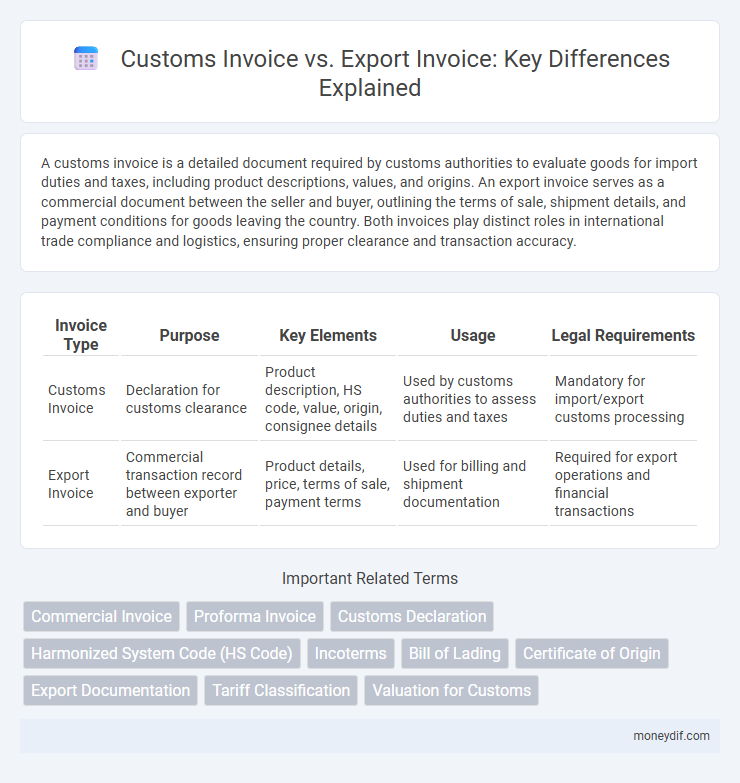
A customs invoice is a detailed document required by customs authorities to evaluate goods for import duties and taxes, including product descriptions, values, and origins. An export invoice serves as a commercial document between the seller and buyer, outlining the terms of sale, shipment details, and payment conditions for goods leaving the country. Both invoices play distinct roles in international trade compliance and logistics, ensuring proper clearance and transaction accuracy.
Table of Comparison
| Invoice Type | Purpose | Key Elements | Usage | Legal Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customs Invoice | Declaration for customs clearance | Product description, HS code, value, origin, consignee details | Used by customs authorities to assess duties and taxes | Mandatory for import/export customs processing |
| Export Invoice | Commercial transaction record between exporter and buyer | Product details, price, terms of sale, payment terms | Used for billing and shipment documentation | Required for export operations and financial transactions |
Overview of Customs Invoice and Export Invoice
A Customs Invoice is a detailed document required by customs authorities to assess duties and taxes applied to imported goods, containing information such as item descriptions, quantities, values, and country of origin. An Export Invoice serves as a commercial document used by exporters to declare the sale and shipment of goods to international buyers, including payment terms, buyer and seller information, and shipping details. While both invoices are essential for international trade, the Customs Invoice primarily facilitates legal compliance and customs clearance, whereas the Export Invoice supports transaction verification and payment processing.
Key Definitions: Customs Invoice vs Export Invoice
A Customs Invoice is a detailed document required by customs authorities for the assessment of duties and taxes, containing precise information about the shipment's value, origin, and contents. An Export Invoice, on the other hand, is primarily a commercial document used between the seller and buyer, outlining the sale terms, payment conditions, and product details. Understanding the distinction is critical for ensuring compliance with international trade regulations and smooth clearance processes.
Main Purposes of Customs and Export Invoices
Customs invoices primarily serve to provide accurate information on the value, quantity, and nature of goods for customs clearance and tariff assessment. Export invoices focus on detailing the transaction between seller and buyer, facilitating payment and shipment processes while documenting terms of sale. Both documents are essential for smooth international trade, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and proper financial settlement.
Essential Elements in a Customs Invoice
A customs invoice must include detailed product descriptions, accurate HS codes, country of origin, and precise values for customs duty assessment, differing from a standard export invoice which mainly focuses on commercial transaction details. Key elements such as consignee and consignor information, terms of sale (Incoterms), and shipment details ensure compliance with customs regulations and facilitate smooth border clearance. Proper documentation minimizes delays, avoids penalties, and enables accurate calculation of import duties and taxes.
Essential Elements in an Export Invoice
An export invoice must include essential elements such as the exporter's and importer's details, accurate description of goods, quantity, unit price, total value, country of origin, harmonized system (HS) code, and terms of delivery and payment. Unlike a customs invoice, which focuses primarily on valuation and classification for duties and taxes, the export invoice serves as a commercial document for international trade, supporting customs clearance and financial transactions. Clear documentation of shipment details, including Incoterms and export license number if applicable, is crucial for compliance and smooth cross-border operations.
Legal Requirements for Each Invoice Type
Customs invoices must comply with specific legal requirements such as detailed product descriptions, Harmonized System (HS) codes, country of origin, and accurate valuation for customs duties assessment. Export invoices require compliance with export regulations, including exporter and consignee details, license numbers if applicable, and currency of transaction for proper trade documentation. Both invoice types serve different regulatory purposes, making adherence to their respective legal frameworks essential for international trade compliance.
