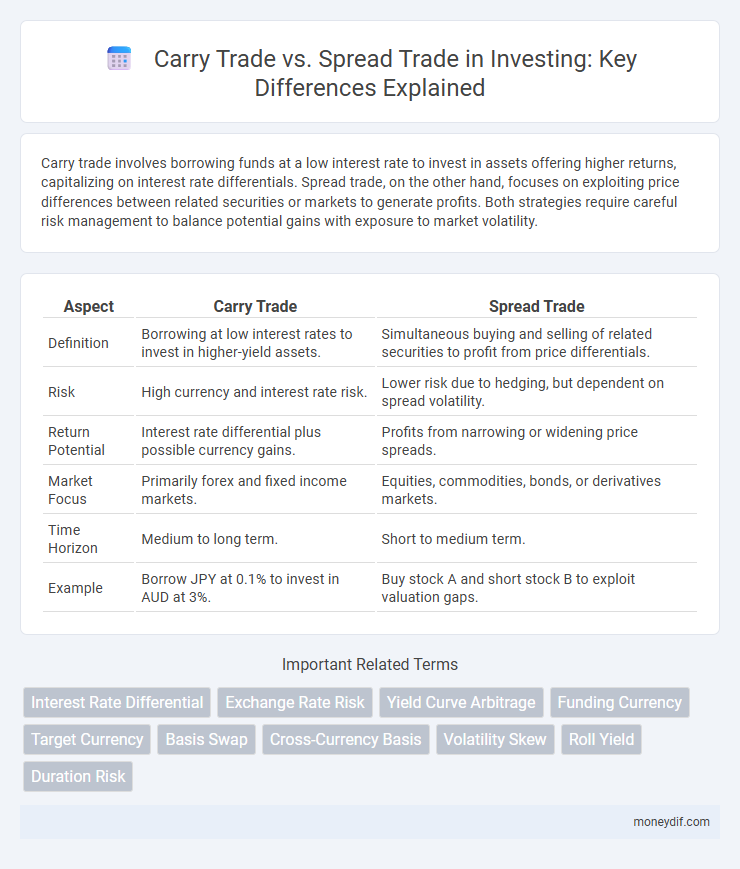
Carry trade involves borrowing funds at a low interest rate to invest in assets offering higher returns, capitalizing on interest rate differentials. Spread trade, on the other hand, focuses on exploiting price differences between related securities or markets to generate profits. Both strategies require careful risk management to balance potential gains with exposure to market volatility.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Carry Trade | Spread Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Borrowing at low interest rates to invest in higher-yield assets. | Simultaneous buying and selling of related securities to profit from price differentials. |
| Risk | High currency and interest rate risk. | Lower risk due to hedging, but dependent on spread volatility. |
| Return Potential | Interest rate differential plus possible currency gains. | Profits from narrowing or widening price spreads. |
| Market Focus | Primarily forex and fixed income markets. | Equities, commodities, bonds, or derivatives markets. |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long term. | Short to medium term. |
| Example | Borrow JPY at 0.1% to invest in AUD at 3%. | Buy stock A and short stock B to exploit valuation gaps. |
Understanding Carry Trade and Spread Trade
Carry trade involves borrowing funds in a currency with a low interest rate and investing in a currency offering a higher interest rate, profiting from the interest rate differential. Spread trade focuses on capitalizing on the price difference between related financial instruments or asset classes, aiming to exploit the volatility or trends in spread movements. Both strategies require risk management but differ in core mechanics--carry trade targets yield arbitrage through interest rates, while spread trade seeks gains through relative price changes.
Key Differences Between Carry Trade and Spread Trade
Carry Trade involves borrowing funds in a low-interest-rate currency to invest in a high-interest-rate currency, profiting from the interest rate differential, while Spread Trade focuses on exploiting price differences between related financial instruments or markets. Carry Trade carries risks related to exchange rate fluctuations and interest rate changes, whereas Spread Trade aims to mitigate risk through hedging by taking offsetting positions. The primary distinction lies in Carry Trade's dependence on macroeconomic factors like interest rate differentials, contrasted with Spread Trade's reliance on relative price movements within correlated assets.
How Carry Trade Works in Practice
Carry trade involves borrowing funds in a currency with low interest rates and investing in assets denominated in a currency with higher interest rates to capture the interest rate differential known as the "carry." Investors profit if the exchange rate remains stable or moves favorably, amplifying gains from interest rate spreads. Effective carry trade strategies rely on careful currency risk management and monitoring global macroeconomic conditions that influence interest rates and currency movements.
Mechanics of Spread Trading Explained
Spread trading involves simultaneously buying one security and selling another related security to exploit price differentials, minimizing market risk by taking offsetting positions. Unlike carry trade, which relies on earning returns from interest rate differentials between currencies, spread trading focuses on identifying and profiting from the relative price movement between two correlated instruments. This strategy requires precise timing and market analysis to capture narrow spreads, making it popular in futures, options, and forex markets for arbitrage opportunities.
