin refers to the amount of equity an investor must maintain in a trading account, serving as a security deposit to cover potential losses on borrowed funds.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Haircut | Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Percentage reduction in asset value to account for risk. | Collateral amount required to open or maintain a position. |
| Purpose | Mitigate credit and market risk by adjusting asset valuation. | Ensure trader's ability to cover potential losses. |
| Application | Used in lending, repo agreements, and securities valuation. | Applied in trading, derivatives, and margin accounts. |
| Calculation | Haircut % = (Market Value - Loan Value) / Market Value x 100 | Margin = Minimum collateral as a percentage of position value. |
| Impact | Reduces loan amount against collateral value. | Limits leverage and controls risk exposure. |
| Example | Asset worth $100, haircut 20% - loan value $80. | Position $1000, margin 25% - collateral $250 required. |
Understanding Haircut and Margin in Finance
Haircut in finance refers to the percentage reduction applied to the market value of an asset when calculating its collateral value to mitigate risk during lending or trading activities. Margin represents the required amount of equity an investor must deposit to borrow funds or enter leveraged positions, ensuring a buffer against potential losses. Both concepts play critical roles in risk management by determining the safety levels in secured transactions and leveraged trading.
Key Differences Between Haircut and Margin
Haircut refers to the percentage reduction applied to the market value of an asset used as collateral to account for risk and potential price volatility, while margin is the amount of equity an investor must deposit to borrow funds for trading or investment purposes. Haircuts are primarily used by lenders or clearinghouses to protect against credit risk, whereas margins mainly determine the investor's required capital to initiate or maintain a leveraged position. Understanding the distinction aids in risk management and compliance with regulatory capital requirements in financial markets.
Role of Haircut in Secured Lending
The haircut in secured lending represents the percentage reduction applied to the market value of collateral to account for potential losses during liquidation, ensuring protection for lenders against price volatility. This risk buffer is crucial in calculating the loan's exposure and determining the amount of funds that can be safely lent. Unlike margin, which is the actual amount of equity a borrower must maintain, the haircut directly influences the collateral valuation used to secure the loan.
Margin Requirements in Financial Trading
Margin requirements in financial trading determine the minimum amount of equity an investor must maintain in their margin account to open or hold a position. Haircuts adjust the value of collateral to account for market risk, reducing the effective collateral amount accepted by brokers or clearinghouses. While margin requirements set the leverage limits, haircuts serve as risk buffers to protect against asset price volatility and ensure sufficient coverage.
How Haircuts Protect Lenders from Risk
Haircuts reduce lenders' exposure to market fluctuations by valuing collateral below its current market price, creating a safety buffer that mitigates potential loss in case of borrower default. This risk management mechanism ensures lenders are protected against sudden declines in asset values, reinforcing the stability of secured loans. Contrasting with margins, which require borrowers to maintain a minimum equity level, haircuts preemptively limit credit risk through conservative collateral valuation.
Margin Calls: Mechanism and Implications
Margin calls occur when the value of an investor's collateral falls below the broker's required maintenance margin, compelling the investor to deposit additional funds or securities to restore the account's equity. The haircut represents the percentage discount applied to the collateral's market value, affecting the initial margin and determining the buffer before a margin call is triggered. Understanding the interplay between haircuts and margin calls is critical for managing leverage risk and maintaining compliance with regulatory capital requirements.
Factors Affecting Haircut Percentage
Haircut percentage in finance is influenced by asset volatility, liquidity, and market conditions, determining the risk buffer lenders apply to collateral value. Higher volatility and lower liquidity increase haircuts to protect against potential asset depreciation during liquidation. Regulatory requirements and creditworthiness of counterparties also play crucial roles in setting appropriate haircut levels.
Margin Types: Initial vs. Maintenance
In finance, margin refers to the collateral investors must deposit when borrowing funds to trade securities, with initial margin being the minimum required at the time of purchase and maintenance margin representing the minimum equity level that must be maintained to avoid a margin call. Initial margin typically ranges from 25% to 50% of the purchase price depending on regulatory requirements and brokerage policies, while maintenance margin usually sits around 25% to 30%. The haircut concept involves the percentage reduction applied to an asset's market value to determine its collateral value, influencing both the initial and maintenance margin calculations.
