Jumbo loans exceed conforming loan limits, providing financing for high-value properties that standard mortgages cannot cover. Super jumbo loans surpass even higher thresholds, typically starting around $1.5 million and requiring stricter credit qualifications and larger down payments. Borrowers choosing between jumbo and super jumbo loans should carefully evaluate interest rates, eligibility criteria, and their financial capacity to manage increased loan amounts.
Table of Comparison
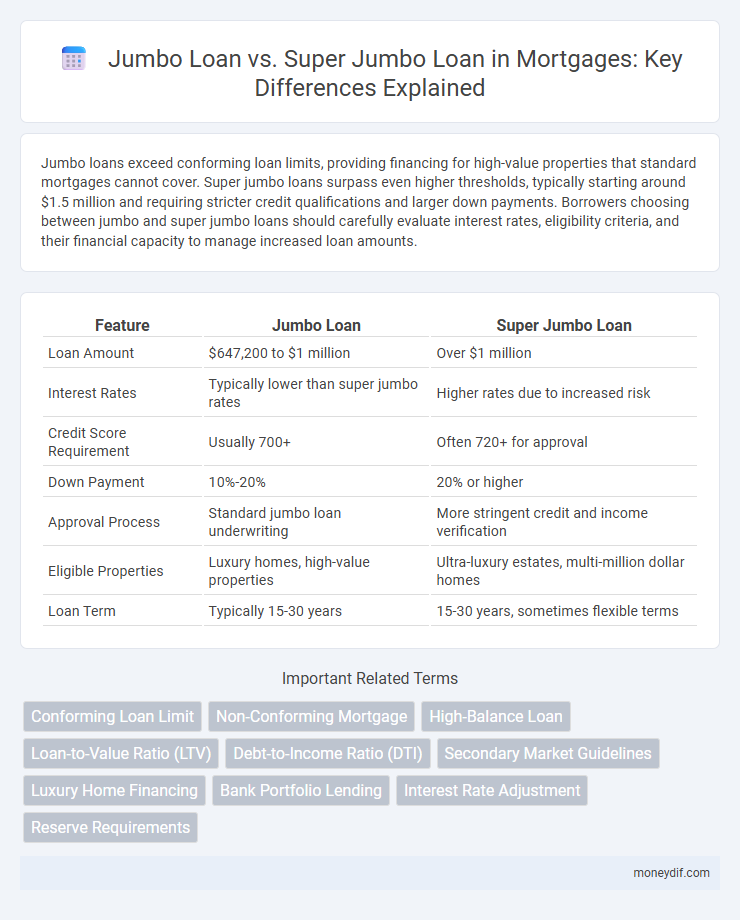
| Feature | Jumbo Loan | Super Jumbo Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Amount | $647,200 to $1 million | Over $1 million |
| Interest Rates | Typically lower than super jumbo rates | Higher rates due to increased risk |
| Credit Score Requirement | Usually 700+ | Often 720+ for approval |
| Down Payment | 10%-20% | 20% or higher |
| Approval Process | Standard jumbo loan underwriting | More stringent credit and income verification |
| Eligible Properties | Luxury homes, high-value properties | Ultra-luxury estates, multi-million dollar homes |
| Loan Term | Typically 15-30 years | 15-30 years, sometimes flexible terms |
Understanding Jumbo Loans: Key Features
Jumbo loans exceed conforming loan limits set by the Federal Housing Finance Agency, typically starting at $726,200 but can vary by region, while super jumbo loans surpass $1 million, catering to luxury property buyers. These loans often require higher credit scores, larger down payments--usually 20% or more--and more extensive documentation due to the increased risk for lenders. Interest rates on jumbo and super jumbo loans may be higher or vary based on market conditions and borrower qualifications, reflecting their non-conforming status.
What is a Super Jumbo Loan?
A Super Jumbo Loan is a type of mortgage that exceeds the limits of a Jumbo Loan, typically starting at $1.5 million and going well beyond $3 million, depending on the lender and region. These loans cater to high-net-worth borrowers seeking to finance luxury properties that require substantial funding beyond conventional loan caps established by entities like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. Interest rates on Super Jumbo Loans often vary significantly due to the increased risk and lower liquidity in the secondary market compared to standard Jumbo Loans.
Jumbo vs. Super Jumbo Loan: Core Differences
Jumbo loans typically finance homes exceeding conventional loan limits, generally ranging up to $850,000, while super jumbo loans cover amounts significantly higher, often surpassing $1.5 million. Super jumbo loans require stricter credit qualifications, larger down payments, and higher interest rates due to increased lending risks. Borrowers seeking super jumbo loans benefit from tailored underwriting criteria and may face more extensive documentation compared to standard jumbo loan processes.
Eligibility Requirements for Jumbo and Super Jumbo Loans
Eligibility requirements for jumbo loans typically include a minimum credit score of 700, a debt-to-income ratio below 43%, and liquid assets of at least six months' worth of mortgage payments. Super jumbo loans demand higher credit scores, often above 720, stricter debt-to-income ratios under 40%, and substantial reserves, sometimes exceeding 12 months of mortgage payments, due to their larger loan amounts exceeding $1.5 million. Both loan types require thorough income verification and are usually offered to borrowers with strong financial profiles to mitigate higher lending risks.
