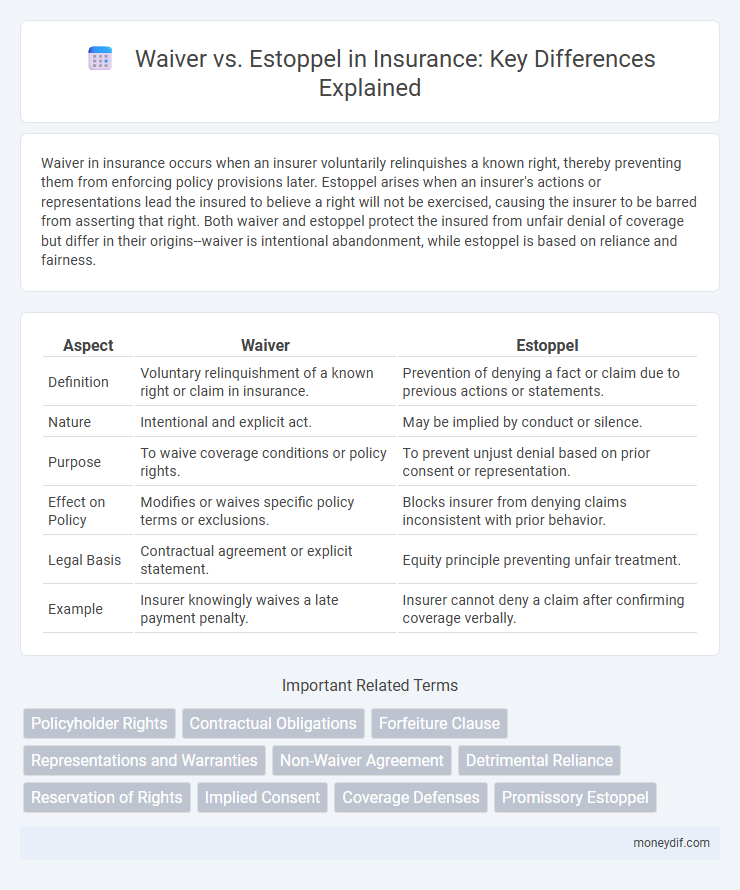
Waiver in insurance occurs when an insurer voluntarily relinquishes a known right, thereby preventing them from enforcing policy provisions later. Estoppel arises when an insurer's actions or representations lead the insured to believe a right will not be exercised, causing the insurer to be barred from asserting that right. Both waiver and estoppel protect the insured from unfair denial of coverage but differ in their origins--waiver is intentional abandonment, while estoppel is based on reliance and fairness.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Waiver | Estoppel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary relinquishment of a known right or claim in insurance. | Prevention of denying a fact or claim due to previous actions or statements. |
| Nature | Intentional and explicit act. | May be implied by conduct or silence. |
| Purpose | To waive coverage conditions or policy rights. | To prevent unjust denial based on prior consent or representation. |
| Effect on Policy | Modifies or waives specific policy terms or exclusions. | Blocks insurer from denying claims inconsistent with prior behavior. |
| Legal Basis | Contractual agreement or explicit statement. | Equity principle preventing unfair treatment. |
| Example | Insurer knowingly waives a late payment penalty. | Insurer cannot deny a claim after confirming coverage verbally. |
Understanding Waiver and Estoppel in Insurance
Waiver in insurance occurs when an insurer voluntarily relinquishes a known right, often leading to the loss of certain policy defenses if not enforced promptly. Estoppel prevents an insurer from denying coverage or policy terms due to previous actions or statements that led the insured to reasonably rely on those representations. Understanding the distinction helps insurers and policyholders clarify coverage boundaries and the enforcement of contractual rights.