Major Risks Associated With Carry and Spread Trades
Carry trades involve borrowing in low-interest-rate currencies and investing in high-interest-rate assets, exposing investors to significant exchange rate risk that can erode profits quickly. Spread trades, relying on the price differential between two related securities, face risks including market volatility and liquidity constraints, which can lead to unexpected losses if spreads widen or narrow contrary to positions. Both strategies require careful risk management, particularly around leverage, interest rate fluctuations, and currency market instability to avoid substantial financial losses.
Profit Opportunities in Carry Trade vs Spread Trade
Carry trade offers profit opportunities by capitalizing on interest rate differentials between currencies, allowing investors to earn returns through the interest rate spread while also benefiting from currency appreciation. Spread trade profits arise from exploiting price differences between related financial instruments, such as futures contracts or bond yields, focusing primarily on market inefficiencies and arbitrage opportunities. Compared to spread trading, carry trade can generate more consistent income in stable interest rate environments but carries higher currency risk.
Essential Tools and Strategies for Each Trade Type
Carry trade strategies require monitoring interest rate differentials and currency volatility through tools like economic calendars, interest rate forecasts, and forex analytics platforms. Spread trade involves utilizing price charts, technical indicators such as moving averages and Bollinger Bands, and risk management software to capitalize on price discrepancies between related assets. Integrating real-time data feeds and automated trading systems enhances decision-making efficiency for both carry and spread trades.
Currency Pairs and Markets Best Suited for Carry and Spread Trades
Carry trade thrives in stable, high-yield currency pairs such as AUD/JPY, NZD/JPY, and USD/TRY, leveraging interest rate differentials in emerging and developed markets with predictable macroeconomic trends. Spread trade performs best in highly liquid forex markets like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/CHF, capitalizing on narrow bid-ask spreads and low transaction costs for frequent long and short positions. Understanding market volatility and central bank policies helps investors optimize strategies between carry trade's interest rate gains and spread trade's execution efficiency.
Historical Performance: Carry Trade vs Spread Trade
Historical performance of carry trade shows consistent profits derived from interest rate differentials, particularly during stable economic periods with low volatility. Spread trade, which capitalizes on price discrepancies between related assets, demonstrates varied returns influenced by market inefficiencies and timing accuracy. Empirical data suggests carry trade outperforms in steady market conditions, while spread trade offers higher potential gains during volatile or trending markets.
Which Strategy Fits Your Investment Goals?
Carry trade involves borrowing in low-interest-rate currencies to invest in higher-yielding assets, generating steady income for long-term investors seeking consistent returns with moderate risk. Spread trade focuses on exploiting price differences between related financial instruments, appealing to active traders aiming for short-term gains through market inefficiencies. Matching your investment goals with the strategy depends on your risk tolerance, time horizon, and desired income stability.
Important Terms
Interest Rate Differential
Interest Rate Differential (IRD) is crucial in carry trade strategies where investors borrow in low-interest currencies to invest in higher-yielding assets, profiting from the gap between borrowing and lending rates. In spread trades, IRD influences the simultaneous buying and selling of related financial instruments, capitalizing on discrepancies in their interest rates to generate returns while managing risk exposure.
Exchange Rate Risk
Exchange rate risk in carry trade arises from currency value fluctuations impacting interest rate differentials, while in spread trade, it affects the profit margin between simultaneous currency position spreads.
Yield Curve Arbitrage
Yield curve arbitrage exploits differences in bond yields across maturities, focusing on the relative value between short-term and long-term rates to generate profits. Carry trade targets earning the interest rate differential by borrowing low-yield currencies to invest in higher-yield assets, whereas spread trade centers on capturing the deviation between different yield spreads along the curve.
Funding Currency
Funding currency in carry trade involves borrowing low-interest-rate currencies to invest in high-yield assets, while spread trade exploits interest rate differentials between currency pairs without direct borrowing.
Target Currency
Target currency selection significantly impacts carry trade returns by influencing interest rate differentials, while spread trade strategies focus on exploiting price discrepancies regardless of currency interest rates.
Basis Swap
Basis swaps facilitate carry trades by exploiting interest rate differentials between currencies, whereas spread trades focus on profiting from yield curve variations within the same currency.
Cross-Currency Basis
Cross-currency basis reflects the cost differential between borrowing currencies in carry trade strategies and exploiting price discrepancies in spread trades within foreign exchange markets.
Volatility Skew
Volatility skew reflects market expectations of asymmetric risk in carry trades, where currency pairs with high interest rate differentials exhibit steeper skew compared to spread trades that focus on relative value within similar volatility ranges.
Roll Yield
Roll yield significantly impacts carry trade returns by capturing the profit from forward price convergence, whereas spread trade focuses on exploiting price differentials between related instruments without relying on roll yield.
Duration Risk
Duration risk in carry trade involves exposure to interest rate fluctuations over time, whereas spread trade primarily focuses on profit from the widening or narrowing of yield differentials between financial instruments.
Carry Trade vs Spread Trade Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com