Credit Score and Down Payment: How They Differ
Jumbo loans typically require a credit score of at least 700 and a down payment of 10% to 20%, while super jumbo loans demand higher credit scores, often 720 or above, alongside larger down payments ranging from 20% to 30%. These stricter requirements for super jumbo loans reflect the increased lender risk associated with loan amounts exceeding conventional jumbo limits. Borrowers with high creditworthiness and substantial down payments are better positioned to secure favorable terms on super jumbo loans.
Borrowing Limits: Jumbo vs. Super Jumbo Loans
Jumbo loans exceed conforming loan limits, typically ranging from $619,750 to $1 million, while super jumbo loans surpass $1 million, often reaching several million dollars. Borrowing limits for jumbo loans vary by county and are set by the Federal Housing Finance Agency, whereas super jumbo loans lack standardized limits and require lenders to set customized thresholds. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for high-net-worth borrowers seeking financing for luxury or high-value properties.
Interest Rates: Comparing Jumbo and Super Jumbo Options
Interest rates on jumbo loans typically range from 0.25% to 0.5% higher than conforming loans due to larger loan amounts and increased lender risk. Super jumbo loans, which exceed standard jumbo limits often above $1.5 million, generally carry even higher rates, reflecting greater underwriting scrutiny and market volatility. Borrowers should expect rate differences influenced by credit scores, down payments, and loan-to-value ratios within these non-conforming loan categories.
Application Process: Steps and Documentation Needed
Applying for a Jumbo Loan requires submitting comprehensive financial documents such as tax returns, W-2s, bank statements, and credit reports to verify income and creditworthiness. Super Jumbo Loans involve a more rigorous application process with stricter documentation standards, including larger asset reserves, detailed debt explanations, and sometimes additional appraisal requirements due to the higher loan amounts. Both loan types demand precise paperwork and thorough underwriting, but Super Jumbo Loans often necessitate enhanced financial disclosures to meet lender guidelines.
Pros and Cons of Jumbo and Super Jumbo Loans
Jumbo loans offer higher borrowing limits than conforming loans, enabling borrowers to purchase luxury properties with competitive interest rates, though they often require stricter credit qualifications and higher down payments. Super jumbo loans extend beyond jumbo loan limits, providing access to extremely high-priced real estate, but typically come with even stricter eligibility criteria, increased interest rates, and more substantial lender scrutiny. Borrowers must weigh the advantage of financing upscale homes against the challenges of higher costs and more rigorous approval processes associated with both loan types.
Which Loan Is Right for You: Jumbo or Super Jumbo?
Choosing between a jumbo loan and a super jumbo loan depends on your property price and financial profile; jumbo loans typically cover amounts above conforming loan limits up to $1 million, while super jumbo loans exceed $1 million. Assess your income, credit score, and down payment capacity, as super jumbo loans often require higher qualifications and larger down payments. Understanding these factors helps determine which loan type aligns with your borrowing needs and investment goals.
Important Terms
Conforming Loan Limit
Conforming loan limits define the maximum loan amount eligible for government-backed mortgages, distinguishing jumbo loans which exceed these limits, while super jumbo loans surpass jumbo loan thresholds with significantly higher borrowing limits.
Non-Conforming Mortgage
Non-conforming mortgages include jumbo loans exceeding conforming loan limits, with super jumbo loans representing higher loan amounts typically above $1.5 million to $3 million, requiring stricter underwriting criteria and higher credit standards.
High-Balance Loan
High-Balance Loans bridge the gap between conforming loan limits and Jumbo Loans, while Super Jumbo Loans exceed standard jumbo thresholds, typically surpassing $1 million in loan amount.
Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV)
Jumbo loans typically have a loan-to-value (LTV) ratio up to 80%, while super jumbo loans often require a lower LTV ratio, usually around 70%, due to their higher loan amounts and increased lender risk.
Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI)
Jumbo loans typically require a debt-to-income ratio below 43%, while super jumbo loans often demand a stricter DTI, commonly under 36%, to qualify due to higher loan amounts and increased lender risk.
Secondary Market Guidelines
Secondary Market Guidelines distinguish Jumbo Loans as mortgage loans exceeding conforming limits up to $1 million, while Super Jumbo Loans surpass $1 million, affecting underwriting standards, interest rates, and investor eligibility.
Luxury Home Financing
Super jumbo loans exceed jumbo loan limits by offering higher financing amounts for luxury homes, typically above $1 million, enabling buyers to secure larger mortgages with tailored terms.
Bank Portfolio Lending
Bank portfolio lending for jumbo loans typically involves loans up to $1 million, while super jumbo loans exceed $1 million, requiring stricter underwriting and higher down payments to mitigate increased risk.
Interest Rate Adjustment
Interest rate adjustment for Jumbo Loans typically ranges from 0.25% to 0.5% lower than Super Jumbo Loans due to differences in loan size risk assessment.
Reserve Requirements
Reserve requirements for Jumbo Loans typically mandate two to six months of payment reserves, whereas Super Jumbo Loans often require six to twelve months due to higher loan amounts and increased lender risk.
Jumbo Loan vs Super Jumbo Loan Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com