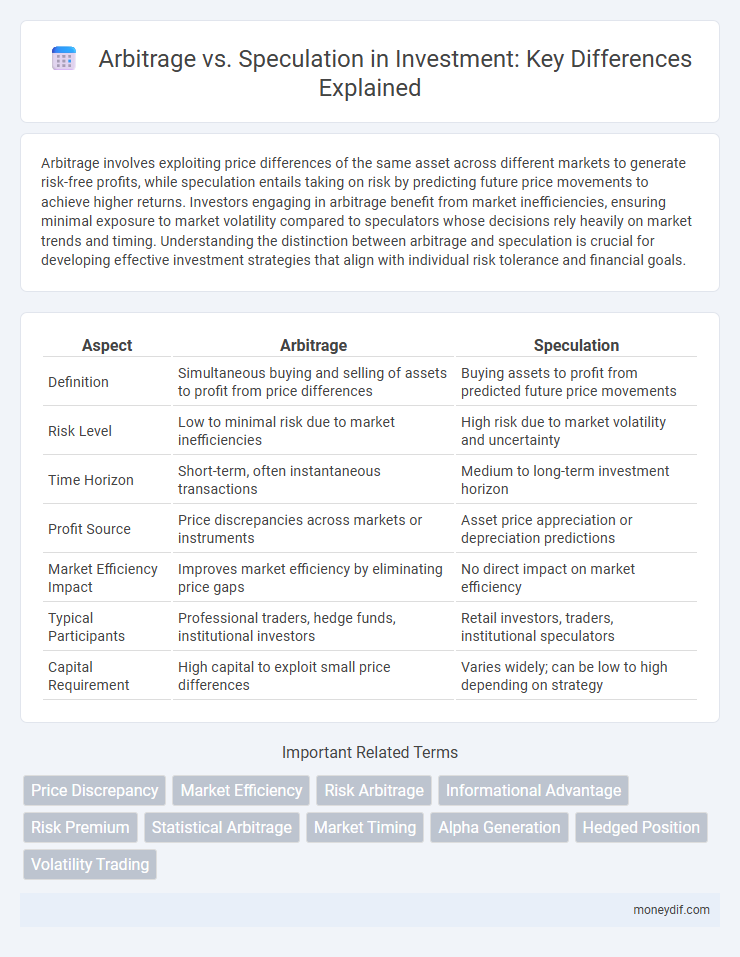
Arbitrage involves exploiting price differences of the same asset across different markets to generate risk-free profits, while speculation entails taking on risk by predicting future price movements to achieve higher returns. Investors engaging in arbitrage benefit from market inefficiencies, ensuring minimal exposure to market volatility compared to speculators whose decisions rely heavily on market trends and timing. Understanding the distinction between arbitrage and speculation is crucial for developing effective investment strategies that align with individual risk tolerance and financial goals.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Arbitrage | Speculation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simultaneous buying and selling of assets to profit from price differences | Buying assets to profit from predicted future price movements |
| Risk Level | Low to minimal risk due to market inefficiencies | High risk due to market volatility and uncertainty |
| Time Horizon | Short-term, often instantaneous transactions | Medium to long-term investment horizon |
| Profit Source | Price discrepancies across markets or instruments | Asset price appreciation or depreciation predictions |
| Market Efficiency Impact | Improves market efficiency by eliminating price gaps | No direct impact on market efficiency |
| Typical Participants | Professional traders, hedge funds, institutional investors | Retail investors, traders, institutional speculators |
| Capital Requirement | High capital to exploit small price differences | Varies widely; can be low to high depending on strategy |
Defining Arbitrage and Speculation
Arbitrage involves simultaneously buying and selling assets in different markets to exploit price discrepancies, ensuring risk-free profits. Speculation entails taking on higher risk by investing in assets with the hope of substantial returns based on market fluctuations. The key distinction lies in arbitrage's focus on riskless gains versus speculation's acceptance of risk for potential reward.
Core Principles of Arbitrage
Arbitrage involves exploiting price discrepancies of identical or similar assets across different markets to secure risk-free profits. Core principles include executing simultaneous buy and sell orders, ensuring no net market exposure, and capitalizing on price inefficiencies without directional market risk. This strategy contrasts with speculation, where investment decisions rely on predicting asset price movements and carrying inherent risk.
Core Principles of Speculation
Speculation in investment revolves around the core principle of anticipating price movements based on market trends and investor psychology, aiming to profit from short-term fluctuations. Unlike arbitrage, which exploits price discrepancies across markets with minimal risk, speculation involves higher risk and leverages market volatility. Successful speculation relies on in-depth market analysis, timing, and risk management to maximize returns.
Risk Profiles: Arbitrage vs Speculation
Arbitrage involves exploiting price differences across markets with minimal risk, typically yielding stable, low-return opportunities due to its market-neutral approach. Speculation carries higher risk by betting on price movements, aiming for substantial gains through market timing or directional bets, which can lead to significant volatility and potential losses. Risk profiles differ as arbitrage prioritizes capital preservation and consistency, while speculation accepts uncertainty for higher reward potential.
Required Skills and Tools
Arbitrage requires strong analytical skills, proficiency in real-time data analysis, and access to sophisticated trading platforms and algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across markets efficiently. Speculation demands a deep understanding of market trends, risk tolerance, and the ability to leverage technical and fundamental analysis tools for making informed predictions. Both strategies benefit from advanced software for monitoring market movements, but arbitrage emphasizes speed and precision, while speculation focuses on market insight and timing.
