An issuer bank is the financial institution that provides credit or debit cards to consumers and manages their accounts, responsible for approving or declining transactions based on available funds or credit limits. A sponsor bank, on the other hand, is a regulatory-compliant bank that enables non-bank entities, like payment facilitators or fintech companies, to access the card networks and process payments. Understanding the distinction between issuer and sponsor banks is crucial for payment processing, as issuer banks handle consumer accounts while sponsor banks facilitate network participation and transaction routing.
Table of Comparison
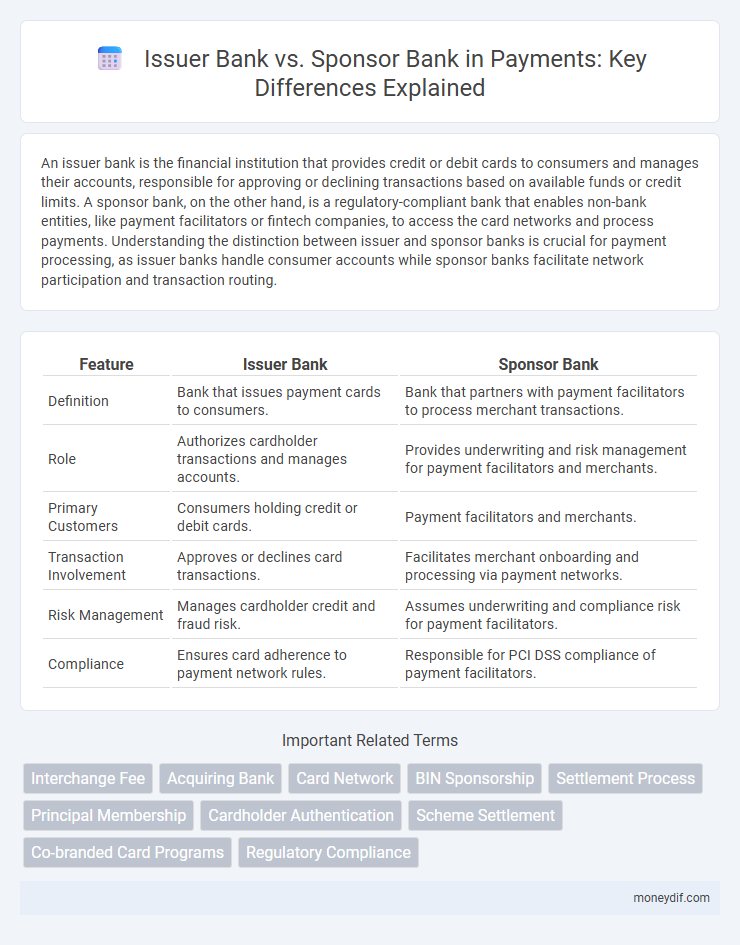
| Feature | Issuer Bank | Sponsor Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bank that issues payment cards to consumers. | Bank that partners with payment facilitators to process merchant transactions. |
| Role | Authorizes cardholder transactions and manages accounts. | Provides underwriting and risk management for payment facilitators and merchants. |
| Primary Customers | Consumers holding credit or debit cards. | Payment facilitators and merchants. |
| Transaction Involvement | Approves or declines card transactions. | Facilitates merchant onboarding and processing via payment networks. |
| Risk Management | Manages cardholder credit and fraud risk. | Assumes underwriting and compliance risk for payment facilitators. |
| Compliance | Ensures card adherence to payment network rules. | Responsible for PCI DSS compliance of payment facilitators. |
Understanding Issuer and Sponsor Banks in Payments
Issuer banks provide cards to consumers, enabling them to make transactions by extending credit or debit facilities. Sponsor banks facilitate payment processing for merchants by partnering with payment networks and acquiring banks, ensuring seamless transaction acceptance. Understanding the distinct roles of issuer and sponsor banks is crucial for optimizing payment workflows and enhancing transaction security.
Key Roles: Issuer Bank vs Sponsor Bank
Issuer banks authorize and fund transactions on behalf of cardholders, managing credit limits, fraud detection, and billing processes. Sponsor banks facilitate the connection between non-bank payment service providers and the card networks, enabling payment acceptance and settlement. Both play critical roles in the payment ecosystem, with issuer banks focusing on consumer credit management and sponsor banks ensuring merchant access to card payment systems.
Core Functions: How Issuer and Sponsor Banks Differ
Issuer banks primarily manage cardholder accounts, authorize transactions, and assume liability for credit risk and fraud. Sponsor banks, on the other hand, provide the regulatory framework and access to payment networks for non-bank entities, enabling them to issue cards or process payments. While issuer banks focus on consumer-facing services, sponsor banks concentrate on compliance, settlement, and network connectivity.
Payment Ecosystem: Placement of Issuer and Sponsor Banks
Issuer banks play a critical role in the payment ecosystem by providing cardholders with payment instruments and managing authorization of transactions, ensuring secure and seamless payment processing. Sponsor banks facilitate payment transactions for non-bank entities, such as payment service providers or fintech companies, by granting access to card networks and settlement systems. Both issuer and sponsor banks form foundational components of the payment infrastructure, enabling efficient fund transfer and transaction validation across merchant and consumer interactions.
Regulatory Responsibilities: Issuer vs Sponsor Bank
Issuer banks directly manage cardholder accounts and comply with regulatory requirements such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws to prevent fraud and ensure transaction security. Sponsor banks enable payment facilitators or merchants to access card networks by underwriting their compliance with payment regulations, including PCI DSS standards and transaction monitoring. Regulatory responsibilities differ as issuer banks handle direct customer verification and risk management, while sponsor banks oversee intermediary compliance and transaction integrity within the payment ecosystem.
