A credit invoice is issued to reduce the amount a customer owes, reflecting returns, discounts, or adjustments that decrease the original invoice total. A debit invoice increases the amount payable, often used to charge for additional services or corrections after the original invoice issuance. Understanding the differences between credit and debit invoices is essential for accurate accounting and effective financial management in business transactions.
Table of Comparison
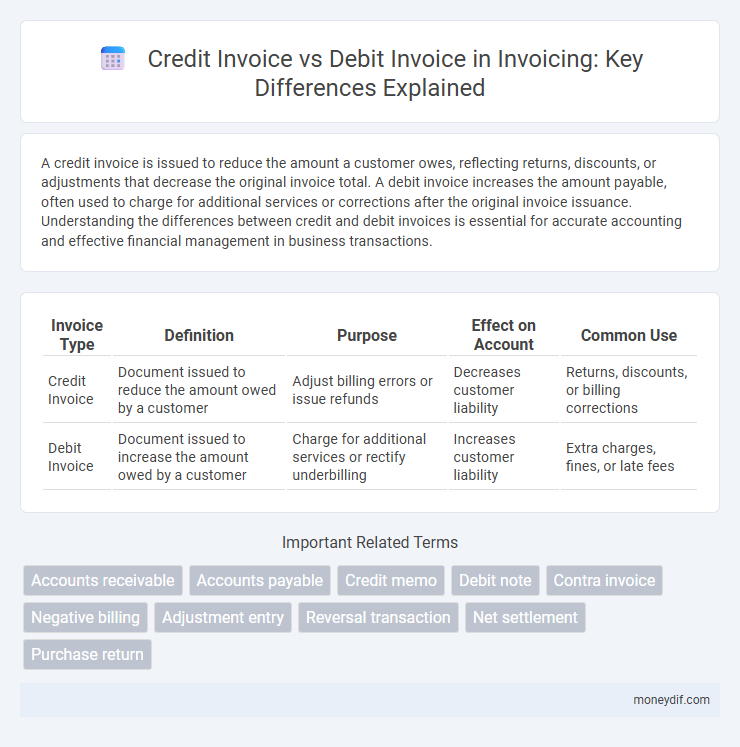
| Invoice Type | Definition | Purpose | Effect on Account | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Credit Invoice | Document issued to reduce the amount owed by a customer | Adjust billing errors or issue refunds | Decreases customer liability | Returns, discounts, or billing corrections |
| Debit Invoice | Document issued to increase the amount owed by a customer | Charge for additional services or rectify underbilling | Increases customer liability | Extra charges, fines, or late fees |
Understanding Credit Invoices
A credit invoice reduces the amount a customer owes by recording a refund, return, or discount on a previous transaction. It adjusts the buyer's account balance to reflect returned goods or services, overpayments, or billing errors, effectively decreasing the total payable amount. Understanding credit invoices is essential for accurate financial reconciliation and maintaining transparent transaction records.
What Is a Debit Invoice?
A debit invoice is a document issued by a seller or service provider to the buyer to increase the amount owed due to additional charges, corrections, or underbilling in a previous transaction. It functions by adjusting the customer's account balance upwards, reflecting expenses such as extra services, penalties, or price adjustments that were not included in the original invoice. Unlike credit invoices that reduce the amount payable, debit invoices serve as a formal notification for additional payment or debt acknowledgment.
Key Differences Between Credit and Debit Invoices
Credit invoices reduce the amount a customer owes by documenting returns, refunds, or discounts, effectively decreasing the original invoice balance. Debit invoices increase the amount due by recording additional charges or fees that were not included in the initial invoice. Key differences include their impact on the accounts receivable balance, purpose--credit invoices for deductions and debit invoices for extra charges--and how they influence financial records and customer payments.
Situations Requiring a Credit Invoice
Situations requiring a credit invoice typically include product returns, overbilling errors, or services not rendered as initially agreed. A credit invoice adjusts the original billing by reducing the amount owed by the customer, correcting discrepancies in the accounts receivable. Businesses issue credit invoices to maintain accurate financial records and ensure customer satisfaction by rectifying billing issues promptly.
