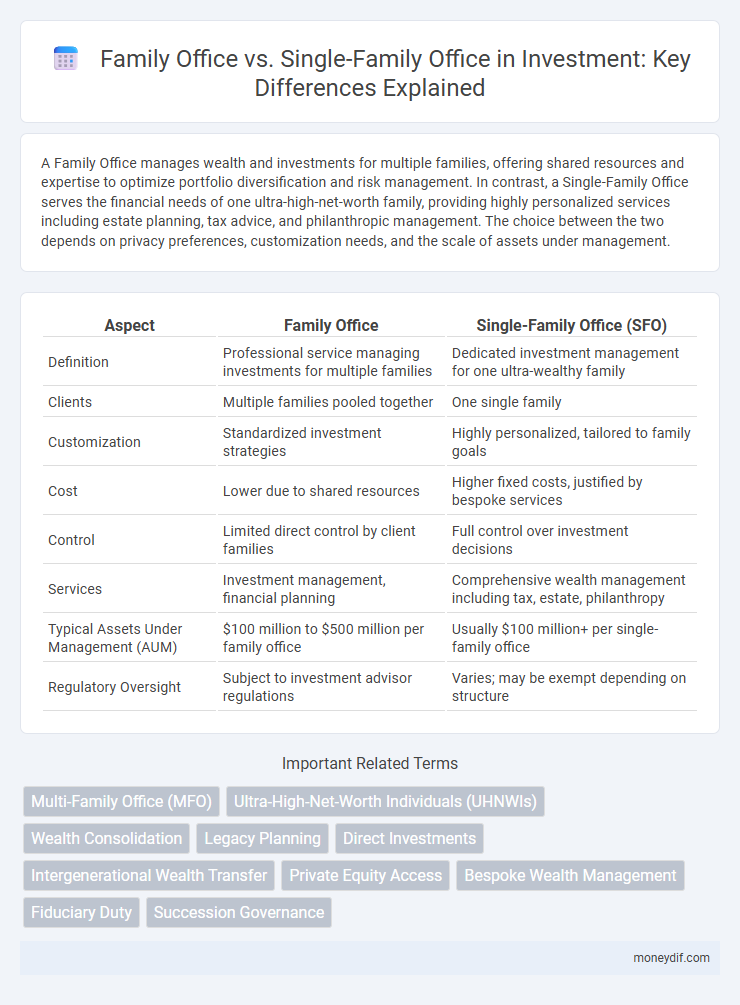
A Family Office manages wealth and investments for multiple families, offering shared resources and expertise to optimize portfolio diversification and risk management. In contrast, a Single-Family Office serves the financial needs of one ultra-high-net-worth family, providing highly personalized services including estate planning, tax advice, and philanthropic management. The choice between the two depends on privacy preferences, customization needs, and the scale of assets under management.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Family Office | Single-Family Office (SFO) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Professional service managing investments for multiple families | Dedicated investment management for one ultra-wealthy family |
| Clients | Multiple families pooled together | One single family |
| Customization | Standardized investment strategies | Highly personalized, tailored to family goals |
| Cost | Lower due to shared resources | Higher fixed costs, justified by bespoke services |
| Control | Limited direct control by client families | Full control over investment decisions |
| Services | Investment management, financial planning | Comprehensive wealth management including tax, estate, philanthropy |
| Typical Assets Under Management (AUM) | $100 million to $500 million per family office | Usually $100 million+ per single-family office |
| Regulatory Oversight | Subject to investment advisor regulations | Varies; may be exempt depending on structure |
Understanding Family Offices: An Overview
Family offices manage the wealth and investments of high-net-worth families, offering tailored financial planning, estate management, and philanthropic coordination. A single-family office (SFO) serves one family exclusively, providing highly personalized services with complete control over investment decisions and confidentiality. In contrast, multi-family offices (MFOs) pool resources from multiple families, offering cost efficiencies but less customization compared to SFOs.
What Is a Single-Family Office?
A Single-Family Office (SFO) is a private wealth management firm established exclusively to serve the financial and personal needs of one affluent family. Unlike multi-family offices, SFOs offer highly customized investment strategies, estate planning, tax services, and philanthropic management tailored to the specific goals and values of the single family they represent. By concentrating resources and expertise, Single-Family Offices provide comprehensive, integrated solutions that preserve and grow generational wealth over the long term.
Key Differences Between Multi-Family and Single-Family Offices
Multi-family offices serve multiple wealthy families, offering a broad range of investment management, estate planning, and financial advisory services under one organizational structure, while single-family offices cater exclusively to one family's unique financial needs and preferences. Multi-family offices benefit from economies of scale and diversified expertise, but may provide less personalized service compared to the highly customized strategies developed by single-family offices. Key differences include levels of control, cost efficiency, and the degree of confidentiality tailored to individual family requirements.
