Authorization hold secures funds on a customer's payment method without transferring the money immediately, ensuring the amount is reserved for a future transaction. Capture finalizes the payment by transferring the authorized funds from the customer's account to the merchant's account. Understanding the difference between authorization hold and capture is essential for managing cash flow and preventing payment disputes effectively.
Table of Comparison
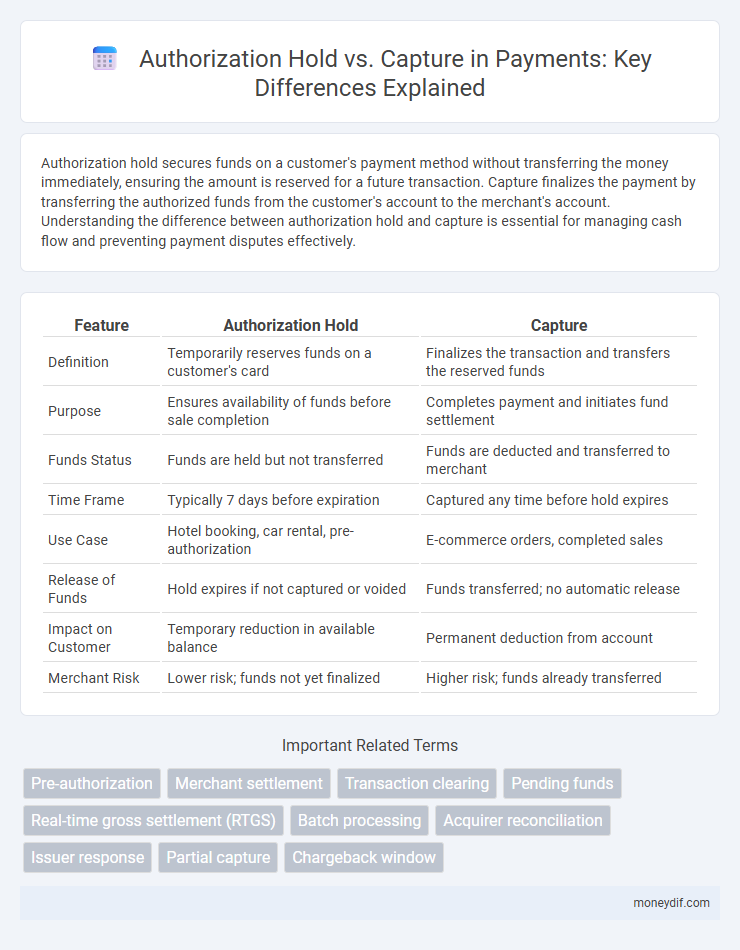
| Feature | Authorization Hold | Capture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporarily reserves funds on a customer's card | Finalizes the transaction and transfers the reserved funds |
| Purpose | Ensures availability of funds before sale completion | Completes payment and initiates fund settlement |
| Funds Status | Funds are held but not transferred | Funds are deducted and transferred to merchant |
| Time Frame | Typically 7 days before expiration | Captured any time before hold expires |
| Use Case | Hotel booking, car rental, pre-authorization | E-commerce orders, completed sales |
| Release of Funds | Hold expires if not captured or voided | Funds transferred; no automatic release |
| Impact on Customer | Temporary reduction in available balance | Permanent deduction from account |
| Merchant Risk | Lower risk; funds not yet finalized | Higher risk; funds already transferred |
Understanding Payment Authorization Hold
Payment authorization hold temporarily reserves funds on a customer's credit or debit card to ensure sufficient balance for a transaction but does not transfer money immediately. This hold guarantees the merchant that the payment amount is available while preventing the cardholder from using these funds elsewhere. Capturing the payment occurs later, finalizing the transaction by withdrawing the authorized amount from the customer's account.
What is Payment Capture?
Payment capture is the process of finalizing a previously authorized transaction by transferring funds from the customer's account to the merchant. After an authorization hold secures the necessary funds, capture confirms the actual payment and completes the sale. This step ensures the merchant receives payment and initiates order fulfillment or service delivery.
Key Differences: Authorization Hold vs Capture
Authorization hold temporarily reserves funds on a customer's credit card without completing the transaction, ensuring the amount is available for payment. Capture finalizes the transaction by transferring the held funds from the customer's account to the merchant, completing the sale. The key difference lies in timing and fund movement: authorization hold secures the amount, while capture processes the actual payment.