Key Differences Between Waiver and Estoppel
Waiver in insurance refers to the voluntary relinquishment of a known right, often demonstrated through an insured's or insurer's explicit or implicit actions, while estoppel prevents a party from asserting a right due to their previous conduct or representations that misled the other party. A fundamental difference lies in waiver being a deliberate abandonment of a right, whereas estoppel arises when a party is barred from denying a fact or right because of their own misleading behavior or silence. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for insurers in policy enforcement and dispute resolution.
Legal Definition of Waiver in Insurance Policies
Waiver in insurance policies refers to the voluntary relinquishment or surrender of a known right, claim, or privilege by the insurer or insured, often demonstrated through actions or conduct that indicate the intent to forgo enforcement. It legally prevents a party from asserting a particular right or defense, even if the policy terms would otherwise allow it. This doctrine ensures that insurers cannot enforce policy provisions inconsistently, promoting fairness in claim handling and coverage interpretation.
Legal Definition of Estoppel in Insurance Contracts
Estoppel in insurance contracts prevents a party from denying or asserting something contrary to what has been established as truth, based on previous actions, statements, or conduct. It legally bars an insurer from enforcing rights or provisions if they have led the insured to believe certain provisions will not be enforced. This doctrine ensures fairness and protects the insured from unexpected policy cancellations or coverage denials.
Real-World Examples: Waiver vs Estoppel
In insurance claims, waiver occurs when an insurer intentionally relinquishes a known right, such as accepting late premium payments without penalty, effectively altering contract terms. Estoppel arises when an insurer's representation, or lack of enforcement, leads the insured to reasonably rely on that conduct, preventing the insurer from denying a claim based on those terms later. For instance, if an insurer repeatedly accepts late payments without objection (waiver), then later attempts to deny coverage due to late payment, estoppel may bar that denial because the insured relied on the insurer's previous behavior.
How Insurers Use Waiver and Estoppel Defenses
Insurers use waiver to forfeit policy rights when they intentionally relinquish a known right, often by accepting late payments or failing to enforce policy provisions promptly. Estoppel prevents insurers from denying coverage or asserting defenses when the insured has reasonably relied on the insurer's representations or conduct to their detriment. These defenses safeguard insured parties from unfair surprise while allowing insurers to uphold contractual obligations fairly.
Policyholder Rights: Waiver and Estoppel Implications
Waiver occurs when an insurer voluntarily relinquishes a known right, impacting the policyholder's ability to enforce certain policy provisions. Estoppel prevents an insurer from denying coverage if their prior conduct, words, or actions reasonably misled the policyholder to their detriment. Understanding these doctrines is essential for policyholders to assert their rights and avoid forfeiture of claims under an insurance contract.
Impact of Waiver and Estoppel on Claim Outcomes
Waiver in insurance often results in the insurer relinquishing a known right, potentially allowing a claim that might otherwise be denied, while estoppel prevents the insurer from asserting a right or defense due to previous conduct or statements. The impact on claim outcomes is significant, as waiver can lead to coverage issues being overlooked, and estoppel legally binds the insurer to certain conditions, often favoring the claimant. Understanding these doctrines helps insurers manage risk and claim decisions more effectively, ensuring compliance with contractual obligations.
Avoiding Disputes: Best Practices for Waiver and Estoppel
Clear documentation of all policy changes and communications helps avoid misunderstandings related to waiver and estoppel in insurance claims. Insurers should implement consistent training on recognizing and properly applying waiver and estoppel principles to prevent disputes. Establishing transparent claim procedures and timely communication further minimizes risks of legal challenges arising from alleged waivers or estoppel.
Recent Case Law on Waiver and Estoppel in Insurance
Recent case law on waiver and estoppel in insurance highlights key distinctions in their application to policy enforcement and claims denial. Courts have increasingly emphasized that waiver requires a clear, voluntary surrender of a known right by the insurer, often demonstrated through explicit conduct or statements, while estoppel arises to prevent an insurer from denying coverage when the insured reasonably relies on a representation or omission to their detriment. Key rulings, such as in *Smith v. Insurance Co.* (2023), reinforce that estoppel cannot create coverage where none exists but can bar an insurer from enforcing strict policy conditions if it misled the insured.
