A Home Equity Loan provides a lump sum with fixed interest rates, ideal for those seeking predictable monthly payments and one-time expenses. In contrast, a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) offers a revolving credit line with variable rates, allowing borrowers to draw funds as needed over a set period. Choosing between them depends on financial needs, whether for a large, planned purchase or ongoing access to funds for flexibility.
Table of Comparison
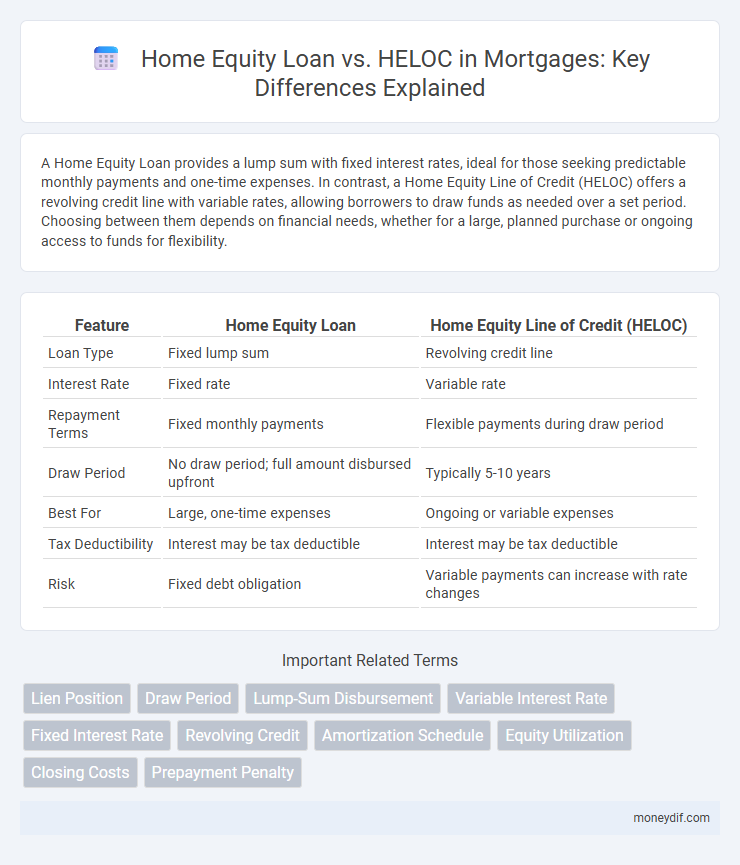
| Feature | Home Equity Loan | Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Type | Fixed lump sum | Revolving credit line |
| Interest Rate | Fixed rate | Variable rate |
| Repayment Terms | Fixed monthly payments | Flexible payments during draw period |
| Draw Period | No draw period; full amount disbursed upfront | Typically 5-10 years |
| Best For | Large, one-time expenses | Ongoing or variable expenses |
| Tax Deductibility | Interest may be tax deductible | Interest may be tax deductible |
| Risk | Fixed debt obligation | Variable payments can increase with rate changes |
Understanding Home Equity: The Basics
Home equity represents the portion of your property's value that you fully own, calculated by subtracting any outstanding mortgage balance from the current market value of the home. Home equity loans provide a lump sum amount with fixed interest rates and repayment terms, making them ideal for large, one-time expenses. Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs) function like revolving credit, offering flexible borrowing and repayment options based on your home's available equity, often with variable interest rates.
What Is a Home Equity Loan?
A Home Equity Loan provides a lump sum amount based on the homeowner's available equity, typically with a fixed interest rate and fixed monthly payments over a set term. This type of loan is ideal for borrowers seeking predictable payments and a one-time expense, often used for major home improvements or debt consolidation. The loan is secured by the property's equity, making it crucial for homeowners to understand their home's current market value and remaining mortgage balance.
What Is a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC)?
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) is a revolving credit facility secured by the equity in your home, allowing borrowers to draw funds up to a predetermined limit during a draw period. Unlike a fixed lump sum home equity loan, a HELOC offers flexible monthly payments based on outstanding balances and typically features variable interest rates. Homeowners use HELOCs for home improvements, debt consolidation, and emergency expenses due to easy access and interest-only payment options during the draw phase.
Key Differences Between Home Equity Loan and HELOC
A Home Equity Loan provides a lump sum with fixed interest rates and payments, ideal for large, one-time expenses, while a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) offers a revolving credit line with variable rates, allowing borrowers to draw funds as needed. Home Equity Loans typically have predictable monthly payments and terms ranging from 5 to 30 years, whereas HELOCs usually involve an interest-only payment period followed by a repayment phase. Understanding these differences helps homeowners select financing based on cash flow needs, interest rate preferences, and intended use of funds.
