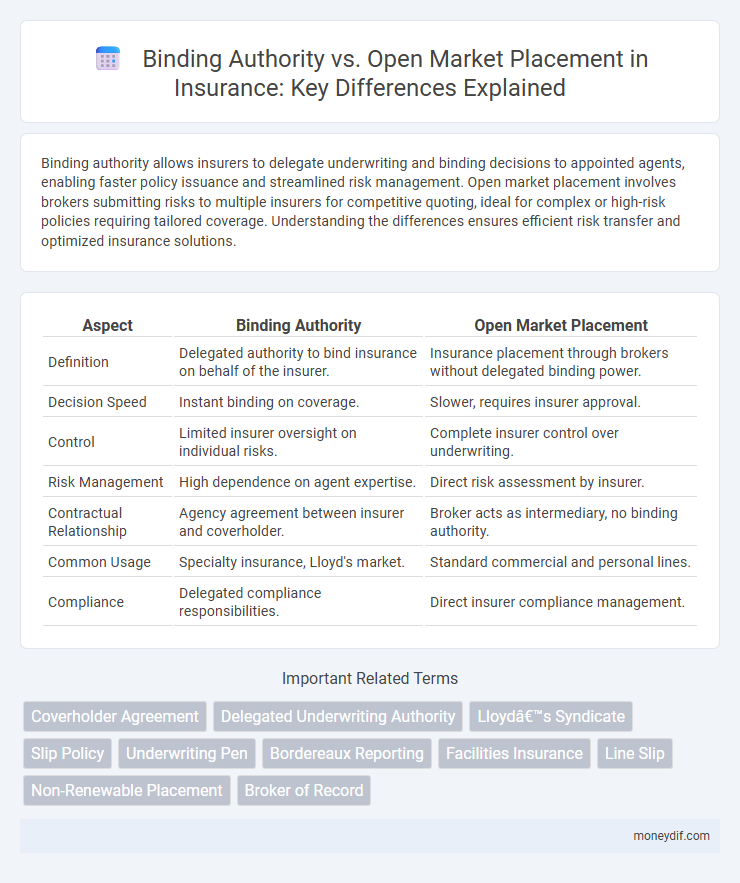
Binding authority allows insurers to delegate underwriting and binding decisions to appointed agents, enabling faster policy issuance and streamlined risk management. Open market placement involves brokers submitting risks to multiple insurers for competitive quoting, ideal for complex or high-risk policies requiring tailored coverage. Understanding the differences ensures efficient risk transfer and optimized insurance solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Binding Authority | Open Market Placement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delegated authority to bind insurance on behalf of the insurer. | Insurance placement through brokers without delegated binding power. |
| Decision Speed | Instant binding on coverage. | Slower, requires insurer approval. |
| Control | Limited insurer oversight on individual risks. | Complete insurer control over underwriting. |
| Risk Management | High dependence on agent expertise. | Direct risk assessment by insurer. |
| Contractual Relationship | Agency agreement between insurer and coverholder. | Broker acts as intermediary, no binding authority. |
| Common Usage | Specialty insurance, Lloyd's market. | Standard commercial and personal lines. |
| Compliance | Delegated compliance responsibilities. | Direct insurer compliance management. |
Understanding Binding Authority in Insurance
Understanding binding authority in insurance is crucial for efficient risk management, as it grants brokers or agents the legal power to underwrite policies and bind coverage on behalf of insurers. This authority streamlines the placement process by enabling immediate coverage without direct insurer approval for each policy, contrasting with open market placement where underwriters must review and approve risks individually. Proper utilization of binding authority accelerates policy issuance, reduces administrative burdens, and enhances client satisfaction by providing swift insurance solutions.
What Is Open Market Placement?
Open Market Placement refers to the process where an insurance broker negotiates coverage terms directly with multiple insurers without any binding authority, allowing clients to access the most competitive rates and tailored policies. This method provides greater flexibility and transparency compared to Binding Authority, where the insurer delegates underwriting power to the broker. Open Market Placement is essential for specialized or high-risk accounts requiring customized insurance solutions.
Key Differences Between Binding Authority and Open Market Placement
Binding authority allows an insurer-appointed agent or broker to underwrite and issue insurance policies on behalf of the insurer within predefined limits, enabling faster coverage issuance. Open market placement involves brokers soliciting quotes from multiple insurers for a client's risk without pre-approved underwriting authority, often leading to more tailored but time-consuming policy procurement. The key differences include control over underwriting, speed of issuance, and the scope of authority granted to intermediaries in the insurance process.
Advantages of Binding Authority Agreements
Binding authority agreements empower brokers to bind coverage instantly without insurer approval, accelerating policy issuance and enhancing client satisfaction. This delegated authority streamlines underwriting processes, reduces administrative overhead, and enables real-time risk assessment based on pre-agreed terms. Insurers benefit from expanded market reach and efficient resource allocation by leveraging broker expertise under binding authority arrangements.
Benefits and Limitations of Open Market Placement
Open Market Placement allows insurers to access a broad range of specialized markets and multiple providers, enhancing coverage options and competitive pricing for complex or large risks. This method offers increased flexibility in underwriting and terms negotiation but can involve longer processing times and higher administrative costs compared to Binding Authority arrangements. The transparency and diversity of the open market improve risk selection but may lack the streamlined efficiency and immediate coverage confirmation found in delegated binding authority models.