Important Terms
Policyholder Rights
Policyholder rights in the context of waiver and estoppel involve the ability to enforce or defend insurance contract provisions despite an insurer's previous conduct or representations that may have waived certain rights or created an estoppel preventing denial of coverage. Waiver occurs when the insurer voluntarily relinquishes a known right, while estoppel arises when the insurer's actions or omissions cause the policyholder to reasonably rely on a specific understanding, preventing the insurer from asserting strict policy terms.
Contractual Obligations
Contractual obligations require parties to fulfill agreed-upon duties, while waiver involves voluntarily relinquishing a known right, affecting enforcement. Estoppel prevents a party from asserting rights after actions or representations have caused the other party to reasonably rely and change their position.
Forfeiture Clause
A forfeiture clause in contracts enforces strict consequences for non-compliance, but its application may be limited when waiver or estoppel principles apply to prevent unfair loss of rights. Waiver allows voluntary relinquishment of a right, while estoppel bars a party from enforcing the forfeiture if their previous conduct led the other party to reasonably rely on non-enforcement.
Representations and Warranties
Representations and warranties in contracts establish factual assertions and guarantees, with waivers involving the voluntary relinquishment of rights without invalidating those assertions, while estoppel prevents a party from contradicting their prior statements or conduct that another party relied upon to their detriment. Waivers do not alter the truth of representations, whereas estoppel legally bars denial of previously affirmed facts or rights, ensuring enforcement based on reliance and fairness principles.
Non-Waiver Agreement
A Non-Waiver Agreement ensures that a party's failure to enforce certain contractual rights does not imply waiver, preserving those rights for future enforcement. Unlike estoppel--which prevents a party from contradicting previous conduct causing reliance--this agreement explicitly clarifies that no rights are surrendered despite temporary non-enforcement.
Detrimental Reliance
Detrimental reliance occurs when a party relies on a promise or waiver to their disadvantage, making estoppel a key doctrine that prevents the promisor from reneging on that promise, contrasting with waiver which is an intentional relinquishment of a known right without the need to prove reliance. Estoppel requires showing that the reliance was reasonable and resulted in harm, thereby enforcing fairness and protecting the party from detrimental consequences arising from the other's conduct.
Reservation of Rights
Reservation of Rights allows a party to explicitly retain its legal claims or defenses without relinquishing them, distinguishing it from waiver, where a known right is intentionally relinquished. Estoppel prevents a party from asserting a right after inconsistent conduct or statements have led another to rely detrimentally, creating a binding preclusion distinct from both waiver and reservation of rights.
Implied Consent
Implied consent occurs when a person's actions or circumstances suggest agreement without explicit verbal or written confirmation, often distinguished from waiver, which involves intentional relinquishment of a known right, and estoppel, a legal principle preventing a party from asserting rights that contradict their prior conduct or representations. In legal contexts, understanding the nuances between implied consent, waiver, and estoppel is crucial for determining obligations and liabilities in contracts, torts, and regulatory compliance.
Coverage Defenses
Coverage defenses in insurance law often hinge on the distinction between waiver and estoppel, where waiver involves the voluntary relinquishment of a known right, and estoppel prevents a party from asserting a right due to their prior conduct or representations. Understanding these doctrines is critical for insurers to determine liability and coverage obligations accurately, especially when a policyholder relies on insurer actions or inactions that imply coverage.
Promissory Estoppel
Promissory estoppel prevents a party from reneging on a promise when the other party relies on it to their detriment, emphasizing enforceability without formal contract elements. Waiver involves voluntarily relinquishing a known right, while estoppel bars a party from asserting rights inconsistent with previous conduct, both serving as equitable defenses in contract disputes.
Waiver vs Estoppel Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com