Interest Rates: Fixed vs. Variable
Home Equity Loans typically offer fixed interest rates, providing predictable monthly payments that help homeowners budget effectively. In contrast, Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs) usually feature variable interest rates, which can fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially lowering initial borrowing costs but increasing payment uncertainty over time. Choosing between the two depends on whether stability or flexibility in interest rates aligns best with the borrower's financial strategy.
Repayment Terms and Flexibility
Home equity loans offer fixed repayment terms with a set monthly payment and a predetermined loan amount, providing predictable budgeting for borrowers. Home equity lines of credit (HELOCs) feature variable repayment schedules and flexible borrowing limits, allowing homeowners to draw funds as needed during the draw period. This flexibility in HELOCs can accommodate fluctuating expenses but may result in variable interest rates and payment amounts over time.
Pros and Cons of Home Equity Loans
Home equity loans offer a fixed interest rate and predictable monthly payments, making budgeting easier compared to the variable rates of a HELOC. They provide a lump sum upfront, ideal for large, one-time expenses, but lack the flexibility of borrowing on demand. However, home equity loans typically have higher initial closing costs and less adaptability for ongoing financial needs.
Pros and Cons of HELOCs
HELOCs offer flexible borrowing with a revolving credit line, allowing homeowners to access funds as needed and pay interest only on the amount used. However, variable interest rates can lead to unpredictable monthly payments, and there is a risk of reduced home equity if property values decline. Drawbacks also include potential fees, interest-only payment periods that do not reduce principal, and stricter qualification requirements compared to standard home equity loans.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Financial Needs
Choosing between a Home Equity Loan and a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) depends on your financial goals and cash flow stability. A Home Equity Loan provides a lump sum with fixed interest rates, ideal for large, one-time expenses, while a HELOC offers a revolving credit line with variable rates, suitable for ongoing or unpredictable costs. Assess your repayment ability, interest rate tolerance, and the purpose of borrowing to select the option that best aligns with your financial strategy.
Home Equity Loan vs HELOC: Which Is Better for You?
Home equity loans provide a lump sum with fixed interest rates, ideal for borrowers seeking predictable payments for large expenses, while HELOCs offer revolving credit with variable rates, granting flexibility for ongoing or unexpected costs. Choosing between a home equity loan and a HELOC depends on financial goals, repayment ability, and the need for budget stability or credit access. Evaluating interest rates, loan terms, and intended use of funds helps determine the most suitable option for leveraging home equity effectively.
Important Terms
Lien Position
Lien position determines the priority of claims on a property in case of default, with first lien holders having superior rights over second lien holders. Home equity loans often hold a second lien position behind the primary mortgage, whereas HELOCs can vary but commonly also occupy the second lien position, impacting interest rates and approval terms.
Draw Period
The Draw Period in a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) typically lasts 5 to 10 years, allowing borrowers to withdraw funds repeatedly, unlike Home Equity Loans which provide a lump sum with no draw period.
Lump-Sum Disbursement
Lump-sum disbursement in a Home Equity Loan provides a fixed amount of money upfront with a set repayment schedule, offering predictable monthly payments and interest rates. In contrast, a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) allows borrowers to draw funds as needed up to a credit limit, with variable interest rates and flexible repayment options based on the outstanding balance.
Variable Interest Rate
Home Equity Loan typically features a fixed interest rate, providing predictable monthly payments, whereas a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) often carries a variable interest rate that fluctuates based on market indexes like the prime rate. Borrowers choosing a HELOC should be prepared for potential rate increases, impacting monthly costs, while fixed-rate home equity loans offer stability over the loan term.
Fixed Interest Rate
Fixed interest rates on home equity loans provide predictable monthly payments, unlike the variable rates typically associated with home equity lines of credit (HELOCs).
Revolving Credit
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) offers revolving credit secured by your home's equity, allowing flexible borrowing and repayments, while a Home Equity Loan provides a fixed lump sum with a fixed interest rate and repayment schedule.
Amortization Schedule
An amortization schedule for a Home Equity Loan shows fixed monthly payments with a consistent principal and interest breakdown, while a HELOC's schedule varies due to its revolving credit nature and fluctuating interest rates.
Equity Utilization
Equity utilization in home financing refers to how much of the available home equity is borrowed through products like Home Equity Loans and Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs). Home Equity Loans provide a lump sum with fixed interest rates, ideal for one-time expenses, while HELOCs offer revolving credit with variable rates, allowing flexible borrowing aligned with ongoing financial needs.
Closing Costs
Closing costs for a Home Equity Loan typically range from 2% to 5% of the loan amount, while HELOCs often have lower or no closing costs, making HELOCs more cost-effective upfront.
Prepayment Penalty
Home Equity Loans often include prepayment penalties that can increase the overall cost if the loan is paid off early, whereas most Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs) typically offer more flexible repayment options without such fees. Understanding the terms of prepayment penalties is crucial for borrowers seeking to minimize upfront and ongoing costs in home equity financing.
Home Equity Loan vs Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com