Crowdfunding offers a diversified approach to investment by pooling small amounts of capital from a large number of individuals, reducing risk exposure while enabling access to a broad range of projects. Angel investing involves high-net-worth individuals providing significant funding, expertise, and mentorship, often leading to deeper involvement in the startup's growth and decision-making processes. Both methods present unique opportunities and challenges, with crowdfunding emphasizing scalability and community support, whereas angel investing prioritizes strategic guidance and higher potential returns.
Table of Comparison
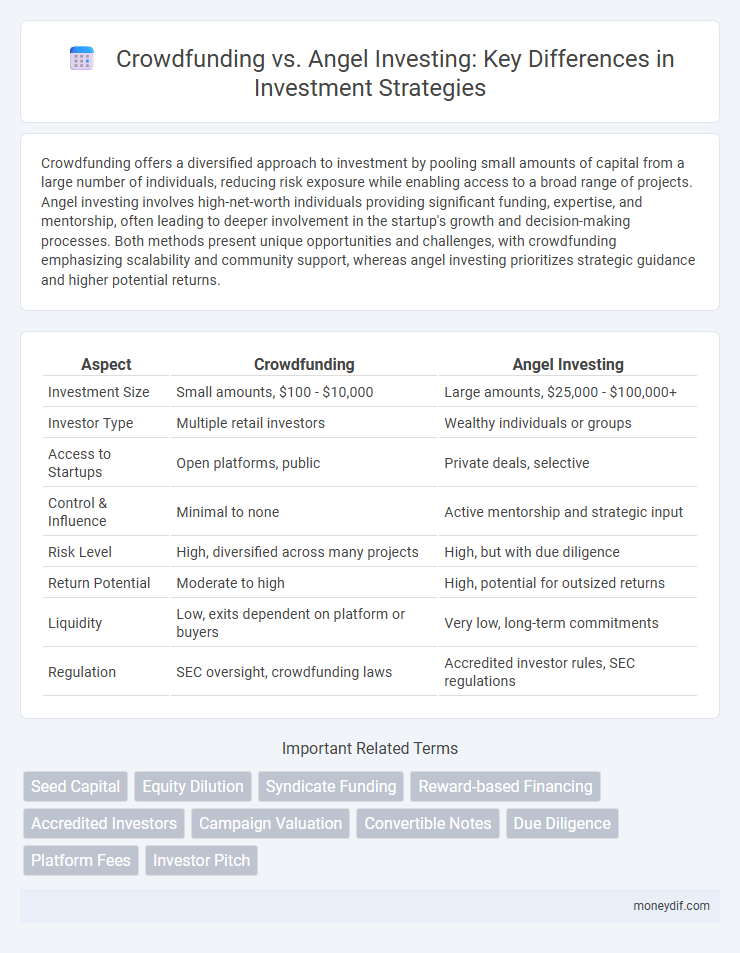
| Aspect | Crowdfunding | Angel Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Size | Small amounts, $100 - $10,000 | Large amounts, $25,000 - $100,000+ |
| Investor Type | Multiple retail investors | Wealthy individuals or groups |
| Access to Startups | Open platforms, public | Private deals, selective |
| Control & Influence | Minimal to none | Active mentorship and strategic input |
| Risk Level | High, diversified across many projects | High, but with due diligence |
| Return Potential | Moderate to high | High, potential for outsized returns |
| Liquidity | Low, exits dependent on platform or buyers | Very low, long-term commitments |
| Regulation | SEC oversight, crowdfunding laws | Accredited investor rules, SEC regulations |
Introduction to Crowdfunding and Angel Investing
Crowdfunding enables startups to raise capital from a large pool of small investors through online platforms, making it accessible and democratized. Angel investing involves high-net-worth individuals providing early-stage funding and mentorship, often in exchange for equity. Both funding methods play crucial roles in startup ecosystems, offering diverse opportunities for entrepreneurs and investors alike.
Key Differences Between Crowdfunding and Angel Investing
Crowdfunding involves raising small amounts of capital from a large number of individuals through online platforms, emphasizing broad public participation and lower entry barriers. Angel investing consists of high-net-worth individuals providing substantial capital along with mentorship and strategic guidance, typically in early-stage startups seeking rapid growth. Key differences include the scale and source of funding, investor involvement level, and regulatory requirements governing each investment type.
How Crowdfunding Works for Investors
Crowdfunding allows investors to pool smaller amounts of capital to fund startups or projects through online platforms, enabling access to diverse investment opportunities with relatively low minimum contributions. Investors receive equity, rewards, or debt repayment based on the funding model, with platforms facilitating due diligence, transaction processing, and regulatory compliance. This method democratizes investment access, reduces individual risk exposure, and offers potential for high returns, though it carries varying levels of risk depending on the project's success.
How Angel Investing Works for Investors
Angel investing involves high-net-worth individuals providing capital to early-stage startups in exchange for equity ownership, typically during the seed or initial growth phases. Investors conduct thorough due diligence, negotiate terms directly with founders, and often offer mentorship or strategic guidance alongside funding. This approach carries higher risk but presents potential for significant returns if the startup successfully scales or exits.
Risks and Rewards: Crowdfunding vs Angel Investing
Crowdfunding presents lower financial entry barriers but often involves higher risks due to less rigorous vetting and investor protection, leading to potentially diluted returns. Angel investing requires significant capital and offers greater risk exposure but provides access to high-growth startups with mentorship opportunities, often yielding substantial long-term rewards. Both investment types carry inherent risks, yet angel investing tends to balance risk with higher potential returns through active involvement and equity stakes.