When to Use a Debit Invoice
A debit invoice is used when a seller needs to increase the amount previously billed, often due to additional goods or services provided after the original invoice. It is appropriate when correcting undercharged amounts, applying additional fees, or adjusting prices due to errors or changes in the transaction. Businesses issue debit invoices to ensure accurate billing and maintain proper financial records.
Step-by-Step Process for Issuing Credit Invoices
Issuing a credit invoice begins with identifying the original invoice details and the reason for the credit, such as returns or billing errors. The next step involves creating the credit invoice document, referencing the original invoice number, adjusting quantities or amounts, and ensuring all tax calculations reflect the credit accurately. Finally, send the credit invoice to the customer, update accounting records to reflect the credit, and reconcile it against the original invoice to maintain accurate financial statements.
How to Create a Debit Invoice
Creating a debit invoice involves detailing additional charges or fees that increase the amount owed by the customer, such as penalties or extra services. Start by referencing the original invoice number and clearly describe the reason for the debit, including the exact amount to be added. Ensure the debit invoice includes all standard elements like the invoice date, customer details, itemized charges, and terms of payment to maintain clarity and proper financial records.
Impact on Accounting and Financial Reporting
Credit invoices reduce the accounts receivable balance, reflecting a decrease in revenue or customer liability, which directly impacts the company's financial statements by lowering reported income. Debit invoices increase accounts receivable or payable, indicating additional revenue or expense, thus affecting the profit and loss accounts and overall financial position. Both types of invoices require accurate tracking in accounting systems to ensure compliance with revenue recognition principles and proper financial reporting.
Common Mistakes with Credit and Debit Invoices
Common mistakes with credit and debit invoices include misclassifying transactions, leading to incorrect account balances and financial reports. Overlooking proper documentation and authorization can result in audit challenges and compliance issues. Ensuring accurate transaction descriptions and correct invoice numbers helps prevent payment disputes and accounting errors.
Best Practices for Managing Credit and Debit Invoices
Effective management of credit and debit invoices involves maintaining accurate records to ensure clear financial tracking and reconciliation. Implement standardized invoice templates and automated accounting software to reduce errors and streamline processing times. Regularly review invoice statuses to promptly address outstanding balances and improve cash flow management.
Important Terms
Accounts receivable
Accounts receivable increases with credit invoices issued to customers for sales on credit and decreases when debit invoices are applied to correct or adjust billing errors.
Accounts payable
Accounts payable management involves accurately recording credit invoices as liabilities and debit invoices as adjustments to supplier balances to ensure precise financial reporting.
Credit memo
A credit memo reduces the amount owed on a credit invoice by correcting overcharges or returns, while a debit invoice increases the amount due on an original invoice for additional charges or adjustments.
Debit note
A debit note serves as a formal request from a buyer to a seller for a credit adjustment, contrasting with a credit invoice issued by the seller to reduce the amount payable, while a debit invoice is generated to increase the amount due.
Contra invoice
A contra invoice is a financial document used to adjust or offset amounts between a credit invoice and a debit invoice, effectively balancing transactions in accounting records. It serves to rectify discrepancies or return goods and services, reducing the payable amount on the debit invoice or the receivable amount on the credit invoice.
Negative billing
Negative billing occurs when the invoiced amount can be reversed or adjusted using credit invoices, which reduce the total payable amount, unlike debit invoices that increase the amount due by documenting additional charges. Credit invoices serve to correct billing errors or provide refunds, whereas debit invoices reflect supplementary costs or changes in the original billing terms.
Adjustment entry
Adjustment entries reconcile discrepancies between credit invoices and debit invoices to ensure accurate accounting records and balances.
Reversal transaction
A reversal transaction corrects errors by offsetting a credit invoice with a corresponding debit invoice to maintain accurate financial records.
Net settlement
Net settlement involves calculating the balance between credit invoices issued and debit invoices received, ensuring that only the difference is paid or received, which optimizes cash flow and minimizes transaction volumes. This process is critical in accounts receivable and payable management, streamlining financial reconciliation by offsetting amounts owed to suppliers against amounts owed by customers.
Purchase return
A purchase return is recorded through a credit invoice issued by the supplier to reduce the amount owed, reflecting the returned goods or services. In contrast, a debit invoice may be issued to adjust the original invoice amount when additional charges or corrections are necessary after the initial transaction.
Credit invoice vs Debit invoice Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com