Buy-and-hold investing emphasizes long-term growth by maintaining a portfolio through market fluctuations, reducing the impact of short-term volatility and transaction costs. Market timing attempts to capitalize on market trends by predicting highs and lows, but it often results in increased risk and potential losses due to timing errors. Studies consistently show that buy-and-hold strategies outperform market timing over extended periods, making them a preferred approach for most investors.
Table of Comparison
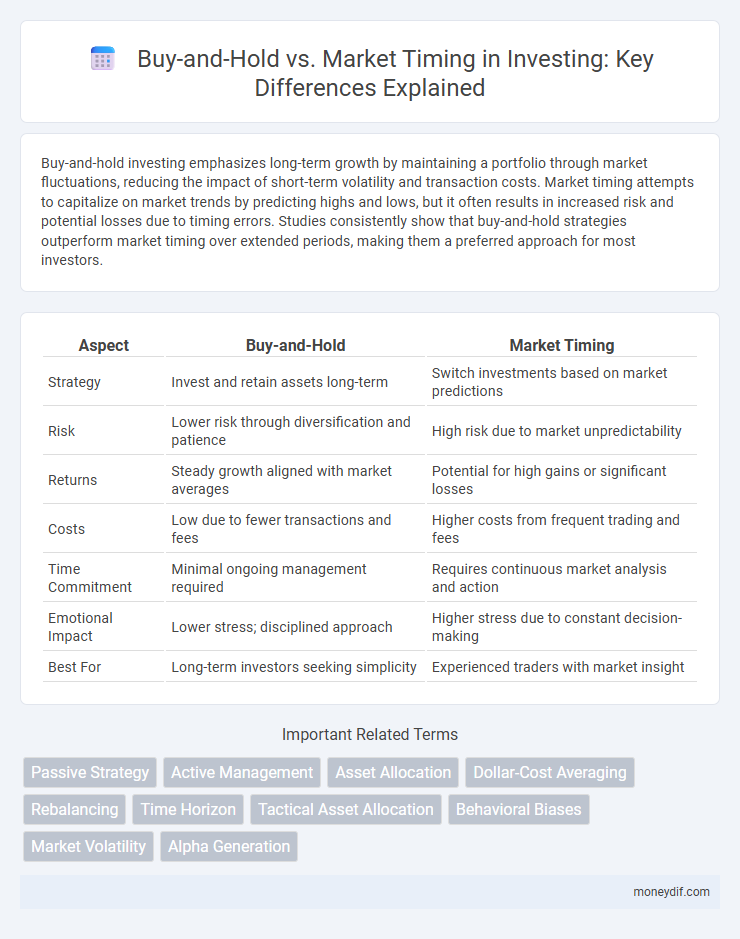
| Aspect | Buy-and-Hold | Market Timing |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy | Invest and retain assets long-term | Switch investments based on market predictions |
| Risk | Lower risk through diversification and patience | High risk due to market unpredictability |
| Returns | Steady growth aligned with market averages | Potential for high gains or significant losses |
| Costs | Low due to fewer transactions and fees | Higher costs from frequent trading and fees |
| Time Commitment | Minimal ongoing management required | Requires continuous market analysis and action |
| Emotional Impact | Lower stress; disciplined approach | Higher stress due to constant decision-making |
| Best For | Long-term investors seeking simplicity | Experienced traders with market insight |
Introduction to Buy-and-Hold and Market Timing Strategies
Buy-and-hold strategy involves purchasing securities and maintaining the investment over long periods to capitalize on market growth and compound interest. Market timing strategy attempts to predict market movements to buy low and sell high, requiring precise forecasting and frequent trading. Historical data shows buy-and-hold often outperforms market timing due to reduced transaction costs and minimized risk of mistiming the market.
Understanding the Core Principles
Buy-and-hold strategy involves purchasing securities and holding them long-term to benefit from market growth and compounding returns. Market timing attempts to predict market highs and lows to buy low and sell high, but often risks missing key market gains due to volatility. Understanding these core principles helps investors align strategies with their risk tolerance and investment goals.
Historical Performance Comparison
Historical performance data indicates that buy-and-hold strategies generally outperform market timing due to consistent exposure to market growth and dividends. Market timing often results in missed gains during key market upswings, reducing overall returns and increasing volatility. Studies show that over long investment horizons, buy-and-hold investors typically achieve higher compound annual growth rates compared to those attempting to time market entries and exits.
Risk Management Approaches
Buy-and-hold investment strategies emphasize long-term risk management by minimizing transaction costs and avoiding market timing errors that can result from emotional decision-making. Market timing involves attempting to predict market highs and lows, which increases the risk of mistiming trades, leading to potential losses and higher volatility exposure. Effective risk management often favors buy-and-hold due to its disciplined approach and reduced sensitivity to short-term market fluctuations.
Impact of Emotions and Behavioral Biases
Emotions and behavioral biases such as fear and greed profoundly impact both buy-and-hold and market timing investment strategies, often leading to suboptimal decisions. Buy-and-hold investors face challenges like loss aversion that may trigger premature selling during market downturns, whereas market timers are more susceptible to overtrading driven by overconfidence and herd behavior. Understanding cognitive biases like anchoring and confirmation bias is essential to mitigate emotional reactions and improve long-term investment outcomes.
