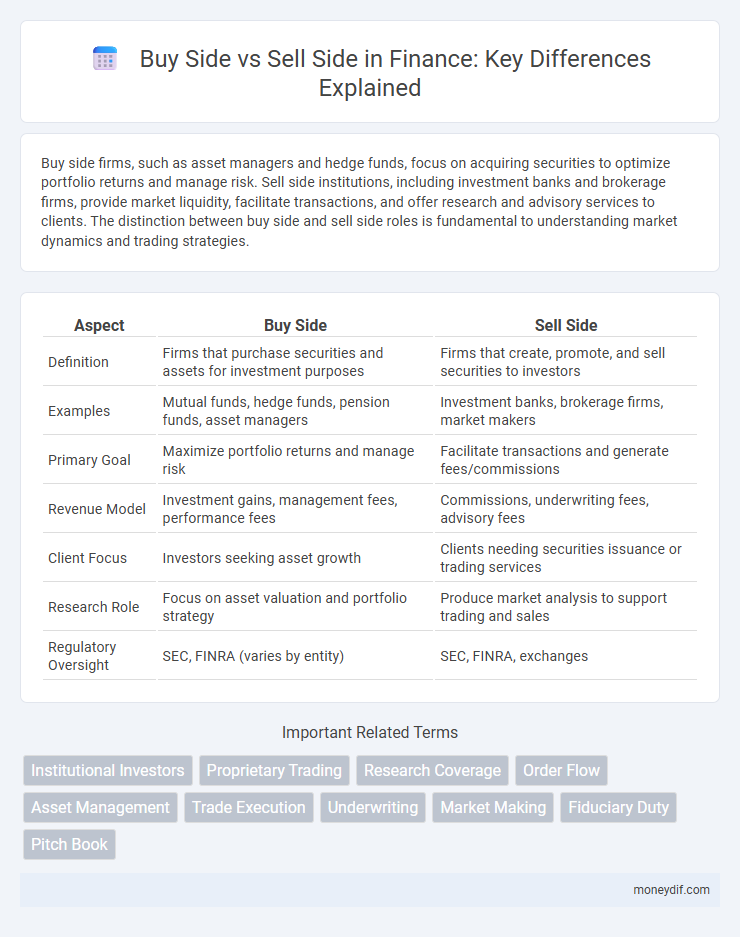
Buy side firms, such as asset managers and hedge funds, focus on acquiring securities to optimize portfolio returns and manage risk. Sell side institutions, including investment banks and brokerage firms, provide market liquidity, facilitate transactions, and offer research and advisory services to clients. The distinction between buy side and sell side roles is fundamental to understanding market dynamics and trading strategies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Buy Side | Sell Side |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Firms that purchase securities and assets for investment purposes | Firms that create, promote, and sell securities to investors |
| Examples | Mutual funds, hedge funds, pension funds, asset managers | Investment banks, brokerage firms, market makers |
| Primary Goal | Maximize portfolio returns and manage risk | Facilitate transactions and generate fees/commissions |
| Revenue Model | Investment gains, management fees, performance fees | Commissions, underwriting fees, advisory fees |
| Client Focus | Investors seeking asset growth | Clients needing securities issuance or trading services |
| Research Role | Focus on asset valuation and portfolio strategy | Produce market analysis to support trading and sales |
| Regulatory Oversight | SEC, FINRA (varies by entity) | SEC, FINRA, exchanges |
Introduction to Buy Side vs Sell Side
Buy side and sell side represent two fundamental segments of the financial markets, where buy side firms such as asset managers, hedge funds, and pension funds focus on investment decisions and portfolio management to maximize returns. Sell side entities, including investment banks, brokers, and dealers, provide advisory services, facilitate transactions, and create liquidity by offering securities to buy side clients. Understanding the distinct roles and interactions between buy side and sell side is critical for optimizing trading strategies, market efficiency, and investment outcomes.
Defining the Buy Side: Roles and Functions
The buy side in finance primarily includes institutional investors such as mutual funds, pension funds, hedge funds, and private equity firms that purchase securities and assets to generate returns for their clients or portfolios. Their core functions involve asset allocation, portfolio management, and conducting in-depth research to identify investment opportunities with strong growth potential. Buy-side analysts and portfolio managers focus on maximizing long-term value by making strategic investment decisions based on market trends, fundamental analysis, and risk assessment.
Understanding the Sell Side: Key Responsibilities
Sell side entities primarily include investment banks, broker-dealers, and market makers that facilitate securities transactions by providing liquidity and market access to buy side clients. Their key responsibilities involve underwriting new issues, distributing securities, conducting market research, and offering advisory services to issuers and investors. Expertise in pricing, market-making, and regulatory compliance ensures efficient transaction execution and capital formation.
Core Differences Between Buy Side and Sell Side
Buy side firms, such as asset managers, hedge funds, and pension funds, focus on purchasing securities to generate returns for their clients or portfolios, emphasizing investment decision-making and portfolio management. Sell side entities, including investment banks and brokerage firms, provide market liquidity, facilitate transactions, and offer research and advisory services to buy side clients. The core difference lies in their primary roles: buy side drives capital allocation and investment strategies, while sell side supports execution, market-making, and client advisory.