Differences in Documentation and Compliance
Customs invoices are specifically designed to meet the regulatory requirements of customs authorities, including detailed descriptions of goods, tariff codes, and country of origin to ensure accurate duty assessment. Export invoices focus on the commercial transaction between exporter and importer, emphasizing terms of sale, payment details, and shipping information, often adhering to international trade standards. Documentation for customs invoices requires strict compliance with import-export laws, while export invoices prioritize contract fulfillment and financial clarity.
Role in International Trade and Customs Clearance
Customs invoices serve as legally required documents detailing the value, quantity, and nature of goods for customs authorities to assess duties and ensure compliance with import regulations during international trade. Export invoices, meanwhile, primarily facilitate the seller's billing process and provide essential information for the buyer, aiding in shipment processing and financial transactions. Both documents play critical roles in customs clearance by verifying the transaction details, but customs invoices are specifically tailored to meet government import-export regulatory requirements.
Common Mistakes with Customs and Export Invoices
Common mistakes with customs and export invoices include incorrect product descriptions, inaccurate valuation, and missing or inconsistent information, which can lead to shipment delays and customs penalties. Many exporters fail to clearly specify the Harmonized System (HS) codes or omit essential details like the country of origin, causing customs clearance complications. Ensuring accurate, complete, and compliant documentation is crucial to avoid costly errors in international trade transactions.
Best Practices for Accurate Invoice Preparation
Accurate invoice preparation requires distinguishing between customs invoices and export invoices, each serving distinct regulatory and transactional purposes. A customs invoice must detail the product description, HS codes, origin, and value for accurate duty assessment, while an export invoice emphasizes payment terms, buyer and seller information, and shipment details for contractual clarity. Ensuring consistency across both documents minimizes delays, compliance issues, and facilitates smooth international trade operations.
Important Terms
Commercial Invoice
A Commercial Invoice serves as a critical document for customs clearance, detailing the transaction value, goods description, and parties involved, distinguishing it from an Export Invoice which primarily focuses on billing and shipment terms. Customs Invoices require specific information for tariff classification and duties calculation, while Export Invoices emphasize payment terms, product quantities, and export compliance data.
Proforma Invoice
A Proforma Invoice serves as a preliminary bill of sale sent to buyers before shipment, detailing the goods, their value, and terms, often required by customs for import clearance to verify shipment content and value. Unlike a Customs Invoice, which is officially used by customs authorities to assess duties and taxes, or an Export Invoice that formalizes the sale for export transactions, the Proforma Invoice primarily facilitates the buyer's approval and customs documentation without demanding payment.
Customs Declaration
A Customs Declaration is a mandatory document detailing the contents, value, and origin of goods for customs clearance, while a Customs Invoice specifically supports this process by providing a detailed commercial transaction record required by customs authorities. An Export Invoice serves as a commercial document for buyer-seller transactions, outlining product descriptions, quantities, and pricing but may lack the specific regulatory information demanded in a Customs Invoice for customs valuation and duty assessment.
Harmonized System Code (HS Code)
The Harmonized System Code (HS Code) is a standardized numerical method of classifying traded products critical for customs invoices, ensuring accurate tariff application and compliance with international trade regulations. Export invoices utilize the HS Code to detail product descriptions and classifications, facilitating customs clearance and minimizing delays at border inspections.
Incoterms
Incoterms define responsibilities for costs and risks in international trade, impacting whether a Customs invoice or Export invoice is required; a Customs invoice is used specifically for customs clearance to declare goods' value, origin, and classification, while an Export invoice serves broader purposes, including billing and shipment documentation. Accurate alignment with applicable Incoterms ensures proper documentation, minimizing delays and compliance issues at customs.
Bill of Lading
A Bill of Lading serves as a crucial shipping document verifying the receipt of goods for transport, while a Customs Invoice provides detailed information about the goods for customs clearance, including valuation and classification data. An Export Invoice focuses on the commercial transaction details between buyer and seller but lacks the specific customs-related information required for regulatory compliance and duty assessment.
Certificate of Origin
A Certificate of Origin certifies the country where goods are produced and is often required by customs alongside a Customs invoice, which details the shipment for import duties, whereas an Export invoice primarily serves as a commercial document between buyer and seller for payment purposes.
Export Documentation
A customs invoice is specifically tailored to meet customs authorities' requirements, detailing the shipment's content, value, and origin for duty assessment and clearance, while an export invoice serves as a commercial document between the exporter and importer, outlining the sale, payment terms, and cargo specifics. Accurate differentiation between customs invoice and export invoice ensures compliance with international trade regulations and smooth customs processing.
Tariff Classification
Tariff classification determines the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for goods, directly impacting duty rates reflected on both customs and export invoices. Discrepancies between the customs invoice, used for regulatory compliance and duty calculation, and the export invoice, detailing sale terms and shipment information, can lead to delays, penalties, or misclassification risks.
Valuation for Customs
Customs valuation primarily relies on the Customs invoice to determine the dutiable value of imported goods, ensuring compliance with the World Trade Organization's Valuation Agreement. Export invoices often differ in format and content, and while they serve as commercial evidence of the transaction, Customs authorities prioritize the Customs invoice for accurate assessment of duties and taxes based on declared transaction value and related costs.
Customs invoice vs Export invoice Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com