Impact of Market Volatility on Haircut and Margin
Market volatility directly increases haircuts as lenders seek to mitigate higher risk by requiring greater collateral buffers. Simultaneously, margin requirements become more stringent to protect against rapidly fluctuating asset prices that could erode collateral value. Elevated volatility amplifies both haircut and margin levels, tightening liquidity and influencing leverage strategies in financial markets.
Practical Examples: Haircut vs. Margin in Action
A haircut represents the percentage reduction applied to the market value of an asset used as collateral, protecting lenders from price volatility, such as a 10% haircut on $100,000 worth of securities valued at $90,000 for loan purposes. Margin refers to the minimum equity a trader must maintain in their margin account, for example, a 50% margin requirement on a $10,000 stock purchase necessitates at least $5,000 of the trader's own funds. In practice, haircuts adjust collateral value to mitigate risk, while margins determine the borrowing capacity and leverage level in trading scenarios.
Important Terms
Collateralization
Collateralization involves securing loans with assets, where the haircut represents the percentage deduction from an asset's market value to adjust for risk, while margin refers to the minimum amount of equity required to maintain a leveraged position. Higher haircuts reduce credit exposure by requiring more collateral, whereas margin ensures adequate asset coverage to protect against market fluctuations.
Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV)
Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV) measures the loan amount as a percentage of the asset's value, where a lower LTV indicates higher borrower equity and reduced risk. Haircut represents the percentage reduction applied to an asset's market value to calculate its collateral value, while margin refers to the minimum equity requirement, both influencing risk management and lending decisions in financial transactions.
Counterparty Risk
Counterparty risk arises when one party in a financial transaction may default, impacting the valuation of collateral through haircuts, which are percentage reductions applied to asset values to mitigate this risk. Margins represent the funds or collateral required to be posted to cover potential losses, with haircuts determining the initial margin levels to ensure adequate protection against counterparty default.
Overcollateralization
Overcollateralization increases protection against default risk by requiring collateral value to exceed the loan amount, and the haircut represents the percentage reduction applied to collateral value while margin denotes the required equity buffer maintained, both balancing risk and liquidity in financial transactions.
Mark-to-Market
Mark-to-Market valuation adjusts asset prices to current market values, directly influencing margin requirements by reflecting real-time risk exposure. Haircuts apply a discount on asset values during collateral assessment, reducing margin lending and safeguarding against market volatility.
Initial Margin
Initial Margin represents the collateral required to cover potential future exposure in a financial transaction, serving as a risk buffer for counterparties. Haircut adjusts the valuation of collateral by applying a discount, lowering the effective collateral value to account for market volatility, whereas Margin refers to the actual amount of funds or assets deposited to meet regulatory or contractual requirements.
Maintenance Margin
Maintenance margin ensures traders keep sufficient equity to cover potential losses, while the haircut represents the percentage reduction applied to an asset's market value to calculate collateral requirements. The haircut adjusts margin requirements by accounting for asset volatility, thereby influencing the maintenance margin level required to sustain positions.
Repo Agreement
A Repo Agreement involves the sale of securities with an agreement to repurchase them at a higher price, where the Haircut represents the percentage difference between the market value of the collateral and the loan amount, acting as a risk buffer. Margin in a repo context refers to the minimum collateral value required to secure the loan, ensuring the lender is protected against fluctuations in asset prices.
Default Risk
Default risk increases as haircut decreases and margin requirements become less stringent, reducing collateral protection against potential losses.
Leverage Ratio
Leverage ratio measures the proportion of debt to equity used in financing, where haircuts represent the percentage reduction applied to the value of collateral, affecting margin requirements in risk management. Higher haircuts increase margin demands, thereby reducing leverage by requiring more equity to support the same level of borrowing.
Haircut vs Margin Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com