Tactical Asset Allocation involves short-term adjustments to a portfolio, capitalizing on market inefficiencies and trends to enhance returns. Strategic Asset Allocation establishes a long-term investment mix based on risk tolerance and financial goals, maintaining consistent diversification across asset classes. Balancing both approaches can optimize portfolio performance by blending disciplined planning with responsive flexibility.
Table of Comparison
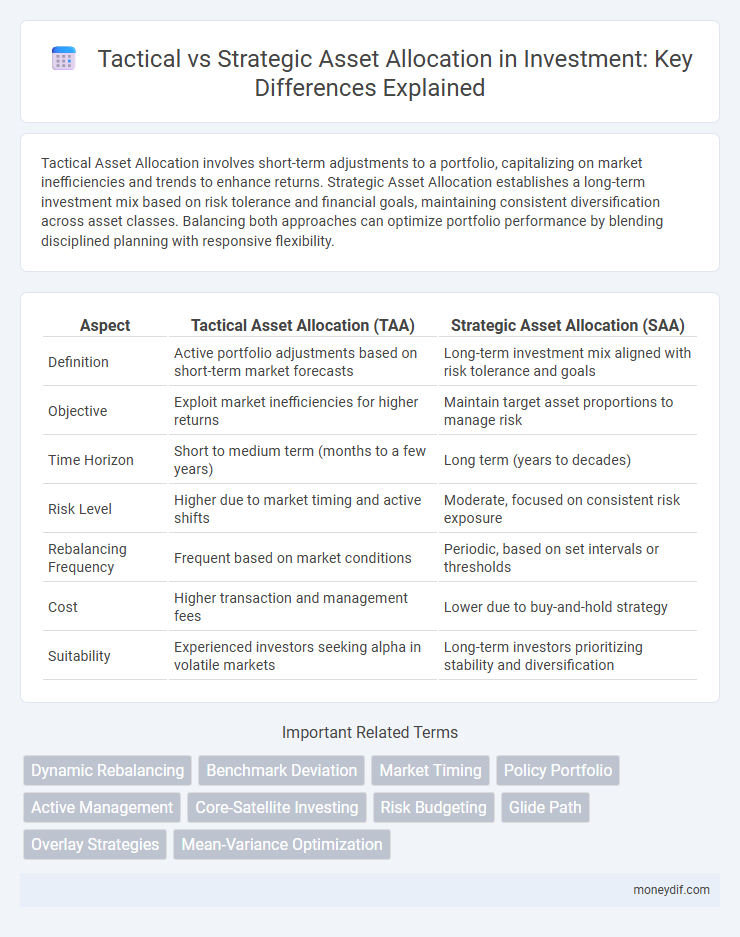
| Aspect | Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA) | Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active portfolio adjustments based on short-term market forecasts | Long-term investment mix aligned with risk tolerance and goals |
| Objective | Exploit market inefficiencies for higher returns | Maintain target asset proportions to manage risk |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term (months to a few years) | Long term (years to decades) |
| Risk Level | Higher due to market timing and active shifts | Moderate, focused on consistent risk exposure |
| Rebalancing Frequency | Frequent based on market conditions | Periodic, based on set intervals or thresholds |
| Cost | Higher transaction and management fees | Lower due to buy-and-hold strategy |
| Suitability | Experienced investors seeking alpha in volatile markets | Long-term investors prioritizing stability and diversification |
Understanding Tactical vs Strategic Asset Allocation
Tactical asset allocation involves actively adjusting portfolio weights to capitalize on short-term market opportunities and achieve immediate performance goals. Strategic asset allocation establishes a long-term investment mix based on an investor's risk tolerance, financial goals, and time horizon, maintaining consistent asset distribution despite market fluctuations. Understanding the difference helps investors balance market timing with disciplined investment planning to optimize risk and return.
Key Principles of Tactical Asset Allocation
Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA) involves actively adjusting portfolio weights based on short-term market forecasts to capitalize on expected opportunities and mitigate risks. Key principles include periodic rebalancing, market timing, and leveraging economic indicators to exploit temporary market inefficiencies while maintaining alignment with long-term strategic objectives. Effective TAA requires disciplined decision-making, continuous monitoring of asset valuations, and risk management strategies to enhance portfolio returns without significantly increasing volatility.
Fundamentals of Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic Asset Allocation involves establishing a long-term investment mix based on an investor's risk tolerance, financial goals, and investment horizon, emphasizing a stable portfolio structure. It relies on fundamental analysis of asset class returns, correlations, and economic expectations to optimize diversification and manage risk systematically. The approach regularly rebalances to maintain target weights, ensuring alignment with the investor's strategic objectives and minimizing market timing risks.
Comparing Investment Time Horizons
Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA) focuses on short- to medium-term investment horizons, allowing portfolio adjustments in response to market opportunities or risks to enhance returns or reduce losses. Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA) targets long-term investment goals by maintaining a fixed asset mix based on an investor's risk tolerance and time frame, providing stability through market fluctuations. Comparing these, TAA suits investors seeking flexibility and active management over months or years, while SAA benefits those prioritizing consistent growth over decades.
