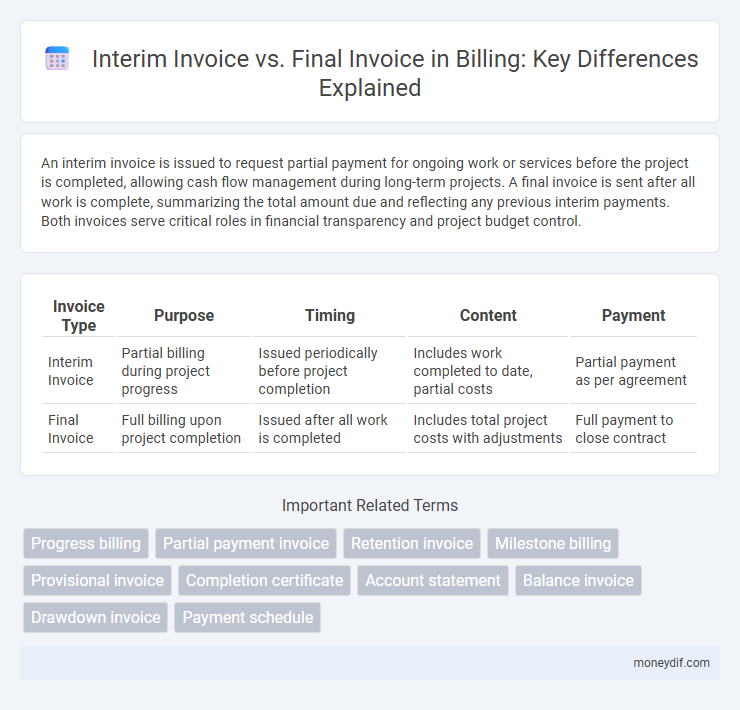
An interim invoice is issued to request partial payment for ongoing work or services before the project is completed, allowing cash flow management during long-term projects. A final invoice is sent after all work is complete, summarizing the total amount due and reflecting any previous interim payments. Both invoices serve critical roles in financial transparency and project budget control.
Table of Comparison
| Invoice Type | Purpose | Timing | Content | Payment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interim Invoice | Partial billing during project progress | Issued periodically before project completion | Includes work completed to date, partial costs | Partial payment as per agreement |
| Final Invoice | Full billing upon project completion | Issued after all work is completed | Includes total project costs with adjustments | Full payment to close contract |
Understanding Interim Invoices
Interim invoices provide partial billing for completed stages of a project, allowing cash flow during ongoing work without waiting for full project completion. These invoices help track progress and manage budgets by outlining specific deliverables or milestones achieved. Understanding interim invoices is crucial for accurate financial planning and ensuring timely payments in multi-phase contracts.
What Is a Final Invoice?
A final invoice is a detailed document issued at the completion of a project or service, summarizing all outstanding charges and confirming full payment is due. It serves as the official request for payment after all work is completed, including any adjustments or additional costs incurred during the project. Unlike an interim invoice, which covers partial payments, the final invoice ensures all financial obligations are settled.
Key Differences Between Interim and Final Invoices
Interim invoices are issued periodically during a project to request partial payments for completed work, while final invoices are sent upon project completion to request the remaining balance. Interim invoices help maintain cash flow and provide financial updates, whereas final invoices finalize the billing process and include any adjustments or outstanding charges. Key differences include timing, purpose, and the scope of payment requested.
When to Use Interim Invoices
Interim invoices are used during ongoing projects or services to request partial payments before the completion of the entire work, providing consistent cash flow and reducing financial risk. They are appropriate when milestones or phases are reached in long-term contracts, allowing clients to pay progressively based on work completed. Final invoices are issued only after the project is fully completed, summarizing all costs, including adjustments from previous interim invoices.
When to Issue a Final Invoice
Issue a final invoice upon completion of all contracted work or delivery of specified goods, indicating the total amount due after accounting for prior interim invoices. This invoice serves as the conclusive billing document, confirming fulfillment of contractual obligations and enabling final payment processing. Timely issuance of the final invoice is critical for accurate financial reconciliation and closing of project accounts.