When to Choose Binding Authority vs Open Market Placement
Binding authority is ideal when insurers require immediate coverage commitments with predefined terms, enabling brokers to bind risks without prior insurer approval, which accelerates the underwriting process for standard or high-volume policies. Open market placement is preferable when risks are unique or complex, requiring tailored underwriting and competitive quotes from multiple insurers to secure optimal coverage and pricing. Choosing between binding authority and open market placement depends on the balance between the need for speed and the complexity or customization of the insurance risk.
Role of Coverholders in Binding Authority
Coverholders play a crucial role in binding authority by acting as delegated agents empowered to underwrite and bind insurance coverage on behalf of insurers, streamlining policy issuance and claims handling. Unlike open market placement where brokers negotiate terms directly with insurers, coverholders have the authority to make binding decisions within agreed parameters, enhancing efficiency and market penetration. Their delegated authority enables faster processing and access to specialized markets, reducing administrative burdens for insurers.
Regulatory Implications of Binding Authority and Open Market Placement
Binding authority grants insurers delegated underwriting power to bind coverage on behalf of carriers, streamlining policy issuance but requiring strict adherence to regulatory compliance and insurer guidelines to mitigate liability risks. Open market placement involves brokers securing coverage directly from multiple insurers without delegated authority, subjecting transactions to broader regulatory oversight and enhanced due diligence for compliance with local insurance laws. Regulatory frameworks mandate robust documentation, transparency, and clear delegation boundaries in binding authority, while open market placements emphasize broker accountability and market conduct standards to protect policyholders and maintain market integrity.
Impact on Policyholders: Binding Authority vs Open Market Placement
Binding Authority allows insurers to delegate underwriting and binding powers to brokers, resulting in faster policy issuance and immediate coverage for policyholders. Open Market Placement involves insurers reviewing and approving policies individually, which can delay coverage start times but may offer more tailored terms and competitive pricing. Policyholders benefit from quicker protection under Binding Authority, while Open Market Placement may provide enhanced customization and potentially better premiums.
Best Practices for Brokers in Both Insurance Placements
Brokers should leverage Binding Authority to expedite coverage by securing underwriting approval upfront, ensuring faster policy issuance and reducing client wait times. For Open Market Placement, thorough market research and tailored submission strategies enhance the likelihood of competitive quotes, while maintaining clear communication with insurers to manage expectations effectively. Best practices include maintaining strong insurer relationships, understanding risk appetite, and employing technology to streamline documentation and compliance in both placement types.
Important Terms
Coverholder Agreement
A Coverholder Agreement establishes the authority granted to a coverholder to underwrite insurance on behalf of an insurer, specifically delineating the scope of their binding authority to accept risks within pre-approved guidelines. Binding authority allows coverholders to issue policies directly, while open market placement involves insurers underwriting risks without predefined limits, requiring separate approval for each transaction.
Delegated Underwriting Authority
Delegated Underwriting Authority (DUA) allows insurers to authorize brokers or coverholders to underwrite policies and issue binding agreements directly, streamlining the Binding Authority process. In contrast, Open Market Placement requires brokers to submit risks for insurer approval without prior delegation, leading to longer turnaround times and less autonomy in underwriting decisions.
Lloyd’s Syndicate
Lloyd's Syndicates frequently utilize Binding Authority agreements to empower coverholders with the authority to underwrite risks on their behalf, streamlining underwriting processes and expanding market reach. In contrast, Open Market Placements involve direct negotiation between brokers and syndicates without delegated authority, allowing for more tailored coverage but often requiring more time and manual intervention.
Slip Policy
Slip policy serves as a provisional document outlining the terms and conditions agreed upon between the broker and insurer under a binding authority arrangement, enabling immediate coverage before the formal policy issuance. In contrast, open market placement involves negotiating terms directly with multiple insurers without predetermined binding authority, often resulting in longer lead times and varied policy commitments.
Underwriting Pen
Underwriting pens streamline the decision-making process by enabling brokers to submit risks directly to insurers within a binding authority framework, bypassing the open market placement that often requires multiple quotes. This method enhances efficiency and speeds up coverage issuance by leveraging delegated underwriting expertise and preset guidelines.
Bordereaux Reporting
Bordereaux reporting provides detailed data on premiums, claims, and exposures essential for managing Binding Authority agreements, allowing underwriters to monitor delegated authority efficiently. In contrast, open market placements rely less on bordereaux, as transactions are negotiated individually without standardized reporting obligations between brokers and underwriters.
Facilities Insurance
Facilities insurance involves pre-arranged agreements where brokers have delegated binding authority from insurers to underwrite risks directly, facilitating faster policy issuance. In contrast, open market placement requires brokers to submit risks to various insurers without pre-existing authority, leading to longer negotiation and underwriting processes.
Line Slip
Line slip serves as a facilitation mechanism within Binding Authority arrangements, enabling brokers to place risks swiftly without individual insurer approval, enhancing efficiency compared to Open Market Placement where each risk requires separate underwriting and acceptance. This streamlined process under Line Slip supports risk distribution among pre-agreed insurers, optimizing portfolio management and reducing time to market in complex insurance scenarios.
Non-Renewable Placement
Non-renewable placement in insurance refers to policies that cannot be renewed automatically, often requiring new underwriting with each term. Binding authority placement allows brokers to accept risks on behalf of insurers within preset limits, providing faster coverage compared to open market placement, where insurers individually assess and accept risks without delegated authority.
Broker of Record
A Broker of Record manages insurance policies by channeling binding authority transactions, enabling underwriters to issue coverage without insurer confirmation, unlike open market placements that require insurer approval for each risk. This role streamlines risk transfer in binding authority scenarios, contrasting with the negotiation and insurer engagement typical of open market placements.
Binding Authority vs Open Market Placement Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com