Risk Management in Tactical and Strategic Approaches
Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA) actively adjusts portfolio weights to exploit short-term market opportunities, aiming to reduce downside risk by responding to market volatility and economic shifts. Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA) establishes a long-term target mix based on risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial goals, prioritizing stability through diversification and disciplined rebalancing. Effective risk management in TAA involves dynamic market analysis and flexible reallocation, while SAA relies on asset class diversification and periodic portfolio review to maintain the desired risk-return profile.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Asset Allocation
Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA) emphasizes flexibility by allowing investors to adjust portfolio weights based on short-term market forecasts and economic conditions, enhancing responsiveness to market volatility. Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA) maintains a long-term, fixed asset mix aligned with an investor's risk tolerance and investment horizon, prioritizing stability over frequent adjustments. The adaptability of TAA enables capitalizing on emerging opportunities, while SAA's disciplined approach seeks to achieve consistent, steady growth through market cycles.
Performance Expectations: Tactical vs Strategic
Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA) aims to capitalize on short-term market opportunities by actively adjusting portfolio weights, often resulting in higher potential returns but increased risk and transaction costs compared to Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA). SAA focuses on maintaining a long-term, stable asset mix aligned with investor goals and risk tolerance, typically delivering more consistent performance with lower volatility. Historical performance data indicates that while TAA can outperform during market inefficiencies, SAA generally provides better risk-adjusted returns over extended periods.
Costs and Implementation Considerations
Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA) typically incurs higher transaction costs due to frequent portfolio adjustments aimed at capitalizing on short-term market opportunities, whereas Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA) involves lower costs by maintaining a long-term, stable investment mix. Implementing TAA requires active management, sophisticated market analysis, and timely decision-making, creating operational complexities and potentially higher management fees. SAA emphasizes disciplined rebalancing aligned with long-term goals, offering cost efficiency and simpler execution despite lower flexibility to respond to market fluctuations.
Suitability for Different Investor Profiles
Tactical Asset Allocation (TAA) suits investors seeking short-term flexibility and willing to take higher risks by actively adjusting their portfolios based on market conditions. Strategic Asset Allocation (SAA) is ideal for long-term investors who prefer a stable, diversified portfolio aligned with their risk tolerance and investment goals. Understanding risk appetite, investment horizon, and market outlook is crucial in choosing between TAA and SAA.
Choosing the Right Asset Allocation Strategy
Tactical asset allocation involves actively adjusting portfolio weights to capitalize on short-term market opportunities, while strategic asset allocation establishes a long-term target based on an investor's risk tolerance and goals. Choosing the right asset allocation strategy depends on factors such as market conditions, investment horizon, and the investor's willingness to tolerate risk and volatility. Combining both methods can enhance portfolio flexibility and improve risk-adjusted returns by balancing discipline with responsiveness.
Important Terms
Dynamic Rebalancing
Dynamic rebalancing enhances Tactical Asset Allocation by frequently adjusting portfolio weights to capitalize on short-term market opportunities, unlike Strategic Asset Allocation which maintains fixed long-term asset targets.
Benchmark Deviation
Benchmark deviation measures the divergence between Tactical Asset Allocation and Strategic Asset Allocation portfolios, quantifying the active risk taken in deviating from the strategic benchmark to capture short-term market opportunities.
Market Timing
Market timing aims to enhance returns by adjusting Tactical Asset Allocation based on short-term market conditions, contrasting with Strategic Asset Allocation's focus on maintaining a long-term, fixed asset mix aligned with investment goals.
Policy Portfolio
Policy portfolio establishes strategic asset allocation as a long-term investment target, while tactical asset allocation allows short-term adjustments to exploit market opportunities.
Active Management
Tactical Asset Allocation actively adjusts portfolio weights based on short-term market conditions to enhance returns, while Strategic Asset Allocation establishes long-term target allocations aligned with an investor's risk tolerance and financial goals.
Core-Satellite Investing
Core-satellite investing balances a stable strategic asset allocation in the core portfolio with tactical asset allocation in the satellite portfolio to optimize risk-adjusted returns and capitalize on market opportunities.
Risk Budgeting
Risk budgeting allocates portfolio risk by strategically setting long-term asset targets while allowing tactical asset allocation to adjust exposures short-term for optimized risk-return balance.
Glide Path
Glide Path adjusts tactical asset allocation over time to gradually shift portfolio risk toward the strategic asset allocation as investment horizons shorten.
Overlay Strategies
Overlay strategies dynamically adjust Tactical Asset Allocation to enhance returns or manage risk while maintaining the long-term objectives of Strategic Asset Allocation.
Mean-Variance Optimization
Mean-Variance Optimization enhances Tactical Asset Allocation by dynamically adjusting portfolio weights to expected returns and risks, contrasting with Strategic Asset Allocation's fixed long-term target allocations.
Tactical Asset Allocation vs Strategic Asset Allocation Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com