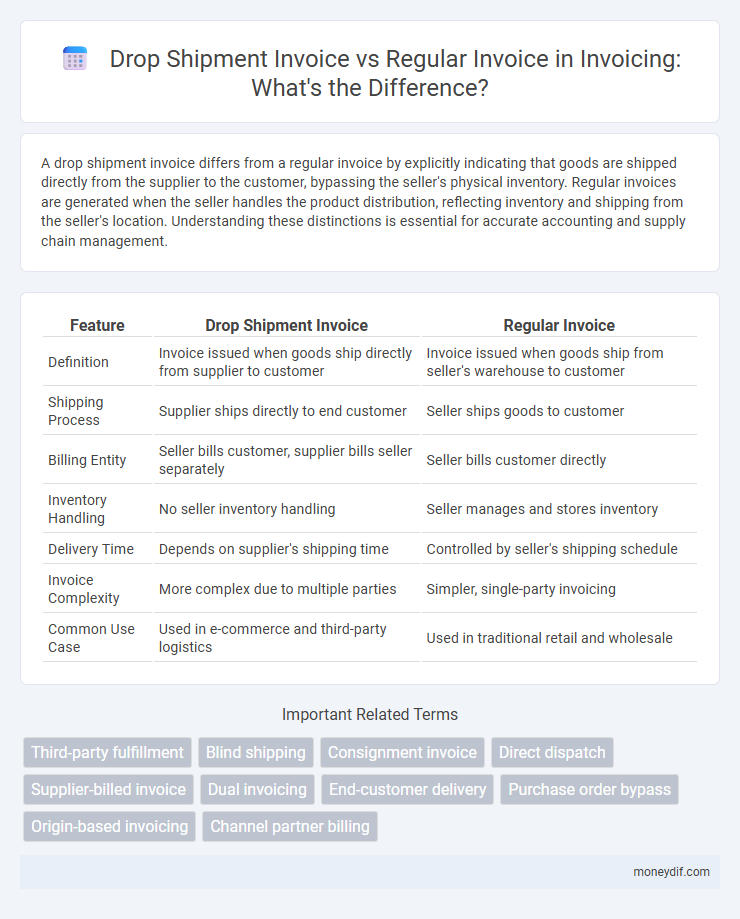
A drop shipment invoice differs from a regular invoice by explicitly indicating that goods are shipped directly from the supplier to the customer, bypassing the seller's physical inventory. Regular invoices are generated when the seller handles the product distribution, reflecting inventory and shipping from the seller's location. Understanding these distinctions is essential for accurate accounting and supply chain management.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Drop Shipment Invoice | Regular Invoice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Invoice issued when goods ship directly from supplier to customer | Invoice issued when goods ship from seller's warehouse to customer |
| Shipping Process | Supplier ships directly to end customer | Seller ships goods to customer |
| Billing Entity | Seller bills customer, supplier bills seller separately | Seller bills customer directly |
| Inventory Handling | No seller inventory handling | Seller manages and stores inventory |
| Delivery Time | Depends on supplier's shipping time | Controlled by seller's shipping schedule |
| Invoice Complexity | More complex due to multiple parties | Simpler, single-party invoicing |
| Common Use Case | Used in e-commerce and third-party logistics | Used in traditional retail and wholesale |
Understanding Drop Shipment Invoices
Drop shipment invoices differ from regular invoices as they detail transactions where the supplier ships products directly to the customer on behalf of the retailer, bypassing the retailer's physical inventory. These invoices must accurately reflect the relationship between the retailer, supplier, and end customer, often including specific drop ship references and separate shipping details. Understanding this distinction is crucial for proper accounting, inventory management, and clear communication in supply chain operations.
What Is a Regular Invoice?
A regular invoice is a standard billing document issued by a seller to a buyer, detailing the products or services provided, quantities, prices, and total amount due. It serves as a formal request for payment and includes payment terms, invoice number, and due date for bookkeeping and accounting purposes. Unlike drop shipment invoices, regular invoices reflect direct sale transactions where the seller holds inventory and ships goods directly to the customer.
Key Differences Between Drop Shipment and Regular Invoices
Drop shipment invoices differ from regular invoices by directly billing the buyer from the supplier who ships goods straight to the customer, bypassing the retailer's inventory. Regular invoices typically involve the retailer purchasing, storing, and then selling products, reflecting inventory handling and two-step shipping. Drop shipment invoices often include supplier details and shipping addresses distinct from the retailer's, emphasizing the direct supplier-to-customer transaction.
Essential Elements in a Drop Shipment Invoice
A drop shipment invoice must include the buyer's information, supplier details, and the drop ship location to ensure accurate delivery and billing. Essential elements also encompass product descriptions, quantities, unit prices, and shipping terms that reflect third-party fulfillment. Clear identification of the drop shipment arrangement distinguishes it from a regular invoice, maintaining transparency between all parties involved.