Costs and Tax Implications
Buy-and-hold investment strategies minimize transaction costs by reducing frequent trading, leading to lower brokerage fees and capital gains taxes compared to market timing, which often incurs higher expenses due to frequent buying and selling. Market timing increases the likelihood of short-term capital gains taxes, which are typically taxed at higher rates than long-term gains realized through buy-and-hold investments. Understanding these cost and tax implications is essential for maximizing after-tax returns and optimizing portfolio growth over time.
Time Commitment and Effort Required
Buy-and-hold investing demands minimal time commitment and effort, as it involves purchasing assets and holding them long-term without frequent monitoring. Market timing requires continuous analysis of market trends, economic indicators, and rapid decision-making, resulting in significant time investment and increased effort. Investors aiming for a low-maintenance portfolio often prefer buy-and-hold to avoid the complexities and stress of timing the market.
Suitability for Different Investor Profiles
Buy-and-hold strategies suit long-term investors seeking steady growth with lower transaction costs and reduced emotional decision-making, ideal for risk-averse individuals or retirees. Market timing appeals to active traders comfortable with high risk and frequent trading, aiming to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations. Understanding personal risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market knowledge is essential to choosing between these approaches effectively.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Buy-and-hold investing is often misunderstood due to the myth that market timing guarantees higher returns, but studies show consistent long-term gains typically outperform attempts to predict short-term market movements. Common misconceptions include the belief that selling during market dips prevents losses, whereas missing just a few key market rallies can significantly reduce overall portfolio growth. Research from financial experts highlights that emotional reactions to market volatility often lead to poor investment decisions, underscoring the value of disciplined, long-term strategies.
Which Strategy Wins: Key Takeaways
Buy-and-hold investing consistently outperforms market timing by capitalizing on long-term market growth and minimizing transaction costs. Research shows investors who stay invested through market fluctuations tend to achieve higher returns than those trying to predict short-term market movements. Key takeaways highlight the importance of patience, discipline, and avoiding emotional decisions to maximize portfolio growth over time.
Important Terms
Passive Strategy
Passive strategy focuses on a Buy-and-Hold approach by maintaining a consistent investment portfolio over time, minimizing trading activity and transaction costs. This method contrasts with Market Timing, which attempts to predict market fluctuations to buy low and sell high but often incurs higher risk and fees without guaranteed success.
Active Management
Active management involves frequent portfolio adjustments aiming to outperform market benchmarks, contrasting with buy-and-hold strategies that emphasize long-term holding regardless of market fluctuations. Market timing, a key component of active management, seeks to capitalize on market volatility but often underperforms due to timing errors and transaction costs.
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation balances investment risk and return by diversifying assets across stocks, bonds, and cash, which supports a buy-and-hold strategy that capitalizes on long-term market growth. Market timing attempts to predict short-term market movements but often leads to suboptimal performance due to the difficulty of accurately forecasting market fluctuations.
Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) reduces the impact of market volatility by investing fixed amounts regularly, contrasting with market timing strategies that attempt to predict short-term price movements. This approach aligns closely with the buy-and-hold philosophy, promoting consistent investment regardless of market conditions to build wealth over time.
Rebalancing
Rebalancing maintains an optimal asset allocation by systematically adjusting portfolio weights, contrasting with buy-and-hold strategies that accept drift without intervention and market timing approaches that attempt to predict market movements. Studies show rebalancing can enhance risk-adjusted returns by capitalizing on market volatility, whereas market timing often incurs higher transaction costs and timing errors, leading to suboptimal performance relative to disciplined buy-and-hold or rebalanced portfolios.
Time Horizon
A longer time horizon enhances the effectiveness of a buy-and-hold strategy by allowing investments to recover from short-term market fluctuations, while market timing attempts to capitalize on short-term price movements but carries higher risks and requires precise predictions. Historical data shows that buy-and-hold investors often achieve more consistent long-term returns compared to market timers, who may miss significant market gains during critical periods.
Tactical Asset Allocation
Tactical Asset Allocation dynamically adjusts portfolio weights based on short- to intermediate-term market forecasts, aiming to capitalize on market inefficiencies and outperform a static Buy-and-Hold strategy. Unlike Buy-and-Hold, which passively maintains fixed asset proportions, Tactical Asset Allocation incorporates market timing signals to reduce downside risk and enhance returns by shifting exposures among equities, bonds, and cash.
Behavioral Biases
Behavioral biases such as overconfidence and loss aversion often lead investors to favor market timing despite evidence supporting the buy-and-hold strategy's superior long-term returns. Data from numerous studies reveal that buy-and-hold investors typically avoid costly emotional decision-making errors, resulting in more consistent wealth accumulation compared to those attempting to time market fluctuations.
Market Volatility
Market volatility significantly impacts the effectiveness of buy-and-hold versus market timing strategies, with buy-and-hold benefiting from long-term market growth despite short-term fluctuations, while market timing attempts to capitalize on price swings but risks mistiming and increased transaction costs. Research shows that consistent buy-and-hold investors generally outperform market timing due to the difficulty in predicting volatile market movements accurately.
Alpha Generation
Alpha Generation strategies often outperform Buy-and-Hold by actively exploiting market timing to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations and economic indicators. This dynamic approach hinges on precise market entry and exit points to generate excess returns beyond passive investment benchmarks.
Buy-and-Hold vs Market Timing Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com