Market Conditions Favoring Arbitrage
Arbitrage thrives in highly efficient markets where price discrepancies between related assets or markets exist temporarily, allowing investors to exploit risk-free profit opportunities. Favorable market conditions include low transaction costs, high liquidity, and synchronized information flow across exchanges, which enhance the velocity and accuracy of arbitrage strategies. In contrast to speculation, arbitrage depends on market inefficiencies rather than predicting price movements, making it less exposed to market volatility and uncertainty.
Market Conditions Favoring Speculation
Speculation thrives in volatile market conditions characterized by rapid price fluctuations and high uncertainty, where traders seek to profit from short-term price movements. Liquidity levels and market inefficiencies create opportunities for speculative strategies to capitalize on mispricings. Unlike arbitrage, speculation depends on market trends and investor sentiment rather than price convergence between related assets.
Potential Returns and Profitability
Arbitrage involves exploiting price discrepancies across markets to achieve low-risk, consistent returns, often with limited profit margins per trade but high total profitability through volume. Speculation carries higher risk by betting on asset price movements, offering the potential for substantial returns but with increased volatility and uncertainty. Investors seeking steady profitability typically prefer arbitrage, while those pursuing significant gains accept speculation's elevated risk.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Arbitrage involves exploiting price differences across markets with minimal risk, often subject to strict regulatory oversight to prevent market manipulation and ensure transparency. Speculation carries higher risk by betting on price movements, attracting regulatory scrutiny aimed at curbing excessive volatility and protecting investors. Ethical considerations emphasize arbitrage's role in market efficiency, while speculation raises concerns about potential market destabilization and conflicts of interest.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Investors
Arbitrage offers investors a low-risk strategy by exploiting price discrepancies across markets, ensuring consistent returns through simultaneous buying and selling. Speculation involves higher risk as investors bet on price movements, aiming for substantial profits by predicting market trends. Choosing the right strategy depends on risk tolerance, investment goals, and market conditions, where arbitrage suits conservative investors and speculation appeals to those seeking aggressive growth.
Important Terms
Price Discrepancy
Price discrepancy occurs when the same asset trades at different prices across markets, enabling arbitrageurs to profit by simultaneously buying low and selling high. Speculators influence price discrepancies by anticipating market movements and taking positions that can either accentuate or reduce these differences, affecting market efficiency.
Market Efficiency
Market efficiency reflects how quickly and accurately prices incorporate all available information, minimizing opportunities for arbitrage--the practice of profiting from price discrepancies across markets. Speculation, contrastingly, involves assuming risk based on anticipated price movements, which can sometimes challenge market efficiency by driving prices away from their fundamental values.
Risk Arbitrage
Risk arbitrage involves exploiting price inefficiencies during mergers and acquisitions by purchasing stock in target companies, aiming to profit from the deal's successful completion, contrasting with speculation that relies on predicting price movements without underlying transactional events. Unlike speculative trading, risk arbitrage uses detailed analysis of deal structures and regulatory outcomes, positioning it as a strategic investment rather than a pure bet on market volatility.
Informational Advantage
Informational advantage in arbitrage involves exploiting price discrepancies across markets using superior data or analysis, enabling risk-free profit opportunities, whereas in speculation it centers on predicting future price movements based on market trends and insights, often involving higher risk. Arbitrage relies on real-time, accurate information to execute simultaneous trades, while speculation benefits from advanced informational analytics to anticipate market shifts.
Risk Premium
Risk premium represents the extra return investors demand for holding a risky asset compared to a risk-free one, playing a crucial role in distinguishing arbitrage from speculation. Arbitrage involves exploiting price discrepancies without bearing significant risk, while speculation entails assuming risk to achieve higher risk premiums through market predictions.
Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage leverages quantitative models and historical price data to identify and exploit temporary pricing inefficiencies across related assets, contrasting with speculation that primarily relies on directional market predictions and investor sentiment. While arbitrage aims for risk-neutral profit through price convergence, speculation involves higher risk exposure betting on asset price movements.
Market Timing
Market timing involves strategically entering or exiting positions based on anticipated price movements, distinct from arbitrage which exploits price discrepancies across markets for risk-free profit; speculation, by contrast, assumes higher risk with the goal of capitalizing on market volatility. Efficient market timing requires deep analysis of market indicators and liquidity patterns, whereas arbitrage relies on simultaneous transactions, and speculation depends heavily on market sentiment and forecasting accuracy.
Alpha Generation
Alpha Generation in finance involves generating excess returns by exploiting market inefficiencies, often through arbitrage strategies that capitalize on price discrepancies without taking significant market risk. In contrast, speculation relies on predicting future price movements and assumes higher risk, aiming for profit through directional bets rather than risk-neutral arbitrage opportunities.
Hedged Position
A hedged position minimizes risk exposure by offsetting potential losses in one asset with gains in another, contrasting with speculative strategies that actively seek profit from price fluctuations without protective offsets. Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across markets for risk-free profits, while speculation involves higher risk by betting on market movements without hedging.
Volatility Trading
Volatility trading exploits price fluctuations to generate profits by leveraging changes in implied volatility rather than directional price movements, distinguishing it clearly from speculation, which bets on asset price directions. Arbitrage in volatility trading focuses on capturing risk-free or low-risk profits through mispriced volatility instruments, whereas speculation involves taking directional volatility risks to benefit from market uncertainties.
Arbitrage vs Speculation Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com