Billing and Payment Flow: Drop Ship vs. Traditional Sales
In drop shipment invoices, billing flows directly from the supplier to the customer, bypassing the retailer's inventory, which accelerates payment cycles and reduces inventory holding costs. Traditional sales invoices involve the retailer billing the customer after purchasing and receiving goods, resulting in longer payment terms and increased working capital requirements. Payment flow in drop shipment models enhances cash flow efficiency by aligning invoicing with actual shipment events, whereas traditional methods require reconciliation between retailer purchase and customer payment timing.
Impact on Accounting and Bookkeeping
Drop shipment invoices impact accounting by requiring separate tracking of inventory fulfillment through third-party suppliers, causing complexities in revenue recognition and cost allocation. Regular invoices streamline bookkeeping as sales and inventory adjustments occur within the same entity, simplifying financial reporting and audit trails. Accurate categorization of drop shipment transactions is essential to maintain compliance with accounting standards and ensure precise financial statements.
Tax Implications: Drop Shipment vs. Regular Invoicing
Drop shipment invoices often require careful tax jurisdiction analysis because the product ships directly from the supplier to the customer, potentially creating nexus in multiple states and impacting sales tax collection responsibilities. Regular invoices typically involve a single point of sale and standardized tax applications based on the seller's location. Understanding the distinctions in nexus and tax obligations between drop shipment and regular invoicing is essential for accurate sales tax compliance and avoiding penalties.
Common Issues in Drop Shipment Invoicing
Drop shipment invoices frequently encounter common issues such as inaccurate billing information, delayed shipment notifications, and discrepancies between the purchase order and the invoice details. These challenges often arise due to the involvement of multiple parties, including the supplier, retailer, and customer, complicating the reconciliation process and payment approval. Ensuring clear communication and proper documentation between all stakeholders is essential to minimize errors and delays in drop shipment invoicing.
Best Practices for Managing Drop Shipment and Regular Invoices
Efficient management of drop shipment and regular invoices requires clear documentation identifying the supplier, shipper, and receiver to ensure accurate billing and inventory control. Implementing integrated accounting and inventory systems helps automate invoice tracking, reduce errors, and streamline payment processes. Establishing consistent communication between vendors, logistics providers, and finance teams enhances transparency and facilitates timely resolution of discrepancies in both drop shipment and regular invoicing.
Choosing the Right Invoicing Approach for Your Business
Choosing the right invoicing approach depends on your supply chain model and customer agreements. Drop shipment invoices involve billing the customer directly from the supplier, reducing inventory handling and improving cash flow, while regular invoices require the seller to manage inventory and shipping before invoicing. Evaluating factors such as inventory control, delivery responsibility, and transaction transparency helps determine the most efficient invoicing method for your business.
Important Terms
Third-party fulfillment
Third-party fulfillment invoices differ from regular invoices by itemizing shipping fees and handling costs separately to accurately reflect drop shipment expenses handled by an external provider.
Blind shipping
Blind shipping in drop shipment invoicing hides supplier details on the invoice, unlike regular invoices which clearly display sender information.
Consignment invoice
Consignment invoices detail goods held by a consignee without transfer of ownership, drop shipment invoices involve direct shipment from supplier to customer without inventory stocking, whereas regular invoices document standard sales transactions with immediate ownership transfer and inventory update.
Direct dispatch
Direct dispatch in drop shipment invoicing enables suppliers to ship products directly to customers, streamlining order fulfillment and differentiating from regular invoices where the seller manages inventory and shipping.
Supplier-billed invoice
Supplier-billed invoices for drop shipments directly charge the retailer for goods shipped from the supplier to the customer, differing from regular invoices where the retailer handles the shipment and billing.
Dual invoicing
Dual invoicing involves issuing separate drop shipment invoices and regular invoices to accurately reflect transaction responsibilities and streamline accounting processes.
End-customer delivery
Drop shipment invoices directly bill the end-customer from the supplier, streamlining end-customer delivery without involving the retailer's inventory, unlike regular invoices where the retailer manages stock and invoices the customer.
Purchase order bypass
Purchase order bypass enables direct drop shipment invoicing by eliminating the standard procurement workflow required for regular invoice processing.
Origin-based invoicing
Origin-based invoicing requires sales tax to be calculated based on the location where the product shipment originates, impacting drop shipment invoices as the tax obligation may shift to the supplier's location instead of the reseller's. Regular invoices typically apply tax rules based on the buyer's location, whereas drop shipment invoices necessitate careful evaluation of origin points to ensure compliance with state-specific tax regulations.
Channel partner billing
Channel partner billing for drop shipment invoices typically involves direct invoicing from the supplier to the customer, unlike regular invoices where the channel partner bills the customer after purchasing the product.
drop shipment invoice vs regular invoice Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com