How Authorization Holds Work in Payments
Authorization holds temporarily reserve funds on a customer's payment method, ensuring the available balance covers the transaction amount without immediately transferring funds. This hold places a pending charge on the card, typically lasting between 1 to 7 days, depending on the issuer and merchant settings. Merchants capture the funds later by submitting the transaction for settlement, converting the hold into a finalized charge upon order fulfillment or service completion.
Steps Involved in Payment Capture
Payment capture involves several critical steps starting with the authorization hold, where funds are temporarily reserved on the customer's credit card to ensure availability. Following the hold, the merchant submits a capture request to finalize the transaction and transfer the reserved funds into their account. This two-step process protects both the customer and merchant by confirming fund availability before the final charge is processed.
Benefits of Using Authorization Holds
Authorization holds improve cash flow management by temporarily reserving funds without immediate withdrawal, allowing merchants to verify available credit before completing a transaction. This process reduces chargeback risks and fraud by ensuring payment legitimacy prior to product shipment or service delivery. Implementing authorization holds enhances customer trust through transparent transaction verification while providing flexibility for order adjustments.
Common Use Cases for Authorization and Capture
Authorization holds are commonly used in industries like hospitality and car rentals to temporarily reserve funds without immediate collection, ensuring payment availability while allowing for adjustments. Capture is frequently utilized in e-commerce and retail transactions to finalize payment once goods are shipped or services are delivered, securing the authorized amount. This two-step process enhances fraud prevention and cash flow management by separating fund reservation from actual charge completion.
Risks and Limitations of Holds and Captures
Authorization holds temporarily reserve funds on a customer's account without transferring money, posing risks such as delayed fund availability and potential customer dissatisfaction due to extended hold durations. Capture finalizes the transaction by transferring the authorized funds but carries limitations like time-sensitive windows for completion and the possibility of declines if the capture amount exceeds the authorized hold. Both processes require careful management to mitigate risks of failed transactions, increased chargebacks, and complications in cash flow forecasting.
Best Practices for Managing Payment Authorization
Payment authorization hold secures funds on a customer's card without immediately finalizing the transaction, allowing merchants to verify funds and prevent fraud. Best practices for managing payment authorization include setting appropriate hold durations based on transaction type and promptly capturing authorized amounts to reduce declined transactions. Regular reconciliation of authorizations and captures ensures accurate financial records and helps maintain customer trust.
FAQs on Authorization Hold vs Capture
Authorization hold temporarily reserves funds on a customer's payment method, ensuring availability without transferring money, while capture finalizes the transaction by withdrawing the authorized amount. Common FAQs highlight the duration of authorization holds, typically 5 to 7 days, and the possibility to modify or complete captures within this timeframe. Merchants must carefully manage the hold-to-capture process to avoid declined payments and ensure seamless customer experience.
Important Terms
Pre-authorization
Pre-authorization temporarily reserves funds on a customer's credit card to ensure payment availability, while capture finalizes the transaction by transferring the reserved funds to the merchant.
Merchant settlement
Merchant settlement involves finalizing transactions by converting authorization holds into captured funds, ensuring payment is securely transferred from the customer's account to the merchant.
Transaction clearing
Transaction clearing involves finalizing payment by capturing authorized funds, where an authorization hold temporarily reserves the amount until the capture confirms the transaction for settlement.
Pending funds
Pending funds represent the amount temporarily reserved during an authorization hold, which only becomes finalized and debited upon capture of the payment.
Real-time gross settlement (RTGS)
Real-time gross settlement (RTGS) enables immediate fund transfer and finality of payments, contrasting with the authorization hold process where funds are reserved but not transferred until capture occurs.
Batch processing
Batch processing in payment systems involves grouping multiple transactions for simultaneous settlement, where authorization holds temporarily reserve funds on a customer's account before the final capture confirms and completes the payment. Proper management of authorization holds versus captures ensures accurate fund availability and reduces the risk of declined transactions or delayed payments during batch settlement.
Acquirer reconciliation
Acquirer reconciliation ensures accurate financial reporting by comparing authorization holds with final captures to identify discrepancies and streamline transaction settlements.
Issuer response
Issuer response determines whether an authorization hold is approved or declined, impacting the subsequent capture process for completing a transaction.
Partial capture
Partial capture allows merchants to finalize a portion of an authorization hold, ensuring that only the authorized amount for delivered goods or services is charged while the remaining hold amount is released.
Chargeback window
The chargeback window typically begins after the payment capture occurs, as authorization holds only reserve funds without finalizing the transaction or triggering chargeback liability.
Authorization hold vs Capture Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com