Types of Firms on the Buy Side
Buy side firms include asset management companies, mutual funds, hedge funds, pension funds, and private equity firms that invest capital to generate returns for clients or beneficiaries. These firms focus on acquiring securities, equities, bonds, and alternative assets through research-driven strategies and portfolio management. Buy side entities prioritize long-term value creation and risk management to optimize investment performance.
Major Players on the Sell Side
Major players on the sell side include investment banks, brokerage firms, and market makers who facilitate trading and liquidity for buy-side clients. Prominent sell-side firms like Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, and JP Morgan provide research, underwriting, and advisory services to institutional investors. These entities drive market efficiency by connecting issuers and investors while offering critical market insights and execution capabilities.
Career Paths: Buy Side vs Sell Side
Buy side careers typically involve asset management, private equity, and hedge funds, where professionals focus on investment decisions and portfolio management to maximize returns. Sell side roles are centered around investment banking, research, and sales and trading, emphasizing client advisory, capital raising, and market-making activities. Both paths require strong analytical skills, but buy side roles demand deeper fundamental analysis while sell side positions prioritize client interaction and market expertise.
Investment Strategies and Approaches
Buy side investment strategies prioritize long-term value creation through asset management, portfolio diversification, and risk-adjusted returns, often employing fundamental analysis and quantitative models to identify undervalued securities. Sell side approaches focus on providing liquidity, market making, and facilitating transactions by offering research, trade execution, and advisory services to institutional clients and investors. Both sides utilize data-driven insights, but buy side strategies emphasize asset accumulation and growth, while sell side strategies concentrate on market access and transaction efficiency.
Revenue Models: How Each Side Makes Money
Buy side firms generate revenue primarily through asset management fees, performance-based incentives, and management of investment portfolios for institutional and retail clients. Sell side firms earn income by underwriting securities, facilitating market-making activities, and charging commissions or spreads on trade executions. While buy side revenue depends on portfolio performance and assets under management, sell side revenue is driven by transaction volume and advisory services.
Current Trends and Future Outlook
The buy side increasingly leverages artificial intelligence and big data analytics to enhance asset management and investment decision-making, driving competitive advantages in portfolio optimization. Meanwhile, the sell side adapts by integrating advanced trading algorithms and real-time market intelligence to improve liquidity provision and client engagement. Future outlook indicates a convergence of buy-side and sell-side technologies, with blockchain and decentralized finance reshaping transaction transparency and operational efficiency.
Important Terms
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors primarily operate on the buy side by managing large-scale assets and making strategic investment decisions, while the sell side consists of firms like investment banks and brokers that facilitate market liquidity and execute trades. Buy-side entities focus on asset management, portfolio optimization, and generating returns, whereas sell-side firms provide research, underwriting, and advisory services to support buy-side transactions.
Proprietary Trading
Proprietary trading involves financial firms using their own capital to trade stocks, bonds, currencies, or derivatives, differentiating it from traditional buy-side activities where asset managers invest client funds. Unlike the sell side, which facilitates market liquidity by acting as intermediaries, proprietary traders aim to generate direct profits from market movements through strategic, high-risk trades.
Research Coverage
Research coverage in the buy side focuses on in-depth analysis to support portfolio management and investment decisions, emphasizing proprietary insights and long-term value. Sell side research prioritizes generating actionable market intelligence and recommendations to facilitate trading, client advisory, and capital raising services.
Order Flow
Order flow represents the real-time stream of buy and sell orders between market participants, crucial for understanding liquidity and price movements. Buy-side firms focus on executing purchase orders to optimize investment outcomes, while sell-side firms provide market-making, liquidity, and research services facilitating efficient order execution.
Asset Management
Buy-side asset management focuses on investment decisions and portfolio construction for institutional clients, while sell-side asset management provides research, advisory, and transaction services to facilitate market liquidity and client trades.
Trade Execution
Trade execution on the buy side involves portfolio managers and institutional investors placing orders to purchase securities, focusing on minimizing market impact and achieving the best possible price. On the sell side, broker-dealers and market makers facilitate these transactions by providing liquidity and executing orders efficiently to capture spreads and commissions.
Underwriting
Underwriting on the buy side involves investment firms rigorously evaluating securities to ensure they meet portfolio criteria before acquisition, focusing on risk assessment and valuation. On the sell side, underwriting entails financial institutions facilitating capital raising by pricing and distributing securities, managing issuer credibility and market demand.
Market Making
Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices, facilitating efficient trade execution for both buy-side institutions such as mutual funds and pension funds, and sell-side entities like investment banks and broker-dealers. By bridging demand and supply, market makers enable tighter bid-ask spreads and improved market depth, benefiting participants on both sides of the trade.
Fiduciary Duty
Fiduciary duty on the buy side involves acting in the best interests of investors by conducting thorough due diligence and securing favorable terms in acquisitions, while the sell side's fiduciary duty requires maximizing shareholder value through effective negotiations and transparent disclosures during the sale process. Both parties must prioritize loyalty, care, and full disclosure to uphold trust and achieve optimal transaction outcomes in mergers and acquisitions.
Pitch Book
PitchBook provides comprehensive data and analytics empowering buy-side investors to evaluate acquisition targets while enabling sell-side professionals to optimize deal sourcing and valuation strategies.
buy side vs sell side Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com