Binders provide temporary insurance coverage immediately upon agreement, ensuring protection until the formal policy is issued. Endorsements modify or add specific terms and conditions to an existing insurance policy, tailoring coverage to the insured's needs. Understanding the distinction between binders and endorsements is crucial for managing timely coverage and policy customization effectively.
Table of Comparison
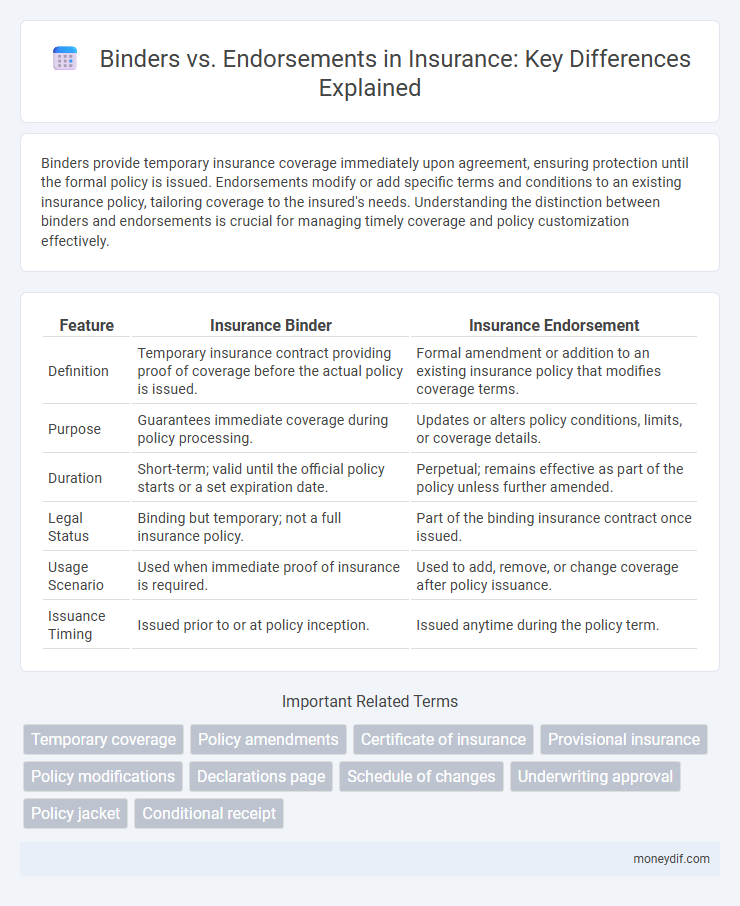
| Feature | Insurance Binder | Insurance Endorsement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary insurance contract providing proof of coverage before the actual policy is issued. | Formal amendment or addition to an existing insurance policy that modifies coverage terms. |
| Purpose | Guarantees immediate coverage during policy processing. | Updates or alters policy conditions, limits, or coverage details. |
| Duration | Short-term; valid until the official policy starts or a set expiration date. | Perpetual; remains effective as part of the policy unless further amended. |
| Legal Status | Binding but temporary; not a full insurance policy. | Part of the binding insurance contract once issued. |
| Usage Scenario | Used when immediate proof of insurance is required. | Used to add, remove, or change coverage after policy issuance. |
| Issuance Timing | Issued prior to or at policy inception. | Issued anytime during the policy term. |
Understanding Insurance Binders
Insurance binders provide temporary proof of coverage, offering immediate protection before the formal policy is issued, typically lasting 30 to 90 days. They outline basic policy terms, limits, and coverage details but lack the comprehensive specifics found in the finalized insurance contract. Understanding binders ensures policyholders have timely protection, preventing coverage gaps during the underwriting process.
What Are Insurance Endorsements?
Insurance endorsements are formal amendments or additions to an existing insurance policy that modify coverage terms, limits, or conditions without requiring the issuance of a new policy. These endorsements can expand, restrict, or clarify the scope of the original insurance contract, providing tailored protection based on specific needs. Common examples include adding coverage for new property, excluding certain perils, or adjusting liability limits, ensuring precise alignment with the insured's risk profile.
Key Differences: Binders vs Endorsements
Binders provide temporary insurance coverage until a formal policy is issued, serving as a short-term proof of insurance, while endorsements are official amendments or additions to an existing insurance policy that modify its terms or coverage. Binders are typically used when immediate coverage is required, often lasting only 30 to 90 days, whereas endorsements permanently adjust the policy's scope, limits, or conditions. The key difference lies in binders offering provisional protection, whereas endorsements offer finalized, documented changes to a policy.