Accessibility and Minimum Investment Requirements
Crowdfunding platforms democratize investment opportunities by allowing individuals to contribute small amounts, often starting at $10 to $100, making it highly accessible to a broad audience. Angel investing typically requires a higher minimum investment, frequently ranging from $25,000 to $100,000, limiting participation to accredited or high-net-worth investors. This contrast highlights crowdfunding as a more inclusive vehicle for early-stage investment, while angel investing offers deeper engagement but with significant financial commitment and investor qualifications.
Due Diligence: Evaluating Opportunities
Due diligence in crowdfunding involves assessing the platform's credibility, review of project details, and careful evaluation of potential risks by individual investors. Angel investing requires thorough analysis of the startup's business model, financial statements, market potential, and founder background to mitigate risks. Both approaches demand critical scrutiny to ensure alignment with investment goals and risk tolerance.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Crowdfunding involves raising capital from a large number of investors through online platforms, subject to securities regulations such as the SEC's Regulation Crowdfunding, which imposes limits on fundraising amounts and investor contributions to protect non-accredited investors. Angel investing typically entails high-net-worth individuals providing capital in exchange for equity, governed by fewer regulatory constraints but requiring compliance with accredited investor standards under SEC Rule 501. Both methods demand thorough due diligence on legal disclosures, compliance with anti-fraud provisions, and adherence to state and federal securities laws to mitigate potential liabilities.
Investor Roles and Influence in Startup Growth
Crowdfunding investors typically provide capital with limited involvement, focusing on funding startups through small contributions from a large group, which offers minimal influence on strategic decisions. Angel investors often bring significant capital alongside expertise, mentorship, and active participation in guiding startup growth, shaping business models, and expanding networks. This hands-on approach by angel investors can accelerate a startup's development compared to the more passive role of crowdfunding contributors.
Choosing the Right Investment Path for Your Goals
Evaluating Crowdfunding versus Angel Investing requires aligning each option with specific financial goals and risk tolerance. Crowdfunding offers diversified, low-entry investment opportunities in startups and projects, ideal for investors seeking exposure with limited capital. Angel investing demands higher capital and active involvement, providing potential for significant returns and influence over company growth, suitable for experienced investors aiming for long-term impact.
Important Terms
Seed Capital
Seed capital often marks the initial funding stage for startups, with crowdfunding providing access to a broad base of small investors through online platforms, while angel investing involves high-net-worth individuals offering significant sums alongside mentorship. Crowdfunding leverages collective contributions to validate market interest, whereas angel investors contribute not only funds but also strategic expertise, increasing the likelihood of early-stage success.
Equity Dilution
Equity dilution occurs when a startup issues new shares, reducing existing shareholders' ownership percentage; in crowdfunding, this often involves many small investors, while angel investing typically involves fewer investors with larger stakes, impacting dilution dynamics differently. Crowdfunding can lead to significant dilution due to numerous investors, whereas angel investors may negotiate terms to limit dilution while retaining substantial influence.
Syndicate Funding
Syndicate funding combines resources from multiple investors to back startups, blending elements of crowdfunding's broad appeal and angel investing's targeted capital and mentorship. This approach leverages group investment power while maintaining the strategic insights commonly found in angel investing, offering startups diversified funding sources and investors shared risk.
Reward-based Financing
Reward-based financing leverages platforms like Kickstarter to attract backers who receive non-financial incentives, contrasting with angel investing where high-net-worth individuals provide capital in exchange for equity stakes and potential influence on startup decisions. Crowdfunding excels in validating market demand at early stages, while angel investing offers substantial funds and mentorship critical for scaling and strategic growth.
Accredited Investors
Accredited investors, who meet specific income or net worth criteria defined by the SEC, play a crucial role in both crowdfunding and angel investing by providing significant capital to startups and early-stage companies. Crowdfunding platforms often open investment opportunities to non-accredited investors but reserve larger, higher-risk investments for accredited investors, whereas angel investing exclusively involves accredited individuals who actively mentor and invest larger sums in entrepreneurial ventures.
Campaign Valuation
Campaign valuation in crowdfunding typically relies on market feedback and audience engagement metrics, while angel investing valuation depends on detailed financial projections, startup potential, and investor negotiations. Crowdfunding valuations often reflect consumer interest and pre-sales enthusiasm, whereas angel investing involves assessing equity stakes and long-term growth opportunities.
Convertible Notes
Convertible notes are debt instruments commonly used in crowdfunding and angel investing to provide early-stage startups with flexible financing; they convert into equity during subsequent funding rounds, typically at a discounted valuation. In crowdfunding, convertible notes allow diverse, smaller investors to participate without setting immediate valuation, while angel investors leverage them for faster deal closure and favorable equity terms.
Due Diligence
Due diligence in crowdfunding focuses on assessing the platform's credibility, campaign transparency, and regulatory compliance, while angel investing requires a deeper evaluation of the startup's financial health, business model, and founder expertise. Angel investors typically conduct intensive market analysis, legal review, and risk assessment to make informed decisions, contrasting with crowdfunding's reliance on public validation and collective investor feedback.
Platform Fees
Platform fees in crowdfunding typically range from 5% to 10% of the total funds raised, covering marketing, payment processing, and administrative costs. In contrast, angel investing usually involves no platform fees as investments are made directly between the investor and startup, although legal and due diligence expenses may apply.
Investor Pitch
Investor pitch effectiveness hinges on highlighting the key differences between crowdfunding and angel investing, where crowdfunding offers access to a large pool of small investors and rapid capital accumulation, while angel investing provides strategic mentorship alongside substantial funding from experienced individuals. Understanding these dynamics enables startups to tailor their pitch by emphasizing scalability and community engagement for crowdfunding or personalized growth potential and long-term support for angel investors.
Crowdfunding vs Angel Investing Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com