Benefits of Interim Invoicing
Interim invoicing enhances cash flow management by providing regular payments throughout a project, reducing financial strain on contractors and suppliers. It allows for early identification and resolution of discrepancies, minimizing disputes and improving project transparency. Frequent billing through interim invoices supports accurate financial tracking and resource allocation, leading to better overall project control.
Advantages of Final Invoicing
Final invoicing provides a comprehensive summary of all goods and services delivered, ensuring accurate payment reconciliation and reducing the risk of disputes with clients. It streamlines accounting processes by consolidating all interim payments, minimizing administrative overhead and improving cash flow visibility. Final invoices also serve as a definitive legal record for tax and audit purposes, enhancing financial compliance and accountability.
Common Use Cases for Interim and Final Invoices
Interim invoices are commonly used in long-term projects or contracts to request partial payments at various milestones, ensuring continuous cash flow and reducing financial risk for service providers. Final invoices are issued upon project completion, summarizing all charges and adjustments to finalize the payment process. Businesses often use interim invoices for progress billing and final invoices for closing accounts and recording completed work.
Best Practices for Managing Interim and Final Invoices
Interim invoices should itemize completed work phases with clear payment terms to maintain cash flow and minimize disputes. Final invoices must reconcile all interim payments and include detailed summaries for transparency and accurate project closure. Consistent documentation and timely communication enhance accuracy and foster trust between clients and vendors throughout the invoicing process.
Choosing the Right Invoice Type for Your Business
Choosing the right invoice type for your business depends on the project timeline and payment structure, where an interim invoice is ideal for ongoing projects requiring staggered payments, while a final invoice is used upon project completion to summarize total costs. Interim invoices improve cash flow and project transparency by breaking down payments into manageable installments, reducing financial strain for clients and businesses alike. Final invoices ensure clarity in the billing process by providing a detailed account of all goods and services delivered, facilitating accurate financial records and timely payment.
Important Terms
Progress billing
Progress billing allows clients to pay for completed project phases, with interim invoices requesting partial payments during the project and the final invoice consolidating all charges for project completion.
Partial payment invoice
Partial payment invoices facilitate staged billing by allowing payments during project progress, distinguishing interim invoices as periodic requests and final invoices as the conclusive billing summary.
Retention invoice
A retention invoice secures withheld contract payments to ensure project completion, contrasting with interim invoices that request partial payments during progress and final invoices that demand full settlement upon project completion.
Milestone billing
Milestone billing involves issuing invoices at predefined project stages, with interim invoices reflecting partial payments for completed milestones, while the final invoice reconciles all previous payments and settles the remaining balance. This method enhances cash flow management and ensures clients pay progressively based on measurable project progress.
Provisional invoice
A provisional invoice estimates costs and quantities pending final measurement, bridging the interim invoice issued during project phases and the final invoice confirming total payment due.
Completion certificate
A completion certificate validates project fulfillment, triggering the transition from interim invoices, which cover partial work progress, to the final invoice that settles the entire contract payment.
Account statement
An account statement details all transactions including interim invoices reflecting partial charges and final invoices representing the total amount due after project completion.
Balance invoice
A balance invoice reflects the remaining payment due after interim invoices have been paid and precedes the final invoice, which confirms project completion and full settlement.
Drawdown invoice
A drawdown invoice allocates partial payment amounts from a contracted total, facilitating cash flow management during project phases, unlike an interim invoice which requests payment for work completed to date, and a final invoice which settles the total contract value after full project completion. Understanding these distinctions ensures accurate financial tracking and compliance with contract terms in construction and service industries.
Payment schedule
The payment schedule for an interim invoice typically involves partial payments tied to project milestones or progress stages, ensuring steady cash flow during ongoing work. In contrast, the final invoice consolidates all previous charges and any remaining balances, serving as the conclusive payment request upon project completion.
Interim invoice vs Final invoice Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com