When Is a Binder Used in Insurance?
A binder is used in insurance to provide temporary proof of coverage before the formal policy is issued, typically during underwriting or policy processing delays. It offers immediate protection for a specified period, usually 30 to 90 days, ensuring the insured is covered while final policy terms and documentation are finalized. Binders are essential in real estate transactions and high-risk insurance cases where coverage confirmation is needed promptly.
Common Uses of Insurance Endorsements
Insurance endorsements are commonly used to modify or expand the coverage of an existing insurance policy, accommodating specific client needs such as adding coverage for valuable personal property or adjusting liability limits. They provide flexibility by allowing policyholders to tailor their insurance contracts without negotiating entirely new policies. Endorsements can address changes in risk exposure, regulatory requirements, or contractual obligations, ensuring that the coverage remains relevant and comprehensive.
Legal Implications: Binder vs Endorsement
Binders provide temporary insurance coverage until a formal policy is issued, creating immediate legal obligations between the insurer and insured. Endorsements modify or add terms to an existing insurance policy, legally altering coverage without issuing a new contract. Understanding the legal distinction is crucial, as binders offer provisional protection while endorsements adjust binding policy conditions.
How Long Does an Insurance Binder Last?
An insurance binder typically lasts between 30 to 90 days, providing temporary coverage until the official policy is issued. The exact duration depends on state regulations and insurer practices, but binders generally expire as soon as the formal policy becomes effective. Policyholders should verify binder expiration dates to ensure continuous protection without gaps.
Modifying Policies with Endorsements
Endorsements modify insurance policies by adding, deleting, or changing coverage terms without issuing a new policy. These policyholders' amendments provide tailored protection to meet specific needs, such as increasing limits or excluding particular risks. Unlike binders, which are temporary agreements providing immediate coverage, endorsements become permanent attachments to the policy documentation.
Binders and Endorsements in Claims Processing
Binders provide temporary insurance coverage during the period before a formal policy is issued, ensuring claims can be processed without delay. Endorsements modify existing insurance policies by adding, removing, or altering coverage terms, directly impacting the scope and settlement of claims. Efficient management of binders and endorsements is crucial for accurate claims adjustment and minimizing potential coverage disputes.
Choosing Between an Insurance Binder and Endorsement
Choosing between an insurance binder and an endorsement depends on the coverage timeline and policy detail customization needs. An insurance binder serves as temporary proof of insurance, effective immediately but limited in scope until the formal policy is issued. Endorsements modify or add specific coverage to an existing policy, ensuring tailored protection without issuing a new contract.
Important Terms
Temporary coverage
Temporary coverage provided by binders offers immediate insurance protection before a formal policy is issued, ensuring risk mitigation during the underwriting process. Unlike endorsements, which modify existing policies to adjust terms or coverage, binders act as standalone agreements granting short-term liability coverage.
Policy amendments
Policy amendments clarify contract modifications where binders provide temporary coverage prior to formal issuance, while endorsements serve as official written changes integrated into existing insurance policies to alter terms, conditions, or coverage. Understanding the distinction ensures accurate risk management, compliance, and effective policy documentation aligned with insurer and regulatory standards.
Certificate of insurance
A Certificate of Insurance summarizes proof of coverage while a Binder provides temporary insurance before the policy is issued and an Endorsement modifies existing policy terms.
Provisional insurance
Provisional insurance uses binders to provide temporary coverage before the formal policy is issued, while endorsements modify existing policies to adjust coverage terms after issuance.
Policy modifications
Policy modifications require endorsements to adjust coverage terms, while binders provide temporary proof of insurance before official policy issuance.
Declarations page
The declarations page summarizes key policy details while binders provide temporary coverage before the official policy issuance, and endorsements modify or add specific terms to the original insurance contract.
Schedule of changes
Binders offer temporary coverage while awaiting policy issuance, whereas endorsements modify or add specific terms to an existing insurance policy.
Underwriting approval
Underwriting approval distinguishes between binders, which provide temporary coverage pending final approval, and endorsements, which modify existing policies after issuance.
Policy jacket
Policy jackets clarify coverage terms by distinguishing binders, which provide temporary insurance, from endorsements that permanently modify existing policy agreements.
Conditional receipt
Conditional receipts provide temporary insurance coverage pending policy approval and differ from binders and endorsements by explicitly requiring specific conditions to be met before coverage becomes effective.
Binders vs Endorsements Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com