Risk Management: Comparing Issuer and Sponsor Banks
Issuer banks hold primary responsibility for managing cardholder risk, including fraud detection, credit approval, and transaction monitoring to prevent defaults. Sponsor banks focus on regulatory compliance and operational risk, enabling fintechs or smaller entities to access payment networks while mitigating exposure through strict due diligence and ongoing oversight. Effective risk management depends on the issuer's direct relationship with customers and the sponsor's role in safeguarding payment infrastructure integrity.
Card Issuance Process: Issuer vs Sponsor Bank Roles
In the card issuance process, the issuer bank is responsible for approving and providing credit or debit cards to customers, managing the cardholder's account and setting credit limits. Sponsor banks facilitate smaller or specialized businesses by partnering with merchant acquirers or third-party processors, enabling card issuance under their banking license. Understanding the issuer bank's direct role in underwriting versus the sponsor bank's enabling function is crucial for payment ecosystem efficiency and compliance.
Merchant Onboarding: Sponsor vs Issuer Bank Involvement
Sponsor banks play a critical role in merchant onboarding by underwriting and acquiring merchants, enabling them to process card payments. Issuer banks, however, focus primarily on providing payment cards to consumers and managing cardholder accounts, with limited direct interaction in merchant onboarding. Understanding the distinct responsibilities of sponsor and issuer banks helps streamline payment processing and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
Impact on Payment Security: Issuer and Sponsor Banks
Issuer banks authenticate cardholder identity and authorize transactions, playing a crucial role in preventing fraud and ensuring payment security. Sponsor banks facilitate merchants' access to payment networks, managing transaction processing and compliance with security standards such as PCI DSS. The collaboration between issuer and sponsor banks strengthens encryption protocols and fraud detection systems, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized payment activities.
Choosing Between Issuer and Sponsor Banks for Payments
Choosing between issuer and sponsor banks depends on the payment processing needs and business model. Issuer banks provide payment cards directly to consumers, enabling transaction authorization and fraud management, while sponsor banks facilitate payment processing for third-party payment service providers (PSPs) and fintechs by underwriting their operations. Selecting the appropriate bank involves evaluating control over customer relationships, compliance requirements, and access to card networks such as Visa or Mastercard.
Important Terms
Interchange Fee
Interchange fees are transaction fees paid by a merchant's sponsor bank to the cardholder's issuing bank to compensate for processing costs and fraud risk. These fees are a critical component in the card payment ecosystem, influencing merchant pricing and cardholder benefits while balancing risk between issuer and sponsor banks.
Acquiring Bank
An Acquiring Bank processes credit and debit card transactions on behalf of a merchant, acting as the sponsor bank that facilitates the merchant's access to the payment network, whereas an Issuer Bank provides cards to consumers and authorizes payment transactions. The Acquiring Bank and Issuer Bank work together within the payment ecosystem to enable seamless transaction approval and settlement.
Card Network
A card network facilitates transactions between issuer banks, which provide payment cards to consumers, and sponsor banks that enable non-issuer institutions to access network services; these networks ensure secure authorization, clearing, and settlement of payments. The differentiation between issuer and sponsor banks is critical for managing cardholder data, regulatory compliance, and transaction flow within global card systems like Visa, Mastercard, and American Express.
BIN Sponsorship
BIN Sponsorship involves a sponsor bank providing access to its Bank Identification Number (BIN) to an issuer bank, enabling the issuer to offer card services without owning a BIN directly. This partnership allows issuer banks to leverage the sponsor bank's infrastructure, compliance, and network connections for payment processing and card issuance.
Settlement Process
The settlement process involves the transfer of securities and funds between the issuer's bank and the sponsor bank to finalize transactions accurately and efficiently. Issuer banks confirm the authenticity and availability of securities, while sponsor banks facilitate payment and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements during settlement.
Principal Membership
Principal Membership allows an issuer bank to directly participate in a payment network, granting it the authority to issue payment cards and manage cardholder accounts. Sponsor banks provide intermediary services for non-principal members by facilitating access to the network without granting full issuer capabilities.
Cardholder Authentication
Cardholder Authentication is a critical security process where the issuer bank validates the identity of the cardholder during a transaction, often using methods such as PIN verification or biometric data. The sponsor bank facilitates this authentication by acting as an intermediary between the merchant and the issuer, ensuring secure communication and transaction approval within the payment network.
Scheme Settlement
Scheme Settlement involves the financial process where the issuer bank, responsible for cardholder accounts and authorizations, transfers payment obligations to the sponsor bank, which facilitates transaction clearing and settlement within the payment network. This collaboration ensures accurate reconciliation of funds and compliance with regulatory standards across intermediaries in card-based transaction ecosystems.
Co-branded Card Programs
Co-branded card programs involve collaboration between issuers, who manage card issuance and credit risk, and sponsor banks, which provide regulatory approval and banking infrastructure. The issuer typically handles customer relationships and operational processes while the sponsor bank ensures compliance with financial regulations and transactions clearing.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance in issuer versus sponsor bank relationships focuses on adhering to financial regulations such as Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Know Your Customer (KYC), and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Issuer banks must verify cardholder identity and transaction legitimacy, while sponsor banks ensure merchant compliance and reporting standards to regulatory authorities.
issuer vs sponsor bank Infographic
 moneydif.com
moneydif.com