Advantages of Single-Family Offices
Single-Family Offices offer personalized investment strategies tailored exclusively to the specific wealth, goals, and risk tolerance of one family, ensuring greater control and confidentiality. They provide direct access to bespoke opportunities, including private equity, real estate, and impact investing, which are often unavailable through Multi-Family Offices. The dedicated team aligned with the family's legacy and values enhances strategic wealth preservation, tax optimization, and intergenerational wealth transfer.
Benefits of Multi-Family Offices
Multi-family offices offer diversified investment opportunities by pooling resources from multiple wealthy families, reducing costs through economies of scale and enhancing access to exclusive deals and top-tier asset managers. They provide comprehensive wealth management services including estate planning, tax optimization, and philanthropy coordination, tailored to the collective needs of their clients. This collaborative approach fosters risk mitigation and strategic portfolio diversification, outperforming the typically limited scope of single-family offices.
Cost Considerations: Family Office Vs Single-Family Office
Family offices typically pool resources to serve multiple families, significantly reducing per-family administrative and operational costs compared to single-family offices, which incur higher expenses due to exclusive, tailored services and dedicated staff. Single-family offices require substantial initial capital and ongoing investment to maintain personalized wealth management, legal, tax, and lifestyle services, making them cost-effective primarily for ultra-high-net-worth families with assets often exceeding $100 million. The cost efficiency of multi-family offices appeals to families seeking comprehensive investment management without the financial burden of establishing and running an independent single-family office.
Governance Structures in Family Offices
Family offices employ distinct governance structures that reflect their operational scope, with multi-family offices typically featuring formalized boards and committees to manage diverse client interests and ensure regulatory compliance. Single-family offices prioritize centralized governance, often led by family members or trusted advisors, enabling tailored decision-making aligned with the family's long-term wealth preservation and legacy goals. Robust governance frameworks in both models are critical for transparency, risk management, and aligning investment strategies with the unique priorities of family stakeholders.
Privacy and Customization: Which Model Excels?
Single-Family Offices (SFOs) excel in privacy by serving one family's wealth, allowing for highly customized investment strategies tailored to unique risk tolerances and legacy goals. Family Offices (multi-family models) offer economies of scale but may compromise individual privacy as resources and information are shared among multiple families. For ultra-high-net-worth families prioritizing confidentiality and bespoke financial services, SFOs provide superior control and personalization in wealth management.
Choosing the Right Family Office Structure
Choosing the right family office structure depends on the complexity of wealth, privacy preferences, and cost considerations. Single-family offices offer tailored services for ultra-high-net-worth families seeking exclusive control and customization, while multi-family offices provide shared resources and diversified expertise at a lower cost. Evaluating asset size, liquidity needs, and governance requirements ensures alignment with long-term investment and legacy goals.
Future Trends in Family Office Services
Future trends in family office services emphasize increased adoption of technology-driven wealth management platforms and artificial intelligence for personalized investment strategies. Growth in environmental, social, and governance (ESG) integration and impact investing reflects rising demand among family offices for sustainable and ethical portfolios. Single-family offices are poised to enhance multi-generational wealth transfer solutions and expand concierge services to support holistic family needs beyond traditional investment management.
Important Terms
Multi-Family Office (MFO)
Multi-Family Offices (MFOs) provide shared wealth management services for multiple families, offering cost efficiencies and diversified expertise compared to Single-Family Offices (SFOs), which serve the exclusive financial needs of a single family.
Ultra-High-Net-Worth Individuals (UHNWIs)
Ultra-High-Net-Worth Individuals (UHNWIs) typically choose Single-Family Offices for personalized wealth management and Family Offices for shared resources and diversified investment strategies.
Wealth Consolidation
Wealth consolidation through a family office offers centralized asset management and tailored services, while a single-family office provides exclusive, customized oversight for one family's unique financial and administrative needs.
Legacy Planning
Legacy planning through a Family Office offers tailored wealth management for multiple families, whereas a Single-Family Office provides exclusive, personalized financial and administrative services dedicated to one family's unique legacy goals.
Direct Investments
Direct investments by family offices differ as single-family offices typically engage in personalized, long-term asset management while multi-family offices focus on diversified client portfolios and shared investment opportunities.
Intergenerational Wealth Transfer
Intergenerational wealth transfer strategies vary between multi-family offices offering diversified services to multiple families and single-family offices providing tailored, exclusive financial management for one family's legacy.
Private Equity Access
Private Equity access varies between Family Offices, which manage multiple wealthy families' investments, and Single-Family Offices, dedicated to one family's tailored strategies and direct deal sourcing.
Bespoke Wealth Management
Bespoke Wealth Management tailors financial strategies uniquely for Family Offices, distinguishing Single-Family Offices by their exclusive service to one family's comprehensive wealth needs.
Fiduciary Duty
Fiduciary duty in a Family Office, especially a Single-Family Office, mandates acting in the utmost good faith and loyalty to manage and protect the family's wealth, investments, and legacy with personalized, transparent, and compliant governance.
Succession Governance
Succession governance in family offices ensures seamless leadership transition and asset preservation, with single-family offices offering tailored, centralized control compared to the diversified oversight typical of multi-family offices.
Family Office vs Single-Family Office Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com